Abstract
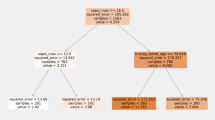
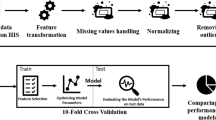
Increasingly, hospitals are collecting huge amounts of data through new storage methods. These data can be use to extract hidden knowledge, which can be crucial to estimate the length of stay of admitted patients in order to improve the management of hospital resources. Hence, this article portrays the performance analysis of different data mining techniques through the application of learning algorithms in order to predict patients’ length of stay when admitted to an Intensive Care Unit. The data used in this study contains about 60,000 records and 28 features with personal and medical information. A full analysis of the results obtained with different Machine Learning algorithms showed that the model trained with the Gradient Boosted Trees algorithm and using only the features that were strongly correlated to the patient’s length of stay, achieved the best performance with 99,19% of accuracy. In this sense, an accurate understanding of the factors associated with the length of stay in intensive care units was achieved.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee, T., Liu, C., Kuo, Y., Mills, M., Fong, J., Hung, C.: Application of data mining to the identification of critical factors in patient falls using a web-based reporting system. Int. J. Med. Inform. 80, 141–150 (2011)
Neto, C., Brito, M., Lopes, V., Peixoto, H., Abelha, A., Machado, J.: Application of data mining for the prediction of mortality and occurrence of complications for gastric cancer patients. Entropy 21(12), 1163 (2019)
Han, J., Pei, J., Kamber, M.: Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques, 3rd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2011)
Baek, H., Cho, M., Kim, S., Hwang, H., Song, M., Yoo, S.: Analysis of length of hospital stay using electronic health records: a statistical and data mining approach. PLoS ONE 13(4), e0195901 (2018)
Veloso, R., et al.: Real-time data mining models for predicting length of stay in intensive care units. In: KMIS 2014 - Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing, pp. 245–254 (2014)
Navaz, A.N., Mohammed, E., Serhani, M.A., Zaki, N.: The use of data mining techniques to predict mortality and length of stay in an ICU. In: 12th International Conference on Innovations in Information Technology (IIT), pp. 1–5. IEEE (2016)
Neto, C., Peixoto, H., Abelha, V., Abelha, A., Machado, J.: Knowledge discovery from surgical waiting lists. Procedia Comput. Sci. 121, 1104–1111 (2017)
Scarlat, A.: MIMIC3d aggregated data - ICU aggregated data as number of interactions between patient and hospital, Version 1. https://www.kaggle.com/drscarlat/mimic3d
Whaley, D.L.: The Interquartile Range: Theory and Estimation. Electronic theses and dissertations. Paper 1030 (2005)
Martins, B., Ferreira, D., Neto, C., Abelha, A., Machado, J.: Data mining for cardiovascular disease prediction. J. Med. Syst. 45(1), 1–8 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by FCT – Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia within the R&D Units Project Scope: UIDB/00319/2020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Neto, C. et al. (2021). Step Towards Predicting Patient Length of Stay in Intensive Care Units. In: Rocha, Á., Adeli, H., Dzemyda, G., Moreira, F., Ramalho Correia, A.M. (eds) Trends and Applications in Information Systems and Technologies. WorldCIST 2021. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1368. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72654-6_28
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72654-6_28
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-72653-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-72654-6
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)