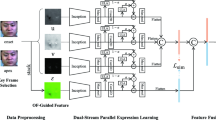
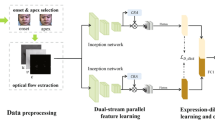
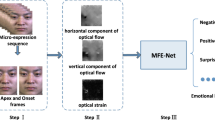
Abstract
Cross-database micro-expression recognition is a great challenging problem due to the short duration and low intensity of micro-expressions from different collection conditions. In this paper, we present a Motion Attention Deep Transfer Network (MADTN) that can focus on the most discriminative movement regions of the face and reduce the database bias. Specifically, we firstly combine the motion information and facial appearance information to obtain the discriminative representation by merging the optical flow fields between three key-frames (the onset frame, the middle frame, the offset frame) and the facial appearance of the middle frame. Then, the deep network architecture extracts cross-domain feature with the superiority of the maximum mean discrepancy(MMD) loss so that the source and target domains have a similar distribution. Results on benchmark cross-database micro-expression experiments demonstrate that the MADTN achieves remarkable performance in many micro-expression transfer tasks and exceed the state-of-the-art results, which show the robustness and superiority of our approach.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borgwardt, K.M., Gretton, A., Rasch, M.J., Kriegel, H.P., Schölkopf, B., Smola, A.J.: Integrating structured biological data by kernel maximum mean discrepancy. Bioinformatics 22(14), e49–e57 (2006)
Chang, C.C., Lin, C.J.: LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. (TIST) 2(3), 1–27 (2011)
Chaudhry, R., Ravichandran, A., Hager, G., Vidal, R.: Histograms of oriented optical flow and binet-cauchy kernels on nonlinear dynamical systems for the recognition of human actions. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1932–1939. IEEE (2009)
Chu, W.S., De la Torre, F., Cohn, J.F.: Selective transfer machine for personalized facial action unit detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3515–3522 (2013)
Chu, W.S., De la Torre, F., Cohn, J.F.: Selective transfer machine for personalized facial expression analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(3), 529–545 (2016)
Csurka, G.: Domain Adaptation in Computer Vision Applications, vol. 8. Springer, Heidelberg (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-58347-1
Ekman, P.: Telling Lies: Clues to Deceit in the Marketplace, Politics, and Marriage, revised edn. WW Norton & Company, New York (2009)
Ekman, P., Friesen, W.V.: Nonverbal leakage and clues to deception. Psychiatry 32(1), 88–106 (1969)
Farnebäck, G.: Two-frame motion estimation based on polynomial expansion. In: Bigun, J., Gustavsson, T. (eds.) SCIA 2003. LNCS, vol. 2749, pp. 363–370. Springer, Heidelberg (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45103-X_50
Fernando, B., Habrard, A., Sebban, M., Tuytelaars, T.: Unsupervised visual domain adaptation using subspace alignment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2960–2967 (2013)
Frank, M., Herbasz, M., Sinuk, K., Keller, A., Nolan, C.: I see how you feel: training laypeople and professionals to recognize fleeting emotions. In: The Annual Meeting of the International Communication Association. Sheraton New York, New York City (2009)
Gong, B., Shi, Y., Sha, F., Grauman, K.: Geodesic flow kernel for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2066–2073. IEEE (2012)
Hassan, A., Damper, R., Niranjan, M.: On acoustic emotion recognition: compensating for covariate shift. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 21(7), 1458–1468 (2013)
Horn, B.K., Schunck, B.G.: Determining optical flow. In: Techniques and Applications of Image Understanding, vol. 281, pp. 319–331. International Society for Optics and Photonics (1981)
Huang, X., Wang, S.J., Zhao, G., Piteikainen, M.: Facial micro-expression recognition using spatiotemporal local binary pattern with integral projection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, pp. 1–9 (2015)
Huang, X., Zhao, G., Hong, X., Zheng, W., Pietikäinen, M.: Spontaneous facial micro-expression analysis using spatiotemporal completed local quantized patterns. Neurocomputing 175, 564–578 (2016)
Itti, L., Koch, C.: Computational modelling of visual attention. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2(3), 194–203 (2001)
Jovanović, M.R., Schmid, P.J., Nichols, J.W.: Sparsity-promoting dynamic mode decomposition. Phys. Fluids 26(2), 024103 (2014)
Khor, H.Q., See, J., Phan, R.C.W., Lin, W.: Enriched long-term recurrent convolutional network for facial micro-expression recognition. In: 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), pp. 667–674. IEEE (2018)
Kim, D.H., Baddar, W.J., Ro, Y.M.: Micro-expression recognition with expression-state constrained spatio-temporal feature representations. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 382–386 (2016)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980 (2014)
Le Ngo, A.C., Liong, S.T., See, J., Phan, R.C.W.: Are subtle expressions too sparse to recognize? In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Digital Signal Processing (DSP), pp. 1246–1250. IEEE (2015)
Le Ngo, A.C., Oh, Y.H., Phan, R.C.W., See, J.: Eulerian emotion magnification for subtle expression recognition. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 1243–1247. IEEE (2016)
Li, X., et al.: Towards reading hidden emotions: a comparative study of spontaneous micro-expression spotting and recognition methods. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 9(4), 563–577 (2017)
