Abstract
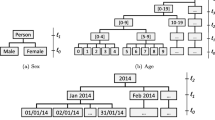
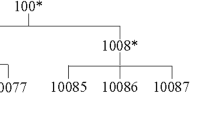
In the data bursting era, an enormous amount of data can be collected. Though, such data can benefit both the data owners and the public, the privacy of collected data is an important concern. To guarantee the privacy of data, the k-anonymous method is applied before publishing the dataset. The dataset needs to have an identical value of at least k records in order to protect the data privacy which could cause data losses. The optimal k-anonymity is concerned with minimizing the data losses and also preserve data privacy. The generalization lattice is created to map all the generalization schemes and use them to find the optimal answer. The larger number of attributes means the larger number of nodes in the generalization lattice. Thus, in the larger number of attributes, the k-anonymous algorithm takes more computation resources and time to determine the answer. Although, due to the limited computation resources and time, the existing optimal k-anonymity algorithms only find the optimal answer on the small dataset. Therefore, in this paper, we design the optimal k-anonymity algorithm with the incremental attribute concept. At m attribute, our algorithm process only the nodes which previously satisfy the k-anonymity from the \(m-1\) attributes. Thus, our algorithm can find the optimal answer at a large number of attributes without reaching the memory limit problem compared with the existing k-anonymity algorithms due to it determines only some necessary nodes in the lattice.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bayardo, R.J., Agrawal, R.: Data privacy through optimal k-anonymization. In: Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Data Engineering, ICDE 2005, pp. 217–228. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC, USA (2005)
El Emam, K., Dankar, F., Issa, R., Jonker, E., Amyot, D., Cogo, E., Corriveau, J.P., Walker, M., Chowdhury, S., Vaillancourt, R., Roffey, T., Bottomley, J.: A globally optimal k-anonymity method for the de-identification of health data. J. Am. Med. Informatics Assoc.: JAMIA 16, 670–82 (2009)
Goldberg, K., Roeder, T., Gupta, D., Perkins, C.: Eigentaste: a constant time collaborative filtering algorithm. Inf. Retrieval 4(2), 133–151 (2001)
Kohlmayer, F., Prasser, F., Eckert, C., Kemper, A., Kuhn, K.A.: Flash: efficient, stable and optimal k-anonymity. In: 2012 International Conference on Privacy, Security, Risk and Trust and 2012 International Conference on Social Computing, pp. 708–717 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/SocialCom-PASSAT.2012.52
Mahanan, W., Art Chaovalitwongse, W., Natwichai, J.: Data anonymization: a novel optimal \(k\)-anonymity algorithm for identical generalization hierarchy data in IoT. Serv. Oriented Comput. Appl. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11761-020-00287-w
Purvank: uber ride reviews dataset (2017). https://www.kaggle.com/purvank/uber-rider-reviews-dataset. Accessed 10 Nov 2020
Samarati, P.: Protecting respondents identities in microdata release. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 13(6), 1010–1027 (2001)
Sweeney, L.: Achieving k-anonymity privacy protection using generalization and suppression. Int. J. Uncertain. Fuzziness Knowl.-Based Syst. 10(5), 571–588 (2002)
Sweeney, L.: k -anonymity: a model for protecting privacy 10(5), 1–14 (2002)
Sweeney, L.A.: Computational disclosure control: A primer on data privacy protection. Ph.D. thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA (2001). AAI0803469
Wong, R.C.W., Li, J., Fu, A.W.C., Wang, K.: (\(\alpha \), k)-anonymity: an enhanced k-anonymity model for privacy preserving data publishing. In: Proceedings of the 12th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD \(\acute{0}\)6, pp. 754–759. ACM, New York, NY, USA (2006)
Zheng, Y.: T-drive trajectory data sample. T-Drive sample dataset (2011). https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/publication/t-drive-trajectory-data-sample/
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mahanan, W., Natwichai, J. (2021). Data Privacy Preservation Algorithm on Large-Scale Identical Generalization Hierarchy Data. In: Barolli, L., Natwichai, J., Enokido, T. (eds) Advances in Internet, Data and Web Technologies. EIDWT 2021. Lecture Notes on Data Engineering and Communications Technologies, vol 65. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-70639-5_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-70639-5_23
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-70638-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-70639-5
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)