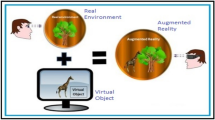
Abstract
What is Virtual Reality (VR)? What is Augmented Reality (AR)? What is the purpose of VR/AR? What are the basic concepts? What are the hard- and software components of VR/AR systems? How has VR/AR developed historically? The first chapter examines these questions and provides an introduction to this textbook. This chapter is fundamental for the whole book. All subsequent chapters build on it and do not depend directly on one another. Therefore, these chapters can be worked through selectively and in a sequence that suits the individual interests and needs of the readers. Corresponding tips on how this book can be used efficiently by different target groups (students, teachers, users, technology enthusiasts) are provided at the end of the chapter, as well as a summary, questions for reviewing what has been learned, recommendations for further reading, and the references used in the chapter.
Dedicated website for additional material: vr-ar-book.org
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azuma R (1997) A survey of augmented reality. Presence Teleop Virt 6(4):355–385
Bell B, Feiner S, Hoellerer T (2002) Information at a glance. IEEE Comp Gr Appl 22(4)., July/August, 6–9
Bricken W (1990) Virtual reality: directions of growth. Notes SIGGRAPH ‘90 Panel (HITL Technical Report R-90-1), University of Washington, Seattle
Bryson S (2013). Virtual Reality: a definition history – a personal essay. ArXiv, abs/1312.4322
Caudell TP, Mizell DW (1992) Augmented reality: an application of heads-up display technology to manual manufacturing processes. In: Proceedings of 25th Hawaii International conference on system sciences, Vol. 2, 659–669
Feiner S, MacIntyre B, Höllerer T (1997) A touring machine: prototyping 3D mobile augmented reality systems for exploring the urban environment, digest of papers. In: First International Symposium on Wearable Computers, pp 74–81
Fuchs H, Livingston MA, Raskar R, Colucci D, Keller K, State A, Crawford JR, Rademacher P, Drake SH, Meyer AA (1998) Augmented reality visualization for laparoscopic surgery. In: Wells WM, Colchester A, Delp S (eds) Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention — MICCAI’98, LNCS, vol 1496. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg
Held RH, Durlach NI (1992) Telepresence. Presence Teleop Virt 1(1):109–112
Kato H, Billinghurst M (1999) Marker tracking and HMD calibration for a video-based augmented reality conferencing system. In: 2nd IEEE and ACM international workshop on augmented reality (IWAR), pp. 85–94, IEEE
Mann S (1999) Mediated Reality. Linux Journal, Article No 5, Issue 59
Mann S, Furness T, Yuan Y, Iorio J, Wang Z (2018) All Reality: Virtual, Augmented, Mixed (X), Mediated (X,Y), and Multimediated Reality. https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.08386
Milgram P, Takemura H, Utsumi A, Kishino F (1995) Augmented reality: a class of displays on the reality-virtuality continuum. Proc SPIE 2351:282–292
Mine MR, Brooks Jr FP, Sequin CH (1997) Moving objects in space: Exploiting proprioception in virtual-environment interaction. In: Proceedings of SIGGRAPH 1997, pp 19–26
Paradiso JA, Landay JA (2009) Guest editors’ introduction: cross-reality environments. IEEE Perv Computing 8(3):14–15
Rekimoto J, Nagao K (1995) The world through the computer: computer augmented interaction with real world environments. In: Proceedings of UIST ‘95, pp 29–36
Rheingold H (1991) Virtual reality. Summit Books, New York
Sadowski W, Stanney KM (2002) Presence in virtual environments. In: Stanney KM (ed) Handbook of virtual environments: design, implementation, and applications. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc, Mahwah
Sheridan TB (1992) Musings on telepresence and virtual presence. Presence Teleop Virt 1(1):120–125
Sherman W, Craig A (2003) Understanding virtual reality. Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo
Slater M (2003) A note on presence terminology. Presence Connect 3:3
Slater M (2009) Place illusion and plausibility can lead to realistic behaviour in immersive virtual environments. Phil Trans R Soc B 364(1535):3549–3557
Slater M, Wilbur S (1997) A framework for immersive virtual environments (FIVE): speculations on the role of presence in virtual environments. Presence Teleop Virt 6(6):603–616
Slater M, Spanlang B, Corominas D (2010) Simulating virtual environments within virtual environments as the basis for a psychophysics of presence. ACM Trans Graph 29(4):92
Stone RJ (1993) In: Earnshaw RA, Gigante MA, Jones H (eds) Virtual reality systems. London, Academic
Sutherland IE (1965) The ultimate display. Proceedings of the IFIP congress, 506–508
Sutherland I (1968) A head mounted three dimensional display. In: Proceedings of the AFIPS fall joint computer conference. Thompson Books, Washington, DC, pp 757–764
Witmer BG, Singer MJ (1998) Measuring presence in virtual environments: a presence questionnaire. Presence Teleop Virt Environ 7(3):225–240
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Recommended Reading
Recommended Reading
-
Angel E, Shreiner D (2015) Interactive computer graphics: a top-down approach with WebGL. Pearson Education, Harlow – Textbook covering the basics of computer graphics, e.g., discussing the generation of images with the computer. It also introduces OpenGL and WebGL, a programming library for computer graphics, and discusses the possibilities of using graphics processors (GPUs) in the form of so-called shaders.
-
Rabin S (2009) Introduction to game development, 2nd edition. Charles River Media, Boston – a standard work on computer games. Due to the manifold points of contact between VR and computer games, literature from the field of computer games is also relevant.
Original scientific literature can be found in specialist journals and conference proceedings which can be researched and accessed in digital libraries (e.g., dl.acm.org, ieeexplore.org, link.springer.com) or via search engines (e.g. scholar.google.com). In the field of VR the IEEE VR Conference (ieeevr.org) takes place annually. Moreover, there is the Eurographics Symposium on Virtual Environments (EGVE) as well as the VR Conferences of euroVR, which are partly jointly organized as Joint Virtual Reality Conference (JVRC). With the focus on AR, ISMAR, the IEEE Symposium for Mixed and Augmented Reality, is held annually. In addition, there are special events that focus on aspects of user interfaces of VR and AR, such as the ACM VRST conference or the 3DUI, the IEEE Symposium for 3D User Interfaces. There are also further events dealing with special applications of VR, for instance in the industrial sector (e.g., VRCAI – ACM International Conference on Virtual Reality Continuum and Its Applications in Industry). Some scientific journals also focus on VR and AR, e.g., Presence – Teleoperators and Virtual Environments by MIT Press, Virtual Reality by Springer Verlag or the Journal of Virtual Reality and Broadcasting (jVRb) as an open access e-journal.
In addition to conference proceedings and professional journals that deal primarily with VR and AR, literature is also recommended that deals with essential aspects of VR and AR, such as Computer Graphics (e.g., ACM SIGGRAPH and the ACM Transactions on Graphics), Computer Vision (e.g., IEEE ICCV) or Human–Machine Interaction (e.g. ACM SIGCHI).
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Doerner, R., Broll, W., Jung, B., Grimm, P., Göbel, M., Kruse, R. (2022). Introduction to Virtual and Augmented Reality. In: Doerner, R., Broll, W., Grimm, P., Jung, B. (eds) Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-79062-2_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-79062-2_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-79061-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-79062-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)