Li, X., Pfister, T., Huang, X., Zhao, G., Pietikäinen, M.: A spontaneous micro-expression database: inducement, collection and baseline. In: 2013 10th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2013)
Liong, S.T., See, J., Wong, K., Phan, R.C.W.: Less is more: micro-expression recognition from video using apex frame. Signal Process. Image Commun. 62, 82–92 (2018)
Liu, Y.J., Zhang, J.K., Yan, W.J., Wang, S.J., Zhao, G., Fu, X.: A main directional mean optical flow feature for spontaneous micro-expression recognition. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 7(4), 299–310 (2015)
Long, M., Wang, J., Sun, J., Philip, S.Y.: Domain invariant transfer kernel learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 27(6), 1519–1532 (2014)
Maas, A.L., Hannun, A.Y., Ng, A.Y.: Rectifier nonlinearities improve neural network acoustic models. In: Proceedings of ICML, vol. 30, p. 3 (2013)
Pan, S.J., Tsang, I.W., Kwok, J.T., Yang, Q.: Domain adaptation via transfer component analysis. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 22(2), 199–210 (2010)
Park, S.Y., Lee, S.H., Ro, Y.M.: Subtle facial expression recognition using adaptive magnification of discriminative facial motion. In: Proceedings of the 23rd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 911–914 (2015)
Peng, M., Wang, C., Chen, T., Liu, G., Fu, X.: Dual temporal scale convolutional neural network for micro-expression recognition. Front. Psychol. 8, 1745 (2017)
Pfister, T., Li, X., Zhao, G., Pietikäinen, M.: Recognising spontaneous facial micro-expressions. In: 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1449–1456. IEEE (2011)
Porter, S., Ten Brinke, L.: Reading between the lies: identifying concealed and falsified emotions in universal facial expressions. Psychol. Sci. 19(5), 508–514 (2008)
Russell, T.A., Chu, E., Phillips, M.L.: A pilot study to investigate the effectiveness of emotion recognition remediation in schizophrenia using the micro-expression training tool. Brit. J. Clin. Psychol. 45(4), 579–583 (2006)
Salter, F., Grammer, K., Rikowski, A.: Sex differences in negotiating with powerful males. Hum. Nat. 16(3), 306–321 (2005)
Wang, Y., See, J., Phan, R.C.-W., Oh, Y.-H.: LBP with six intersection points: reducing redundant information in LBP-TOP for micro-expression recognition. In: Cremers, D., Reid, I., Saito, H., Yang, M.-H. (eds.) ACCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 9003, pp. 525–537. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16865-4_34
Wu, H.Y., Rubinstein, M., Shih, E., Guttag, J., Durand, F., Freeman, W.: Eulerian video magnification for revealing subtle changes in the world. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 31(4), 1–8 (2012)
Xu, F., Zhang, J., Wang, J.Z.: Microexpression identification and categorization using a facial dynamics map. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 8(2), 254–267 (2017)
Yan, W.J., Li, X., Wang, S.J., Zhao, G., Liu, Y.J., Chen, Y.H., Fu, X.: CASME II: an improved spontaneous micro-expression database and the baseline evaluation. PloS one 9(1), e86041(2014)
Zhang, K., Zhang, Z., Li, Z., Qiao, Y.: Joint face detection and alignment using multitask cascaded convolutional networks. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 23(10), 1499–1503 (2016)
Zhao, G., Pietikainen, M.: Dynamic texture recognition using local binary patterns with an application to facial expressions. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 29(6), 915–928 (2007)
Zhou, Z., Zhao, G., Pietikäinen, M.: Towards a practical lipreading system. In: CVPR 2011, pp. 137–144. IEEE (2011)
Zong, Y., Huang, X., Zheng, W., Cui, Z., Zhao, G.: Learning a target sample re-generator for cross-database micro-expression recognition. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 872–880 (2017)
Zong, Y., Zheng, W., Cui, Z., Zhao, G., Hu, B.: Toward bridging microexpressions from different domains. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 50, 5047–5060 (2019)
Zong, Y., Zheng, W., Hong, X., Tang, C., Cui, Z., Zhao, G.: Cross-database micro-expression recognition: a benchmark. In: Proceedings of the 2019 on International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, pp. 354–363 (2019)
Zong, Y., Zheng, W., Huang, X., Shi, J., Cui, Z., Zhao, G.: Domain regeneration for cross-database micro-expression recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 27(5), 2484–2498 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Key Research and Development Program of China under Grant 2018YFB1305200, in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61921004, Grant 61902064, Grant 81971282, Grant U2003207, and Grant 62076064, and in part by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grant 2242018K3DN01.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xia, W., Zheng, W., Zong, Y., Jiang, X. (2021). Motion Attention Deep Transfer Network for Cross-database Micro-expression Recognition. In: Del Bimbo, A., et al. Pattern Recognition. ICPR International Workshops and Challenges. ICPR 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12663. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-68796-0_49
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-68796-0_49
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-68795-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-68796-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)