Abstract
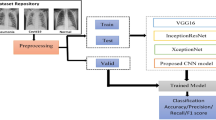
AI-based medical image processing has made significant progress, and it has a significant impact on biomedical research. Among the imaging variants, Chest x-rays imaging is cheap, simple, and can be used to detect influenza, tuberculosis, and various other illnesses. Researchers discovered that coronavirus spreads through the lungs, causing severe injuries during the COVID19 pandemic. As a result, chest x-rays can be used to detect COVID-19, making it a more robust detection method. In this paper, a RegNet hierarchical deep learning-based model has been proposed to detect COVID-19 positive and negative cases using CXI. The RegNet structure is designed to develop a model with a small number of epochs and parameters. The performance measurement found that the model takes five periods to reach a total accuracy of 98.08%. To test the model, we used two sets of data. The first dataset consists of 1200 COVID-19 positive CXRs and 1,341 COVID-19 negative CXRs, and the second dataset consists of 195 COVID-19 positive CXRs and 2,000 COVID-19 negative CXRs; all of these are publicly available. We obtained precision of 99.02% and 97.13% for these datasets, respectively. As a result of this finding, the proposed approach could be used for mass screening, and, as far as we are aware, the results achieved indicate that this model could be used as a screen guide.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaiser, M.S., et al.: iWorkSafe: towards healthy workplaces during COVID-19 with an intelligent pHealth app for industrial settings. IEEE Access 9, 13814–13828 (2021)
Jaiswal, A.K., et al.: Identifying pneumonia in chest X-rays: a deep learning approach. Measurement 145, 511–518 (2019)
Aradhya, V.M., Mahmud, M., Guru, D.S., Agarwal, B., Kaiser, M.S.: One-shot cluster-based approach for the detection of COVID-19 from chest X-ray images. Cogn. Comput. 1–9 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-020-09774-w
Mahmud, M., Kaiser, M.S.: Machine learning in fighting pandemics: a COVID-19 case study. In: Santosh, K., Joshi, A. (eds.) COVID-19: Prediction, Decision-Making, and Its Impacts, vol. 60, pp. 77–81. Springer, Singapore (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-9682-7_9
Singh, A.K., Kumar, A., Mahmud, M., Kaiser, M.S., Kishore, A.: COVID-19 Infection detection from chest X-ray images using hybrid social group optimization and support vector classifier. Cogn. Comput. 1–13 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-021-09848-3
Mahmud, M., Kaiser, M.S., McGinnity, T.M., Hussain, A.: Deep learning in mining biological data. Cogn. Comput. 13(1), 1–33 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-020-09773-x
Baltruschat, et al.: Comparison of deep learning approaches for multi-label chest X-ray classification. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 1–10 (2019)
Noor, M.B.T., Zenia, N.Z., Kaiser, M.S., Al Mamun, S., Mahmud, M.: Application of deep learning in detecting neurological disorders from magnetic resonance images: a survey on the detection of Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and Schizophrenia. Brain Inform. 7(1), 1–21 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40708-020-00112-2
Ruiz, J., Mahmud, M., Modasshir, M., Kaiser, M.S.: 3D DenseNet ensemble in 4-way classification of Alzheimer’s disease. In: : Mahmud, M., Vassanelli, S., Kaiser, M.S., Zhong, N. (eds.) International Conference on Brain Informatics, pp. 85–96. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59277-6_8
Mahmud, M., et al.: A brain-inspired trust management model to assure security in a cloud based IoT framework for neuroscience applications. Cogn. Comput. 10(5), 864–873 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-018-9543-3
Rabby, G., Azad, S., Mahmud, M., Zamli, K.Z., Rahman, M.M.: TeKET: a tree-based unsupervised keyphrase extraction technique. Cogn. Comput. 12(4), 811–833 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-019-09706-3
Kaiser, M.S., et al.: Advances in crowd analysis for urban applications through urban event detection. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 19(10), 3092–3112 (2017)
Yadav, S.S., Jadhav, S.M.: Deep convolutional neural network based medical image classification for disease diagnosis. J. Big Data 6(1), 1–18 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-019-0276-2
Santosh, K.C., Dhar, M.K., Rajbhandari, R., Neupane, A.: Deep neural network for foreign object detection in chest X-rays. In: 2020 IEEE 33rd International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), pp. 538–541. IEEE (2020)
Santosh, K.C.: AI-Driven tools for coronavirus outbreak: need of active learning and cross-population train/test models on multitudinal/multimodal data. J. Med. Syst. 44(5), 1–5 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-020-01562-1
