Abstract
The domain of Subject-oriented Business Process Management (S-BPM) is somewhat outstanding due to its embracing of Subject Orientation. However, at the same time, it is also a classic BPM domain concerned with typical aspects like creation and exchange of diagrammatic process models, elicitation of domain knowledge, and implementing process (models) into organisations and IT systems. Nevertheless, the Abstract State Machine (ASM) concept, a formal and abstract specification means for algorithms, has been and is fundamental and an important cornerstone for the S-BPM community. The first formal specifications for S-BPM has been developed by Egon Börger using ASM means—namely a specification for an interpreter engine for the subject-oriented modeling language PASS, the Parallel Activity Specification Schema. However, for the sake of intuitive and comprehensive use, ASM can be enriched with defining the passive aspects of PASS, namely the (data) structure of process models and data object appearing in the processes. Here it is useful to complement ASM description means with concepts that are better suited for that tasks. This work analyzes how the S-BPM research community has combined ASM with the Web Ontology Language (OWL) to generate a precise, while comprehensible, system specification for the execution of formal, subject-oriented process models. Furthermore, it will be argued why this combination is worthwhile overcoming the weaknesses of both generic and technology independent specification approaches.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
In an extended version of subject-orientation shared objects are also possible but are not considered here [9].
- 2.
Implementation of a subject = realization in form of a human, IT-System, or other technology.
- 3.
Thereby the availability of each
 can change, depending on the dynamic state of the
can change, depending on the dynamic state of the
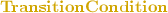 during execution. For example, the
during execution. For example, the
 enables or disables a
enables or disables a
 based on the availability of a Message in the Inputpool according to the
based on the availability of a Message in the Inputpool according to the
 .
.
References
Web ontology language (owl). https://www.w3.org/OWL/
Berghaus, M.: Luhmann leicht gemacht. Böhlau Verlag (2011)
Börger, E., Stärk, R.: Abstract State Machines: A Method for High-Level System Design and Analysis. Springer, Heidelberg (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-18216-7
Börger, E.: A subject-oriented interpreter model for S-BPM. Appendix. In: Fleischmann, A., Schmidt, W., Stary, C., Obermeier, S., Börger, E. (eds.) Subjektorientiertes Prozessmanagement. Hanser-Verlag, München (2011)
Börger, E., Stärk, R.F.: Abstract State Machines: A Method for High-Level System Design and Analysis. Springer, Berlin (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-18216-7
Dori, D.: Object-Process Methodology for Structure-Behavior Codesign. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15865-0_7
Einstein: Zitat albert einstein. https://www.sasserlone.de/zitat/190/albert.einstein/
Farahbod, R.: CoreASM: an extensible modeling framework & tool environment for high-level design and analysis of distributed systems. Ph.D. Dissertation (2009)
Fleischmann, A., Stary, C.: Dependable data sharing in dynamic IoT-systems - subject-oriented process design, complex event processing, and blockchains. In: Betz, S., Elstermann, M., Lederer, M. (eds.) S-BPM ONE 2019, 11th International Conference on Subject Oriented Business Process Management. ICPC published by ACM Digital Library, Association of Computing Machinery (ACM) (2019)
Fleischmann, A., Schmidt, W., Stary, C., Obermeier, S., Boerger, E.: Subject-Oriented Business Process Management. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-32392-8
Gemino, A., Wand, Y.: A framework for empirical evaluation of conceptual modeling techniques. Requirements Eng. 9, 248–260 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00766-004-0204-6
Habermas, J.: Theory of Communicative Action Volume 1, Volume 2. Suhrkamp Paperback Science (1981)
Hoare, A.: Communicating Sequential Processes. Prentice Hall, Hoboken (1985)
I2PM: Standard document for pass (2019). https://github.com/I2PM/Standard-Documents-for-Subject-Orientation. Accessed 22 Jan 2020
Jolak, et al.: Software engineering whispers: the effect of textual vs. graphical software design descriptions on software design communication. Empir. Softw. Eng. 25, 4427–4471 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10664-020-09835-6
Luhmann, N.: Social Systems. Suhrkamp Verlag (1984)
Milner, R.: Communication and Concurrency. Prentice Hall, Hoboken (1989)
Milner, R.: Communicating and Mobile Systems: The Pi-Calculus. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1999)
Römpp, M.: Habermas leicht gemacht. Böhlau Verlag (2015)
Stachowiak, H.: Allgemeine Modelltheorie. Springer, Heidelberg (1973)
Thalheim B.: The theory of conceptual models, the theory of conceptual modelling and foundations of conceptual modelling. In: Embley, D., Thalheim, B. (eds.) Handbook of Conceptual Modeling. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15865-0_17
Wolski, A., Borgert, S., Heuser, L.: A coreASM based reference implementation for subject oriented business process management execution semantics. In: Betz, S., Elstermann, M., Lederer, M. (eds.) S-BPM ONE 2019, 11th International Conference on Subject Oriented Business Process Management. ICPC published by ACM Digital Library, Association of Computing Machinery (ACM) (2019)
Wolski, A., Borgert, S., Heuser, L.: An extended subject-oriented business process management execution semantics. In: Betz, S., Elstermann, M., Lederer, M. (eds.) S-BPM ONE 2019, 11th International Conference on Subject Oriented Business Process Management. ICPC published by ACM Digital Library, Association of Computing Machinery (ACM) (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Elstermann, M., Wolski, A., Fleischmann, A., Stary, C., Borgert, S. (2021). The Combined Use of the Web Ontology Language (OWL) and Abstract State Machines (ASM) for the Definition of a Specification Language for Business Processes. In: Raschke, A., Riccobene, E., Schewe, KD. (eds) Logic, Computation and Rigorous Methods. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12750. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-76020-5_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-76020-5_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-76019-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-76020-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)





 can change, depending on the dynamic state of the
can change, depending on the dynamic state of the
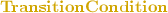 during execution. For example, the
during execution. For example, the
 enables or disables a
enables or disables a
 based on the availability of a Message in the Inputpool according to the
based on the availability of a Message in the Inputpool according to the
 .
.