Abstract
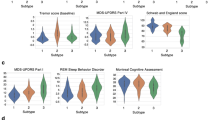
Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disease characterised by heterogeneity of the sets of symptoms patients experience and the trajectories of disease progression. The PPMI study includes patients’ symptoms explaining different aspects of patients’ life, i.e. motor, non-motor, and autonomic symptoms. This paper proposes a multi-view clustering approach for determining groups of Parkinson’s disease patients from the PPMI study with distinct disease trajectories over 4 years. The proposed multi-view clustering approach searches groups of patients who share similar disease progression trajectories over multiple types of symptoms. We detected two groups of patients with different disease progression trajectories and significant differences in severity of motor, non-motor, and autonomic symptoms. On the other hand, while we did not detect any significant differences between the patients from the two groups based on their demographics, medications treatment or their disease types, we identified over-sensitivity to bright light as a possible early screening symptom for type of disease progression.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
MDS-UPDRS is Movement Disorder Society sponsored revision of the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale.
- 2.
Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative, https://www.ppmi-info.org/.
References
Bickel, S., Scheffer, T.: Multi-view clustering. In: Proceedings of the 4th IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, ICDM 2004, pp. 19–26. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC, USA (2004)
Cohen, W.W.: Fast effective rule induction. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 115–123 (1995)
Fereshtehnejad, S.M., Postuma, R.B., Dagher, A., Zeighami, Y.: Clinical criteria for subtyping Parkinson’s disease: biomarkers and longitudinal progression. Brain 140(7), 1959–1976 (2017)
Goetz, C., et al.: Movement disorder society-sponsored revision of the unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale (MDS-UPDRS): scale presentation and clinimetric testing results. Move. Disord. 23(15), 2129–2170 (2008)
Hubert, L., Arabie, P.: Comparing partitions. J. Classif. 2(1), 193–218 (1985)
Jankovic, J., et al.: Variable expression of Parkinson’s disease - a base-line analysis of the DATATOP cohort. Neurology 40(10), 1529–1529 (1990)
Marek, K., et al.: The Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative (PPMI). Prog. Neurobiol. 95(4), 629–635 (2011)
Rousseeuw, P.J.: Silhouettes: a graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 20, 53–65 (1987)
Stebbins, G.T., Goetz, C.G., Burn, D.J., Jankovic, J., Khoo, T.K., Tilley, B.C.: How to identify tremor dominant and postural instability/gait difficulty groups with the movement disorder society unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale: comparison with the unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale. Mov. Disord. 28(5), 668–670 (2013)
Steering, D.: DATATOP: a multicenter controlled clinical trial in early Parkinson’s disease. Arch. Neurol. 46(10), 1052–1060 (1989)
Strehl, A., Ghosh, J.: Cluster ensembles–a knowledge reuse framework for combining multiple partitions. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 3, 583–617 (2002)
Valmarska, A., Miljkovic, D., Lavrač, N., Robnik-Šikonja, M.: Analysis of medications change in Parkinson’s disease progression data. J. Intell. Inf. Syst. 51(2), 301–337 (2018)
Valmarska, A., Miljkovic, D., Robnik–Šikonja, M., Lavrač, N.: Connection between the Parkinson’s disease subtypes and patients’ symptoms progression. In: Riaño, D., Wilk, S., ten Teije, A. (eds.) AIME 2019. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 11526, pp. 263–268. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-21642-9_32
Visser, M., Marinus, J., Stiggelbout, A.M., Van Hilten, J.J.: Assessment of autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease: the SCOPA-AUT. Mov. Disord. 19(11), 1306–1312 (2004)
Acknowledgment
The research was supported by the Slovenian Research Agency (research core funding programs P2-0209, P6-0411 and P2-0103) and the Slovenian Ministry of Education, Science and Sport (project R 2.1 - Public call for the promotion of researchers at the beginning of a career 2.1). Data used in the preparation of this article were obtained from the Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative (PPMI) (www.ppmi-info.org/data). For up-to-date information on the study, visit www.ppmi-info.org.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Valmarska, A., Lavrač, N., Robnik–Šikonja, M. (2021). Stratification of Parkinson’s Disease Patients via Multi-view Clustering. In: Tucker, A., Henriques Abreu, P., Cardoso, J., Pereira Rodrigues, P., Riaño, D. (eds) Artificial Intelligence in Medicine. AIME 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12721. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-77211-6_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-77211-6_25
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-77210-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-77211-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)