Abstract
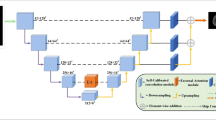
Semantic segmentation plays an essential role in brain tumor diagnosis and treatment planning. Yet, manual segmentation is a time-consuming task. That fact leads to hire the Deep Neural Networks to segment brain tumor. In this work, we proposed a variety of 3D U-Net, which can achieve comparable segmentation accuracy with less graphic memory cost. To be more specific, our model employs a modified attention block to refine the feature map representation along the skip-connection bridge, which consists of parallelly connected spatial and channel attention blocks. Dice coefficients for enhancing tumor, whole tumor, and tumor core reached 0.752, 0.879 and 0.779 respectively on the BRATS- 2020 valid dataset.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakas, S., et al.: Segmentation labels and radiomic features for the pre-operative scans of the TCGA-LGG collection. Cancer Imaging Arch. 286 (2017)
Bakas, S., Akbari, H., Sotiras, A., et al.: Advancing The Cancer Genome Atlas glioma MRI collections with expert segmentation labels and radiomic features. Sci. Data 4, 170117 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2017.117
Bakas, S., et al.: Identifying the best machine learning algorithms for brain tumor segmentation, progression assessment, and overall survival prediction in the BRATS challenge. CoRR abs/1811.02629 (2018). (1811)
Bakas, S., et al.: Segmentation labels and radiomic features for the pre-operative scans of the TCGA-GBM collection. Cancer Imaging Arch. Nat. Sci. Data 4, 170117 (2017)
Menze, B.H., et al.: The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (BRATS). IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 34(10), 1993–2024 (2014)
Agravat, R.R., Raval, M.S.: Deep learning for automated brain tumor segmentation in MRI images. In: Soft Computing Based Medical Image Analysis, pp. 183–201. Elsevier (2018)
Kamnitsas, K., et al.: DeepMedic for brain tumor segmentation. In: Crimi, A., Menze, B., Maier, O., Reyes, M., Winzeck, S., Handels, H. (eds.) BrainLes 2016. LNCS, vol. 10154, pp 138–149. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-55524-9_14
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J.-Y., Kweon, I.S.: CBAM: convolutional block attention module. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11211, pp. 3–19. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1
He, K., et al.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2016)
Ha, Q., et al.: MFNet: towards real-time semantic segmentation for autonomous vehicles with multi-spectral scenes. In: 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). IEEE (2017)
Wu, Y., He, K.: Group normalization. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11217, pp. 3–19. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01261-8_1
Oktay, O., et al.: Attention U-Net: learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.03999 (2018)
Abraham, N., Khan, N.M.: A novel focal Tversky loss function with improved attention u-net for lesion segmentation. In: 2019 IEEE 16th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2019). IEEE (2019)
Li, S., et al.: Attention dense-u-net for automatic breast mass segmentation in digital mammogram. IEEE Access 7, 59037–59047 (2019)
Cheng, D., et al.: SeNet: structured edge network for sea–land segmentation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 14(2), 247–251 (2016)
Mondal, A.K., Dolz, J., Desrosiers, C.: Few-shot 3D multi-modal medical image segmentation using generative adversarial learning. CoRR abs/1810.12241 (2018). https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.12241
Acknowledge
The project is supported by Sichuan Science and Technology Program. It is partially funded by Grant SCITLAB-0013 of Intelligent Terminal Key Laboratory of SiChuan Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Jun, W., Haoxiang, X., Wang, Z. (2021). Brain Tumor Segmentation Using Dual-Path Attention U-Net in 3D MRI Images. In: Crimi, A., Bakas, S. (eds) Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. BrainLes 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12658. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72084-1_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72084-1_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-72083-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-72084-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)