Abstract
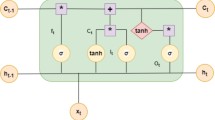
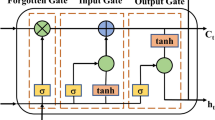
El Nino is an important research issue in meteorology. In this paper, we propose a time series model to predict the NINO index. In this model, variational mode decomposition (VMD) is applied to extract multiple sub-signals, the long short term memory network (LSTM) is used to fit these sub-signals. Aiming at the optimization of parameters, we design a K-means neighbor particle swarm optimization (KMPSO) based on comprehensive learning particle swarm optimization (CLPSO), which optimizes the parameters of VMD and LSTM. El Nino data is widely concerned due to its strong relevance to world climate change. We conduct experiments on El Nino data, and put forward a forecast model, which has better forecast skills than other models. Experiments results demonstrate that the proposed method extends forecast time limits, and improves the accuracy prediction.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saint-Lu, M., Braconnot, P., Leloup, J., Marti, O.: The role of El Nino in the global energy redistribution: a case study in the mid-holocene. Clim. Dyn. 52(12), 7135–7152 (2019)
Malherbe, J., Landman, W.A., Olivier, C., Sakuma, H., Luo, J.: Seasonal forecasts of the SINTEX-F coupled model applied to maize yield and streamflow estimates over north-eastern South Africa. Meteorol. Appl. 21(3), 733–742 (2014)
Goddard, L., Baethgen, W., Bhojwani, H.: The international research institute for climate and society: why, what and how. Earth Perspect. 1, 1–14 (2014)
Pillai, P.A., et al.: How distinct are the two flavors of El Nino in retrospective forecasts of climate forecast system version 2 (CFSv2)? Clim. Dyn. 48(11–12), 3829–3854 (2017)
Lambert, S., Marcus, S., De Viron, O.: Atmospheric torques and earth’s rotation: what drove the millisecond-level length-of-day response to the 2015–16 El Nino? Earth Syst. Dyn. Discuss. 8, 1–14 (2017)
Xue, Y., Kumar, A.: Evolution of the 2015/16 El Nino and historical perspective since 1979. Sci. China (Earth Sci.) 60(09), 1572–1588 (2017)
Ham, Y.G., Kim, J.H., Luo, J.J.: Deep learning for multi-year ENSO forecasts. Nature 573, 568–572 (2019)
Wang, D., Luo, H., Grunder, O., Lin, Y.: Multi-step ahead wind speed forecasting using an improved wavelet neural network combining variational mode decomposition and phase space reconstruction. Renew. Energy 113, 1345–1358 (2017)
Han, L., Zhang, R., Wang, X., Bao, A., Jing, H.: Multi-step wind power forecast based on VMD-LSTM. IET Renew. Power Gener. 13(10), 1690–1700 (2019)
Gao, L., Kirby, M., ud Din Ahmad, M., Mainuddin, M., Bryan, B.A.: Automatic calibration of a whole-of-basin water accounting model using a comprehensive learning particle swarm optimiser. J. Hydrol. 581, 124281 (2020)
Lee, C.Y., Huang, K.Y., Shen, Y.X., Lee, Y.C.: Improved weighted k-nearest neighbor based on PSO for wind power system state recognition. Energies 13(20), 5520 (2020)
Griffin, D., Lim, J.: Signal estimation from modified short-time Fourier transform. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Sig. Process. (ASSP) 32, 804–807 (1983)
An, N., Zhao, W., Wang, J., Shang, D., Zhao, E.: Using multi-output feedforward neural network with empirical mode decomposition based signal filtering for electricity demand forecasting. Energy 49, 279–288 (2013)
Liang, J.J., Qin, A.K., Suganthan, P.N., Baskar, S.: Comprehensive learning particle swarm optimizer for global optimization of multimodal functions. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 10(3), 281–295 (2006)
Ong, W., Tan, A., Vengadasalam, V., Tan, C., Ooi, T.: Real-time robust voice activity detection using the upper envelope weighted entropy measure and the dual-rate adaptive nonlinear filter. Entropy 19, 487 (2017)
Doi, T., Storto, A., Behera, S.K., Navarra, A., Yamagata, T.: Improved prediction of the Indian Ocean dipole mode by use of subsurface ocean observations. J. Clim. 30(19), 7953–7970 (2017)
Rashid, H.A.: Factors affecting ENSO predictability in a linear empirical model of tropical air-sea interactions. Sci. Rep. 10(3), 1740–1745 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This paper is supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFB1004300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Shen, C., Ni, Q., Zhao, S., Zhang, M., Wang, Y. (2021). An Improved El Nino Index Forecasting Method Based on Parameters Optimization. In: Tan, Y., Shi, Y. (eds) Advances in Swarm Intelligence. ICSI 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12690. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-78811-7_43
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-78811-7_43
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-78810-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-78811-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)