Abstract
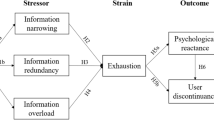
Based on the psychological reactance, this study tries to explore the dark side and grey role of the personalization recommendation system of short-form video application in understanding the discontinuance behavior. Specifically, two major depressing consequences of the personalization recommendation system are proposed, namely, privacy concerns and perceived information narrowing. Specifically, personalization recommendation system of short-form video App has significant positive influence on both privacy concern and perceived information narrowing. Besides, the empirical study shows perceived information narrowing is positively related to psychological reactance. However, personalization recommendation system does not lead to discontinuous usage behavior through privacy concerns or perceived information narrowing. Although personalization recommendation has not an indirect effect on discontinuous usage behavior, personalization recommendation has a potential risk to create psychological pressure on users, making personalized recommendations counterproductive. This study renders new insights on the dark side of the personalization recommendation system and provides practical suggestions for short-form video application providers.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nunes, P.F., Kambil, A.: Personalization? No thanks. Harv. Bus. Rev. 79(4), 32–33 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1111/1468-0440.00114
Piggot, J.: Micro-Segmentation and Personalization in Information Systems in the Financial Service Industry. (2015). https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.1.3073.9366
Lee, G., Lee, W.J.: Psychological reactance to online recommendation services. Inf. Manage. 46(8), 448–452 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2009.07.005
Fitzsimons, G., Lehmann, D.: Reactance to recommendations: when unsolicited advice yields contrary responses. Market. Sci. 23(1), 82–94 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1287/mksc.1030.0033
Berk, M., Blank, J., Daniels, D., Schatsky, D.: Beyond the personalization myth: cost-effective alternatives to influence intent. Jupiter Research Site Technologies and Operations (2003). 2
Aguirre, E., Mahr, D., Grewal, D., Ruyter, K.D., Wetzels, M.: Unraveling the personalization paradox: the effect of information collection and trust-building strategies on online advertisement effectiveness. J. Retail. 91(1), 34–49 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretai.2014.09.005
Chen, Q., Feng, Y.Q., Liu, L.N., Tian, X.: Understanding consumers’ reactance of online personalized advertising: a new scheme of rational choice from a perspective of negative effects. Int. J. Inf. Manage. 44(FEB), 53–64(2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2018.09.001.
Newell, S., Marabelli, M.: Strategic opportunities (and challenges) of algorithmic decision-making: a call for action on the long-term societal effects of ‘datification.’ J. Strat. Inf. Syst. 24(1), 3–14 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsis.2015.02.001
Pariser, E.: The Filter Bubble: How the New Personalized Web Is Changing What We Read and How We Think. Penguin, London (2011)
Zhang, X., Wu, Y., Liu, S.: Exploring short-form video application addiction: socio-technical and attachment perspectives. Telemat. Inform. 44(SEP), 101–121 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2019.101243.
O'Connell, C.: 24% of Users Abandon an App After One Use (2017). https://info.localytics.com/blog/24-of-users-abandon-an-app-after-one-use.
Hossein, A., Rafsanjani, N., Salim, N., Aghdam, A.R., Fard, K.B.: Recommend. Syst. Rev. 3(5), 47–52 (2013)
Pu, P., Chen, L., Hu, R.: Evaluating recommender systems from the user’s perspective: survey of the state of the art. User Model. User-Adap. Interact. 22(4–5), 317–355 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11257-011-9115-7
Jannach, D., Zanker, M., Felfernig, A., Friedrich, G.: Recommender Systems: An Introduction. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2011)
Yue, S., Larson, M., Hanjalic, A.: Collaborative filtering beyond the user-item matrix: a survey of the state of the art and future challenges. ACM Comput. Surv. 47(1), 1–45 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1145/2556270
Su, X., Khoshgoftaar, T.: A survey of collaborative filtering techniques. Adv. Artif. Intell. 2009(12), 1–9 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/421425
Pimenidis, E., Polatidis, N.,Mouratidis, H.: Mobile recommender systems: identifying the major concepts. J. Inf. Sci. 165–176 (2018). https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.24011.08488
Portilla, I.: Privacy concerns about information sharing as trade-off for personalized news. El profesional de la información 27(1), 19–26 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3145/epi.2018.ene.02
Taddei, S., Contena, B.: Privacy, trust and control: Which relationships with online self-disclosure? Comput. Hum. Behav. 29(3), 821–826 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2012.11.022
Posner, R.: The economics of privacy. Am. Econ. Rev. 71(2), 405–409 (19 81). https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2580411.
