Abstract
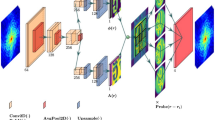
The ultra-fast all-optical solid-state framing camera (UASFC) is a new type of X-ray ultra-fast diagnostic technology. It uses X-ray excitation to change the refractive index distribution of the ultra-fast detection chip, and time-tuned multi-wavelength probe light for ultra-fast detection on the order of picoseconds or less. Due to the uneven intensity of the probe light wavelength and spatial diffraction, the noise of the detection image is too high, which directly affects the spatial and temporal resolution of the system. To improve the detection performance of the UASFC system, we adopted NLM image optimization technology based on a convolutional neural network, using 50 shots of the reticle image as the learning set and iterating the weight of the NLM image optimization filter. The CCD image obtained by the four-channel wavelength spectroscopy system is noise-reduced and optimized, which greatly improves the image contrast and edge definition, reduces image noise, and further improves the time and space resolution of the UASFC system.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, K.L., Stewart, R.E., Steele, P.T., Vernon, S.P., Hsing, W.W.: Ultrafast semiconductor x-ray detector. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101(3), 031107 (2012)
Vernon, S.P., et al.: X-ray bang-time and fusion reaction history at picosecond resolution using RadOptic detection. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 83(10), 10d307 (2012)
Apruzese, J.P., Thornhill, J.W., Whitney, K.G., et al.: Comparative analysis of time-resolved and time-integrated x-ray data from long pulse Z-pinch implosions on Saturn. Phys. Plasmas 8(8), 3799–3809 (2001)
Lazier, S.E., Barber, T.L., Derzon, M.S., et al.: Time and space resolved measurements of visible-light and soft x-ray emission from foam z-pinch plasmas and implosions. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 68(1), 660–663 (1997)
Byrd, J.M., Feng, J., Huang, G., et al.: Progress on modeling of ultrafast x-ray streak cameras. In: IEEE Proceedings of Particle Accelerator Conference, pp. 3961–3963 (2007)
Oertel, J.A.: A large-format gated x-ray framing camera. In: Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering, vol. 5194, pp. 214–222 (2004)
Hilsabeck, T.J., Hares, J.D., Kilkenny, J.D., et al.: Pulse-dilation enhanced gated optical imager with 5 ps resolution. Rev. Sci. Instrum 81(10), 10E317 (2010)
Bionta, M.R., Hartmann, N., Weaver, M., et al.: Spectral encoding method for measuring the relative arrival time between x-ray/optical pulses. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85(8), 083116 (2014)
Gao, G.L., He, K., Tian, J.S., Zhang, C.M., Zhang, J., Wang, T., et al.: Ultrafast all-optical solid-state framing camera with picosecond temporal resolution. Opt. Exp. 25, 8721 (2017)
Gao, G.L., Tian, J.S., Wang, T., He, K., Zhang, C.M., et al.: Ultrafast all-optical imaging technique using low-temperature grown GaAs/AlxGa1-xAs multiple quantum well semiconductor. Phys. Lett. A 381, 3594–3598 (2017)
Chen, P., Qian, H., Zhu, M.: Fast Gaussian particle filtering algorithm. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. (2008)
Elad, M.: On the origin of the bilateral filter and ways to improve it. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 11(10), 1141–1151 (2002)
Haichun, N.: Enhancement and binary representation of laser facula. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 35(8), 916–918 (2003)
Liu, J.B., Liu, B.Z.: Non-local mean image denoising method based on deep learning. Comput. Simul. 37(8), 228–234 (2020)
Buades, A., Coll, B., Morel, J.M.: A non-local algorithm for image denoising. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, vol. 2, pp. 60–65 (2005)
Hu, J., Lu, H.L., Zhang, J.: Laser image enhancement based on convolutional neural network. Laser J. 41(9), 147–150 (2020)
Dai, Z., Yang, Y.: Ultrasound image denoising based on deep learning. Inf. Technol. 9, 57–60 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhou, J. et al. (2021). Research on Deep Learning Denoising Method in an Ultra-Fast All-Optical Solid-State Framing Camera. In: Sun, X., Zhang, X., Xia, Z., Bertino, E. (eds) Artificial Intelligence and Security. ICAIS 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12736. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-78609-0_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-78609-0_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-78608-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-78609-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)