Abstract
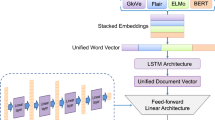
Humor detection from written sentences has been an interesting and challenging task in the last few years. Most of the prior studies have been explored the traditional approaches of embedding, e.g., Word2Vec or Glove. Recently Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) sentence embedding has also been used for this task. In this paper, we propose a framework for humor detection in short texts taken from news headlines. Our proposed framework attempts to extract information from written text via the use of different layers of BERT. After several trials, weights were assigned to different layers of the BERT model. The extracted information was then sent to a Bi-GRU neural network as an embedding matrix. We utilized the properties of some external embedding models. A multi-kernel convolution in our neural network was also employed to extract higher-level sentence representations. This framework performed very well on the task of humor detection.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Google code archive - long-term storage for google code project hosting, July 2013. https://code.google.com/archive/p/word2vec/
Abadi, M., et al.: Tensorflow: a system for large-scale machine learning. In: 12th \(\{\)USENIX\(\}\) Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (\(\{\)OSDI\(\}\) 16), pp. 265–283 (2016)
Alammar, J.: The illustrated BERT, ELMo, and co. (How NLP cracked transfer learning), December 2018. http://jalammar.github.io/illustrated-bert/
Annamoradnejad, I., Zoghi, G.: ColBERT: using BERT sentence embedding for humor detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.12765 (2020)
van den Beukel, S., Aroyo, L.: Homonym detection for humor recognition in short text. In: Proceedings of the 9th Workshop on Computational Approaches to Subjectivity, Sentiment and Social Media Analysis, pp. 286–291 (2018)
Branwen, G.: GPT-3 creative fiction (2020)
Cascade-correlation, R., Chunking, N.S.: 2 Previous work 9(8), 1–32 (1997)
Chen, P.Y., Soo, V.W.: Humor recognition using deep learning, pp. 113–117 (2018). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/n18-2018
Chung, J.: Gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling. arXiv:1412.3555v1 [cs. NE ], pp. 1–9, 11 December 2014
De Oliveira, L., Rodrigo, A.L.: Humor detection in yelp reviews (2015). Accessed 15 Dec 2019
Devlin, J., Chang, M.W., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In: NAACL HLT 2019 – 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies - Proceedings of the Conference 1(Mlm), pp. 4171–4186 (2019)
Hossain, N., Krumm, J., Gamon, M.: “President vows to cut \(<\)Taxes\(>\) hair”: dataset and analysis of creative text editing for humorous headlines (iv), pp. 133–142 (2019). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/n19-1012
Hossain, N., Krumm, J., Gamon, M., Kautz, H., Corporation, M.: SemEval-2020 Task 7: assessing humor in edited news headlines (2019) (2020)
Kiddon, C., Brun, Y.: That’s what she said: double entendre identification. In: Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, pp. 89–94 (2011)
Kim, Y.: Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification, pp. 1746–1751 (2014)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.L.: A: a m s o, pp. 1–15 (2015)
Mihalcea, R., Strapparava, C.: Making computers laugh: investigations in automatic humor recognition. In: Proceedings of Human Language Technology Conference and Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 531–538 (2005)
Mikolov, T., Grave, E., Bojanowski, P., Puhrsch, C., Joulin, A.: Advances in pre-training distributed word representations. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2018) (2018)
Owens, J.D., Houston, M., Luebke, D., Green, S., Stone, J.E., Phillips, J.C.: GPU computing. Proc. IEEE 96(5), 879–899 (2008)
Pennington, J.: Blue. https://nlp.stanford.edu/projects/glove/
Purandare, A., Litman, D.: Humor: prosody analysis and automatic recognition for f* r* i* e* n* d* s. In: Proceedings of the 2006 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 208–215 (2006)
Ritchie, G.: Developing the incongruity-resolution theory. Technical report (1999)
Taylor, J.M., Mazlack, L.J.: Computationally recognizing wordplay in jokes theories of humor (1991) (2000)
Taylor, J.M., Mazlack, L.J.: Computationally recognizing wordplay in jokes. In: Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society, vol. 26 (2004)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), pp. 5999–6009, December 2017
Weller, O., Seppi, K.: Humor detection: a transformer gets the last laugh. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.00252 (2019)
Xiao, H.: BERT-as-service (2018). https://github.com/hanxiao/bert-as-service
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Japan International Cooperation Agency – JICA under Innovative Asia program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Miraj, R., Aono, M. (2021). Combining BERT and Multiple Embedding Methods with the Deep Neural Network for Humor Detection. In: Qiu, H., Zhang, C., Fei, Z., Qiu, M., Kung, SY. (eds) Knowledge Science, Engineering and Management. KSEM 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12817. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-82153-1_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-82153-1_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-82152-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-82153-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)