Abstract
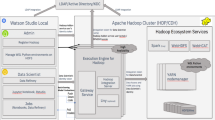
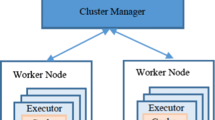
Since observational astronomy has turned into data-driven astronomy recently, analyzing this huge data effectively to extract useful information is becoming an important and essential task day by day. In this paper, we developed a neural network model to analyze redshift data of million of extragalactic objects. In order to do that, two different approaches for faster training of neural networks have been proposed. The first approach deals with the training model using Lipschitz-based adaptive learning rate in a single node/machine whereas the second approach discusses processing astronomy data in a multinode clustered environment. This approach can scale up to accommodate multiple nodes when necessary to handle bulk data using Apache spark and Elephas. Additionally, this paper also addresses the scalability and storage issue by implementing the model on the cloud. We used the distributed processing capability of the spark that reads data directly from HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System) of multiple machines and our experimental results show that using these approaches we can reduce training time and CPU time tremendously which is a crucial requirement while dealing with the extensive dataset. Although we have tested our experiment on a subset of huge data it can be scaled to process data of any size as well without much hurdle.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tallada, P., et al.: CosmoHub: interactive exploration and distribution of astronomical data on Hadoop. Astron. Comput. 32, 100391 (2020)
Borne, K.D.: Astroinformatics: a 21st century approach to astronomy. arXiv preprint arXiv:0909.3892 (2009)
Ball, N.M., Brunner, R.J.: Data mining and machine learning in astronomy. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 19(07), 1049–1106 (2010)
Kremer, J., et al.: Big universe, big data: machine learning and image analysis for astronomy. IEEE Intell. Syst. 32(2), 16–22 (2017)
Fluke, C.J., et al.: Surveying the reach and maturity of machine learning and artificial intelligence in astronomy. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.: Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 10(2), e1349 (2020)
Baron, D.: Machine learning in astronomy: a practical overview. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.07248 (2019)
Barchi, P.H., et al.: Machine and deep learning applied to galaxy morphology-a comparative study. Astron. Comput. 30, 100334 (2020)
Wadadekar, Y.: Estimating photometric redshifts using support vector machines. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 117(827), 79 (2004)
Collister, A.A., Lahav, O.: ANNz: estimating photometric redshifts using artificial neural networks. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 116(818), 345 (2004)
Garofalo, M., Botta, A., Ventre, G.: Astrophysics and big data: challenges, methods, and tools. Proc. Int. Astron. Union 12(S325), 345–348 (2016)
Ball, N.M.: CANFAR+ Skytree: a cloud computing and data mining system for astronomy. arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.3996 (2013)
Hong, S., et al.: Constraining cosmology with big data statistics of cosmological graphs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 493(4), 5972–5986 (2020)
Vujčić, V., Darko, J.: Real-time stream processing in astronomy. In: Knowledge Discovery in Big Data from Astronomy and Earth Observation, pp. 173–182. Elsevier (2020)
Brahem, M., Zeitouni, K., Yeh, L.: Astroide: a unified astronomical big data processing engine over spark. IEEE Trans. Big Data 6(3), 477–491 (2018)
Zhang, Z., et al.: Kira: processing astronomy imagery using big data technology. IEEE Trans. Big Data 6(2), 369–381 (2016)
Zečević, P., et al.: AXS: a framework for fast astronomical data processing based on Apache Spark. Astron. J. 158(1), 37 (2019)
Williams, B.F., et al.: Reducing and analyzing the PHAT survey with the cloud. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 236(1), 4 (2018)
Araya, M., et al.: JOVIAL: notebook-based astronomical data analysis in the cloud. Astron. Comput. 25, 110–117 (2018)
Yedida, R., Saha, S., Prashanth, T.: LipschitzLR: using theoretically computed adaptive learning rates for fast convergence. Appl. Intell. 51(3), 1460–1478 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-01892-0
Spark Homepage. https://spark.apache.org/. Accessed 29 Jan 2021
PySpark Homepage. https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/api/python/index.html. Accessed 29 Jan 2021
elephas Homepage. https://github.com/maxpumperla/elephas
Pence, W.D., et al.: Definition of the flexible image transport system (fits), version 3.0. Astron. Astrophys. 524, A42 (2010)
SDSS Homepage. https://sdss.org. Accessed 29 Jan 2021
VIPERS Homepage. http://vipers.inaf.it/. Accessed 29 Jan 2021
KIDS Homepage. http://kids.strw.leidenuniv.nl/. Accessed 29 Jan 2021
casjob Homepage. https://skyserver.sdss.org/casjobs/. Accessed 29 Jan 2021
AWS Homepage. https://aws.amazon.com/. Accessed 29 Jan 2021
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sen, S., Saha, S., Chakraborty, P., Singh, K.P. (2021). Implementation of Neural Network Regression Model for Faster Redshift Analysis on Cloud-Based Spark Platform. In: Fujita, H., Selamat, A., Lin, J.CW., Ali, M. (eds) Advances and Trends in Artificial Intelligence. From Theory to Practice. IEA/AIE 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12799. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-79463-7_50
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-79463-7_50
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-79462-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-79463-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)