Das, D., Santosh, K.C., Pal, U.: Truncated inception net: COVID-19 outbreak screening using chest X-rays. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 43(3), 915–925 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-020-00888-x
Mukherjee, H., Ghosh, S., Dhar, A., Obaidullah, S.M., Santosh, K.C., Roy, K.: Deep neural network to detect COVID-19: one architecture for both CT Scans and Chest X-rays. Appl. Intell. 51(5), 2777–2789 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-01943-6
Mukherjee, H., Ghosh, S., Dhar, A., Obaidullah, S.M., Santosh, K.C., Roy, K.: Shallow convolutional neural network for COVID-19 outbreak screening using chest X-rays. Cogn. Comput. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-020-09775-9
Togacar, M., et al.: COVID-19 detection using deep learning models to exploit Social Mimic Optimization and structured chest X-ray images using fuzzy color and stacking approaches. Comput. Biol. Med. 121, 103805 (2020)
Narin, A., et al.: Automatic detection of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) using X-ray images and deep convolutional neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2003.10849 (2020)
Huang, C., et al.: Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. The lancet 395(10223), 497–506 (2020)
Fang, Y., et al.: Sensitivity of chest CT for COVID-19: comparison to RT-PCR. Radiology 296(2), E115–E117 (2020)
Ng, M.Y., et al.: Imaging profile of the COVID-19 infection: radiologic findings and literature review. Radiol.: Cardiothorac. Imaging 2(1), e200034 (2020)
Li, Y., Xia, L.: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): role of chest CT in diagnosis and management. Am. J. Roentgenol. 214(6), 1280–1286 (2020)
Ye, Z., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Huang, Z., Song, B.: Chest CT manifestations of new coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a pictorial review. Eur. Radiol. 30(8), 4381–4389 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-06801-0
Zhou, S., Wang, Y., Zhu, T., Xia, L.: CT features of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia in 62 patients in Wuhan, China. Am. J. Roentgenol. 214(6), 1287–1294 (2020)
Bassi, P.R., Attux, R.: A deep convolutional neural network for COVID-19 detection using chest X-rays. arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.01578 (2020)
Majeed, T., Rashid, R., Ali, D., Asaad, A.: COVID-19 detection using CNN transfer learning from X-ray images. medRxiv (2020)
Ozturk, T., Talo, M., Yildirim, E.A., Baloglu, U.B., Yildirim, O., Acharya, U.R.: Automated detection of COVID-19 cases using deep neural networks with X-ray images. Comput. Biol. Med. 121, 103792 (2020)
Xu, J., et al.: RegNet: Self-regulated network for image classification. arXiv preprint arXiv:2101.00590 (2021)
Hussain, E., et al.: CoroDet: A deep learning based classification for COVID-19 detection using chest X-ray images. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 142, 110495 (2021)
Chowdhury, M.E., et al.: Can AI help in screening viral and COVID-19 pneumonia? IEEE Access 8, 132665–132676 (2020)
Rahman, T., et al.: Exploring the effect of image enhancement techniques on COVID-19 detection using chest X-ray images (2020)
Minaee, S., et al.: Deep-COVID: predicting COVID-19 from chest X-ray images using deep transfer learning. Med. Image Anal. 101794 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2020.101794
Radosavovic, I., et al.: Designing network design spaces. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10428–10436 (2020)
Aradhya, V.N.M., et al.: One-shot cluster-based approach for the detection of COVID–19 from chest X-ray images. Cogn. Comput. 1–9 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-020-09774-w
Mahmud, M., Kaiser, M.S., Hussain, A., Vassanelli, S.: Applications of deep learning and reinforcement learning to biological data. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 29(6), 2063–2079 (2018)
Shah, P.M., et al.: Deep GRU-CNN model for COVID-19 detection from chest X-rays data. IEEE Access (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3077592
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mahbub, M.K., Biswas, M., Miah, A.M., Shahabaz, A., Kaiser, M.S. (2021). COVID-19 Detection Using Chest X-Ray Images with a RegNet Structured Deep Learning Model. In: Mahmud, M., Kaiser, M.S., Kasabov, N., Iftekharuddin, K., Zhong, N. (eds) Applied Intelligence and Informatics. AII 2021. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1435. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-82269-9_28
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-82269-9_28
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-82268-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-82269-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)