Mai, J.: Three models of privacy: new perspectives on informational privacy. Nordicom Rev. 37, 171–175 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1515/nor-2016-0031
Youn, S.: Determinants of online privacy concern and its influence on privacy protection behaviors among young adolescents. J. Consum. Aff. 43(3), 389–418 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6606.2009.01146.x
Mohamed, N., Ahmad, I.: Information privacy concerns, antecedents and privacy measure use in social networking sites: evidence from Malaysia. Comput. Hum. Behav. 28(6), 2366–2375 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2012.07.008
Li, Y.: Theories in online information privacy research: a critical review and an integrated framework. Decis. Support Syst. 54(1), 471–481 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2012.06.010
Sunstein, C.R.: Republic. com. Princeton University Press. Princeton (2002)
Chen, T.: Opportunities, anomalies and governance of new media under capital logic: case study of wechat subscription “Mi Meng”. In: 2nd International Symposium on Social Science and Management In-novation (SSMI 2019). Atlantis Press. https://doi.org/10.26914/c.cnkihy.2019.048893
Bennett, W.L., Lyengar, S.: A new era of minimal effects? The changing foundations of political communication. J. Commun. 58(4), 707–731 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-2466.2008.00410.x
Sude, D.J., Pearson, G.D.H., Knobloch-Westerwick, S.: Journal pre-proof Self-expression just a click away source interactivity impacts on confirmation bias and political attitudes. Comput. Hum. Behav. 114, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2020.106571.
Hundt, M., Schneider, B., Mennatallah, E.F., Daniel, A.K., Alexandra, D.: Visual analysis of geolocated echo chambers in social media. In: EuroVis 2017 Eurographics/IEEE VGTC Conference on Visualization 2017, pp. 125–128 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2312/eurp.20171185.
Negroponte, N.: Being Digital. Alfred A. Knopf, New York(1995)
Chandler, T.: Why discipline strategies are bound to fail. Clear. House J. Educ. Strat. Issues Ideas 64(2), 124–126 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1080/00098655.1990.9955826
Brehm, J.W.: A Theory of Psychological Reactance. Academic Press, New York (1966)
Kwon, S., Chung, N.: The moderating effects of psychological reactance and product involvement on online shopping recommendation mechanisms based on a causal map. Electron. Commerce Res. Appl. 9(6), 522–536 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elerap.2010.04.004
Edwards, S., Li, H., Lee, J.: Forced exposure and psychological reactance: antecedents and consequences of the perceived intrusiveness of pop-up ads. J. Advert. 31(3), 83–95 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1080/00913367.2002.10673678
Youn, S., Kim, S.: Understanding ad avoidance on Facebook: antecedents and outcomes of psychological reactance. Comput. Hum. Behav. 98, 232–244 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2019.04.025
Dillard, J., Shen, L.: On the nature of reactance and its role in persuasive health communication. Commun. Monogr. 72(2), 144–168 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1080/03637750500111815
Moyer-Gusé, E.: Toward a theory of entertainment persuasion: explaining the persuasive effects of entertainment-education messages. Commun. Theory 18(3), 407–425 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2885.2008.00328.x
Han, K., Kim, S.: Toward more persuasive diabetes messages: effects of personal value orientation and freedom threat on psychological reactance and behavioral intention. J. Health Commun. 24(2), 95–110 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/10810730.2019.1581304
Lee, G., Lee, J., Sanford, C.: The roles of self-concept clarity and psychological reactance in compliance with product and service recommendations. Comput. Hum. Behav. 26(6), 1481–1487 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2010.05.001
Samah, N., Ali, M.: Individual differences in online personalized learning environment. Educ. Res. Rev. 6(7), 516–521 (2011). https://doi.org/10.5897/ERR.9000199
Lee, S., Lee, Y., Lee, J., Park, J.: Personalized e-services: consumer privacy concern and information sharing. Soc. Behav. Pers. Int. J. 43(5), 729–740 (2015). https://doi.org/10.2224/sbp.2015.43.5.729
Guo, X., Gan, X.Y.: Burst your bubbles: reflection on the formation and resolution of filter bubbles in an era of recommendation algorithm. Global Media J. 5(2), 76–90 (2018)
Rajat, K.B., Pradip, K.B., Rashmi, J.: A rule-based automated machine learning approach in the evaluation of recommender engine. Benchmark. Int. J. 27(10), 2721–2757(2020). https://doi.org/10.1108/BIJ-01-2020-0051.
