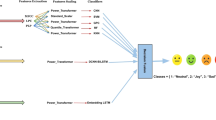
Abstract
Emotions of learners are crucial and important in e-learning as they promote learning. To investigate the effects of emotions on improving and optimizing the outcomes of e-learning, machine learning models have been proposed in the literature. However, proposed models so far are suitable for offline mode, where data for emotion classification is stored and can be accessed boundlessly. In contrast, when data arrives in a stream, the model can see the data once and real-time response is required for real-time emotion classification. Additionally, researchers have identified that single data modality is incapable of capturing the complete insight of the learning experience and emotions. So, multi-modal data streams such as electroencephalogram (EEG), Respiratory Belt (RB), electrodermal activity data (EDA), etc., are utilized to improve the accuracy and provide deeper insights in learners’ emotion and learning experience. In this paper, we propose a Real-time Multimodal Emotion Classification System (ReMECS) based on Feed-Forward Neural Network, trained in an online fashion using the Incremental Stochastic Gradient Descent algorithm. To validate the performance of ReMECS, we have used the popular multimodal benchmark emotion classification dataset called DEAP. The results (accuracy and F1-score) show that the ReMECS can adequately classify emotions in real-time from the multimodal data stream in comparison to the state-of-the-art approaches.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Eurecat Technology Centre of Catalonia, Spain: https://www.eurecat.org/.
References
Ayata, D., Yaslan, Y., Kamaşak, M.: Emotion recognition via random forest and galvanic skin response: comparison of time based feature sets, window sizes and wavelet approaches. In: Medical Technologies National Congress, pp. 1–4 (2016)
Ayata, D., Yaslan, Y., Kamasak, M.F.: Emotion recognition from multimodal physiological signals for emotion aware healthcare systems. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 40, 149–157 (2020)
Bahreini, K., Nadolski, R., Westera, W.: Towards multimodal emotion recognition in e-learning environments. Interact. Learn. Environ. 24(3), 590–605 (2016)
Baltrušaitis, T., Ahuja, C., Morency, L.: Multimodal machine learning: a survey and taxonomy. IEEE TPAMI 41(2), 423–443 (2019)
Bertsekas, D.P.: Incremental gradient, subgradient, and proximal methods for convex optimization: a survey. Optim. Mach. Learn. 1–38, 3 (2010)
Bifet, A., Holmes, G., Kirkby, R., Pfahringer, B.: Moa: massive online analysis. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 11, 1601–1604 (2010)
Blikstein, P., Worsley, M.: Multimodal learning analytics and education data mining: using computational technologies to measure complex learning tasks. J. Learn. Anal. 3, 220–238 (2016)
Bota, P., Wang, C., Fred, A., Silva, H.: Emotion assessment using feature fusion and decision fusion classification based on physiological data: are we there yet? Sensors 20(17), 4723 (2020)
Candra, H., et al.: Investigation of window size in classification of eeg-emotion signal with wavelet entropy and support vector machine. In: 37th Annual Int’l Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp. 7250–7253 (2015)
Di Mitri, D., Scheffel, M., Drachsler, H., Börner, D., Ternier, S., Specht, M.: Learning pulse: a machine learning approach for predicting performance in self-regulated learning using multimodal data, pp. 188–197. ACM (2017)
Ekman, P.: An argument for basic emotions. Cogn. Emot. 6(3–4), 169–200 (1992)
Faria, A.R., Almeida, A., Martins, C., Gonçalves, R., Martins, J., Branco, F.: A global perspective on an emotional learning model proposal. Telem. Inf. 34(6), 824–837 (2017)
Finch, D., Peacock, M., Lazdowski, D., Hwang, M.: Managing emotions: a case study exploring the relationship between experiential learning, emotions, and student performance. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 13(1), 23–36 (2015)
Hanjalic, A.: Extracting moods from pictures and sounds: towards truly personalized tv. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 23(2), 90–100 (2006)
Hayes, T.L., Kanan, C.: Lifelong machine learning with deep streaming linear discriminant analysis. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops (2020)
Huang, H., Hu, Z., Wang, W., Wu, M.: Multimodal emotion recognition based on ensemble convolutional neural network. IEEE Access 8, 3265–3271 (2020)
Islam, M.R., Ahmad, M.: Wavelet analysis based classification of emotion from eeg signal. In: International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Engineering, pp. 1–6 (2019)
Knörzer, L., Brünken, R., Park, B.: Emotions and multimedia learning: the moderating role of learner characteristics. J. Comp. Assist. Learn. 32(6), 618–631 (2016)
Koelstra, S., et al.: Deap: a database for emotion analysis;using physiological signals. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 3(1), 18–31 (2012)
Lee, D.H., Anderson, A.K.: Reading what the mind thinks from how the eye sees. Psychol. Sci. 28(4), 494–503 (2017)
Liu, W., Zheng, W., Lu, B.: Multimodal emotion recognition using multimodal deep learning. CoRR abs/1602.08225 (2016)
Mitri, D.D., Schneider, J., Specht, M., Drachsler, H.: The big five: addressing recurrent multimodal learning data challenges, vol. 2163. CrossMML (2018)
Nandi, A., Xhafa, F., Subirats, L., Fort, S.: A survey on multimodal data stream mining for e-learner’s emotion recognition. In: 2020 International Conference on Omni-layer Intelligent Systems (COINS), pp. 1–6 (2020)
Nandi, A., Xhafa, F., Subirats, L., Fort, S.: Real-time emotion classification using eeg data stream in e-learning contexts. Sensors 21(5), 1589 (2021)
Prieto, L., Sharma, K., Kidzinski, L., Rodríguez-Triana, M., Dillenbourg, P.: Multimodal teaching analytics: automated extraction of orchestration graphs from wearable sensor data. J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 34(2), 193–203 (2018)
Savran, A.: Multifeedback-layer neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 18(2), 373–384 (2007)
Schlosberg, H.: Three dimensions of emotion. Psych. Rev. 61(2), 81–88 (1954)
Smith, L.N.: Cyclical learning rates for training neural networks. In: IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pp. 464–472 (2017)
Subasi, A.: Eeg signal classification using wavelet feature extraction and a mixture of expert model. Expert Syst. Appl. 32(4), 1084–1093 (2007)
Yin, Z., Zhao, M., Wang, Y., Yang, J., Zhang, J.: Recognition of emotions using multimodal physiological signals and an ensemble deep learning model. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 140, 93–110 (2017)
Zhang, J., Yin, Z., Chen, P., Nichele, S.: Emotion recognition using multi-modal data and machine learning techniques: a tutorial and review. Inf. Fus. 59, 103–126 (2020)
Zhang, Y., Cheng, C., Zhang, Y.: Multimodal emotion recognition using a hierarchical fusion convolutional neural network. IEEE Access 9, 7943–7951 (2021)
Zheng, W., Liu, W., Lu, Y., Lu, B., Cichocki, A.: Emotionmeter: a multimodal framework for recognizing human emotions. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 49(3), 1110–1122 (2019)
Acknowledgement
Work partially funded by ACCIÓ under the project TutorIA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Nandi, A., Xhafa, F., Subirats, L., Fort, S. (2021). Real-Time Multimodal Emotion Classification System in E-Learning Context. In: Iliadis, L., Macintyre, J., Jayne, C., Pimenidis, E. (eds) Proceedings of the 22nd Engineering Applications of Neural Networks Conference. EANN 2021. Proceedings of the International Neural Networks Society, vol 3. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-80568-5_35
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-80568-5_35
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-80567-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-80568-5
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)