Abstract
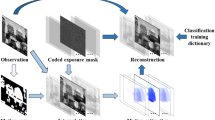
In this paper, a deep neural network with interpretable motion compensation called CS-MCNet is proposed to realize high-quality and real-time decoding of video compressive sensing. Firstly, explicit multi-hypothesis motion compensation is applied in our network to extract correlation information of adjacent frames (as shown in Fig. 1), which improves the recover performance. And then, a residual module further narrows down the gap between reconstruction result and original signal. The overall architecture is interpretable by using algorithm unrolling, which brings the benefits of being able to transfer prior knowledge about the conventional algorithms. As a result, a PSNR of 22 dB can be achieved at 64x compression ratio, which is about \(4\%\) to \(9\%\) better than state-of-the-art methods. In addition, due to the feed-forward architecture, the reconstruction can be processed by our network in real time and up to three orders of magnitude faster than traditional iterative methods.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Candes, E.J., Tao, T.: Near-optimal signal recovery from random projections: universal encoding strategies? IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 52, 5406–5425 (2006)
Donoho, D.L.: Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 52, 1289–1306 (2006)
Duarte, M.F., Davenport, M.A., Takhar, D., Laska, J.N., Sun, T., Kelly, K.F., Baraniuk, R.G.: Single-pixel imaging via compressive sampling. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 25, 83–91 (2008)
Candes, E.J., Wakin, M.B.: An introduction to compressive sampling. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 25, 21–30 (2008)
Candès, E.J., Romberg, J.K., Tao, T.: Stable signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate measurements. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 59, 1207–1223 (2006)
Baraniuk, R., Davenport, M.A., DeVore, R.A., Wakin, M.B.: A simple proof of the restricted isometry property for random matrices. Constr. Approx. 28, 253–263 (2008)
Zhou, J., Zhou, J., Guo, L.: Angular intra prediction based measurement coding algorithm for compressively sensed image. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia Expo Workshops (ICMEW), pp. 1–6 (2018)
Yang, J., Yuan, X., Liao, X., Llull, P., Sapiro, G., Brady, D.J., Carin, L.: Gaussian mixture model for video compressive sensing. In: 2013 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, pp. 19–23 (2013)
Daubechies, I., Defrise, M., De Mol, C.: An iterative thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems with a sparsity constraint. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 57, 1413–1457 (2004)
He, L., Carin, L.: Exploiting structure in wavelet-based Bayesian compressive sensing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 57, 3488–3497 (2009)
Metzler, C.A., Maleki, A., Baraniuk, R.G.: From denoising to compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 62, 5117–5144 (2016)
Qu, X., et al.: Undersampled MRI reconstruction with patch-based directional wavelets. Magn. Reson. Imaging 30, 964–977 (2012)
Zhan, Z., Cai, J., Guo, D., Liu, Y., Chen, Z., Qu, X.: Fast multiclass dictionaries learning with geometrical directions in MRI reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 63, 1850–1861 (2016)
Mun, S., Fowler, J.E.: Residual reconstruction for block-based compressed sensing of video. In: 2011 Data Compression Conference, pp. 183–192 (2011)
Xu, K., Ren, F.: Csvideonet: A real-time end-to-end learning framework for high-frame-rate video compressive sensing. In: 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp. 1680–1688 (2018)
Yao, H., Dai, F., Zhang, S., Zhang, Y., Tian, Q., Xu, C.: DR2-Net: deep residual reconstruction network for image compressive sensing. Neurocomputing 359, 483–493 (2019)
Iliadis, M., Spinoulas, L., Katsaggelos, A.K.: Deep fully-connected networks for video compressive sensing. Digit. Signal Proc. 72, 9–18 (2018)
Kulkarni, K., Lohit, S., Turaga, P., Kerviche, R., Ashok, A.: ReconNet: non-iterative reconstruction of images from compressively sensed measurements. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 449–458 (2016)
Zhang, J., Ghanem, B.: ISTA-Net: interpretable optimization-inspired deep network for image compressive sensing. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1828–1837 (2018)
Gregor, K., LeCun, Y.: Learning fast approximations of sparse coding. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2010, Madison, WI, USA. Omnipress, pp. 399–406 (2010)
Yang, Y., Sun, J., Li, H., Xu, Z.: ADMM-CSNet: a deep learning approach for image compressive sensing. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 42, 521–538 (2020)
Erhan, D., Bengio, Y., Courville, A., Manzagol, P., Vincent, P., Bengio, S.: Why does unsupervised pre-training help deep learning? J. Mach. Learn. Res. 11, 625–660 (2010)
Tekalp, A.M.: Digital Video Processing, 2nd edn. Prentice Hall Press, New York (2015)
Jain, J., Jain, A.: Displacement measurement and its application in interframe image coding. IEEE Trans. Commun. 29, 1799–1808 (1981)
Tramel, E.W., Fowler, J.E.: Video compressed sensing with multihypothesis. In: 2011 Data Compression Conference, pp. 193–202 (2011)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 770–778 (2016)
Soomro, K., Zamir, A.R., Shah, M.: UCF101: a dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in the wild. ArXiv abs/1212.0402 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Huang, B., Zhou, J., Yan, X., Jing, M., Wan, R., Fan, Y. (2021). CS-MCNet: A Video Compressive Sensing Reconstruction Network with Interpretable Motion Compensation. In: Ishikawa, H., Liu, CL., Pajdla, T., Shi, J. (eds) Computer Vision – ACCV 2020. ACCV 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12623. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-69532-3_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-69532-3_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-69531-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-69532-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)