Nguyen, C.T.: Echo Chambers and Epistemic Bubbles. Cambridge Unniversity Press 17(2), 141–161 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1017/epi.2018.32
Beheshti, A., Yakhchi, S., Mousaeirad, S., Ghafari, S.M., Goluguri, S.R., Edrisi, M.A.: Towards cognitive recommender systems. Algorithms 13(8), 12–13 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/a13080176
Belknap, J.K., Ondrusek, G., Berg, J., Waddingham, S.: Barbiturate dependence in mice: effects of continuous vs. discontinuous drug administration. Psychopharmacology 51(2), 195–198 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00431740.
Furneaux, B., Wade, M.R.: An exploration of organizational level information systems discontinuance intentions. MIS Q. 35(3), 573–598 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2011.11.004
Lakshmanan, A., Krishnan, H.S.: The aha! experience: Insight and discontinuous learning in product usage. J. Market. 75(6), 105–123 (2011). https://doi.org/10.2307/41406862
Zhao, L., Lu, X., Hu, Y.: a proposed theoretical model of discontinuous usage of voice-activated intelligent personal assistants (IPAs). In: PACIS (2018)
Zhao, L., Lu, Y.B., Yang, J., Zhang, S.W.: Get tired of socializing as social animal? An empirical explanation on discontinuous usage behavior in social network services. In PACIS (2015)
Luqman, A., Cao, X., Ali, A., Masood, A., Yu, L.: Empirical investigation of Facebook discontinues usage intentions based on SOR paradigm. Comput. Hum. Behav. 70(5), 544–555 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2017.01.020
Wu, K.W., Huang, S.Y., Yen, D.C., Popova, I.: The effect of online privacy policy on consumer privacy concern and trust. Comput. Hum. Behav. 28(3), 889–897 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2011.12.008
Naveen, F.A., Krishnan, M.S.: The personalization privacy paradox: an empirical evaluation of information transparency and the willingness to be profiled online for personalization. MIS Q. 30(1), 13–28 (2006). https://doi.org/10.2307/25148715
Pappas, I.O., Kourouthanassis, P.E., Giannakos, M.N., Chrissikopoulos, V.: Sense and sensibility in personalized e-commerce: how emotions rebalance the purchase intentions of persuaded customers. Psychol. Market. 34(10), 972–986 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/mar.21036
Huang, C.D., Goo, J., Nam, K., Yoo, C.W.: Smart tourism technologies in travel planning: the role of exploration and exploitation. Inf. Manage. 54(6), 757–770 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2016.11.010
Maier, C., Laumer, S., Weinert, C., Weitzel, T.: The effects of technostress and switching stress on discontinued use of social networking services: a study of Facebook use. Inf. Syst. J. 25(3), 275–308 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1111/isj.12068
Du, J., You, J.: Consumers’ willingness to adopt personalized push under the effect of “information cocoon house”: the perspective of psychological resistance. Enterpr. Econ., 103–110(2019).
Ringle, C.M., Wende, S., Becker, J.M.: SmartPLS 3. SmartPLS GmbH, Boenningstedt (2015)
Teo, H.H., Wei, K.K., Benbasat, I.: Predicting intention to adopt interorganizational linkages: an institutional perspective. Society for Information Management and The Management Information Systems Research Center (2003). https://doi.org/10.2307/30036518.
Fornell, C., Larcker, D.F.: Structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error: algebra and statistics. J. Market. Res., 382–388 (1981). dhttps://doi.org/10.2307/3150980.
Straub, D., Gefen, D.: Validation guidelines for IS positivist research. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 24 (2004). 10.17705/1CAIS.01324.
Wang, Y., Wang, P., Zhang, L., Zhang, W.: Research on the “Information Cocoons” of content intelligent distribution platform from the perspective of network information ecological chain. Res. Library Sci. 2 (2018)
Alyson, L.Y., Anabel, Q.H.: Information revelation and internet privacy concerns on social network sites: a case study of Facebook. Communities Technol. (2009). https://doi.org/10.1145/1556460.1556499
Chen, J.V., Tran, A., Nguyen, T.: Understanding the discontinuance behavior of mobile shoppers as a consequence of technostress: an application of the stress-coping theory. Comput. Human Behav. 83–93 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2019.01.022.
Huang, C.K., Chen, S.H., Tang, C.P., Huang, H.Y.: A trade-off dual-factor model to investigate discontinuous intention of health app users: fFrom the perspective of information disclosure. J. Biomed. Inform. 2–10 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2019.103302
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Li, J., Zhao, H., Hussain, S., Ming, J., Wu, J. (2021). The Dark Side of Personalization Recommendation in Short-Form Video Applications: An Integrated Model from Information Perspective. In: Toeppe, K., Yan, H., Chu, S.K.W. (eds) Diversity, Divergence, Dialogue. iConference 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12646. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-71305-8_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-71305-8_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-71304-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-71305-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)