Abstract
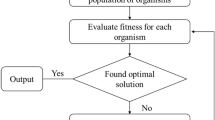
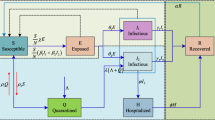
In this study, based on the characteristics and the transmission mechanism of COVID-19, SEIR epidemiological model is employed for modeling and analysis, utilizing the data of Hubei Province. To optimize the key epidemic parameters of the proposed SEIR model, a stochastic computational intelligence approach, the Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) is introduced. To better analyze the epidemic, the data between January 20, 2020 to March 25, 2020 is selected and divided into four stages. The parameters are dynamically changeable at different stages of the epidemic, which shows the effectiveness of public health prevention and control measures. Moreover, the Genetic Algorithm (GA) and the Bacterial Foraging Optimization (BFO) are also executed for comparison. The experimental results demonstrate that all swarm intelligence algorithms mentioned above can help forecast COVID-19, and PSO shows the advantages of faster convergence speed and the capability of finding a better set of solutions in fewer iterations, particularly.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao, S., Lin, Q., Ran, J., et al.: Preliminary estimation of the basic reproduction number of novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in China, from 2019 to 2020: a data-driven analysis in the early phase of the outbreak. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 92, 214–217 (2020)
Zhao, S., Musa, S., Lin, Q., et al.: Estimating the unreported number of novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) cases in China in the first half of january 2020: a data-driven modelling analysis of the early outbreak. J. Clin. Med. 9(2), 388 (2020)
Yang, Z., Zeng, Z., Wang, K.: Modified SEIR and AI prediction of the epidemics trend of COVID-19 in China under public health interventions. J. Thorac. Dis. 12(3), 165 (2020)
Huang, L., Wei, Y., Shen, S., et al.: Evaluation of predictive models for novel coronavirus pneumonia. Chin. J. Health Stat. 37(03), 322–326 (2020)
Kermack, W.O., McKendrick, A.G.: Contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B-Contain. Papers Abiological Char. 115(772), 700–721 (1927)
Wu, J.T., Leung, K., Leung, G.M.: Nowcasting and forecasting the potential domestic and international spread of the 2019-nCoV outbreak originating in Wuhan, China: a modelling study. Lancet 395(10225), 689–697 (2020)
Peng, L., Yang, W., Zhang, D., et al.: Epidemic analysis of COVID-19 in China by dynamical modeling (2020). arXiv:2002.06563
Wang, H., Wang, Z., Dong, Y., et al.: Phase-adjusted estimation of the number of Coronavirus Disease 2019 cases in Wuhan. China. Cell Discov. 6(1), 10 (2020)
Fang, Y., Nie, Y., Penny, M.: Transmission dynamics of the COVID-19 outbreak and effectiveness of government interventions: a data-driven analysis. J. Med. Virol. 92(6), 645–659 (2020)
Kennedy, J., Eberhart, R.: Particle swarm optimization. In: 1995 IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks Proceedings, pp. 1942–1948 (1995)
Zeng, N., Qiu, H., Wang, Z., et al.: A new switching-delayed-PSO-based optimized SVM algorithm for diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurocomputing 320, 195–202 (2018)
Navaneeth, B., Suchetha, M.: PSO optimized 1-D CNN-SVM architecture for real-time detection and classification applications. Comput. Biol. Med. 108, 85–92 (2019)
The National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China (NHC). http://www.nhc.gov.cn/. Accessed 25 Feb 2021
Wuhan Municipal Health Commission., http://wjw.hubei.gov.cn/. Accessed 25 Feb 2021
Aron, J.L., Schwartz, I.B.: Seasonality and period-doubling bifurcations in an epidemic model. J. Theor. Biol. 110(4), 665–679 (1984)
Shi, Y., Eberhart, R.C.: Empirical study of particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of the 1999. Congress on Evolutionary Computation-CEC99, pp. 1945–1950 (1999)
Acknowledgement
The work described in this paper was supported by The Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.71971143, 71571120); Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Grant No. 2020A1515010749); Key Research Foundation of Higher Education of Guangdong Provincial Education Bureau (Grant No. 2019KZDXM030), and Guangdong Province Postgraduate Education Innovation Research Project (Grant No. 2019SFKC46).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Qiu, H., Chen, J., Niu, B. (2021). Multi-stage COVID-19 Epidemic Modeling Based on PSO and SEIR. In: Tan, Y., Shi, Y. (eds) Advances in Swarm Intelligence. ICSI 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12689. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-78743-1_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-78743-1_24
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-78742-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-78743-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)