Abstract
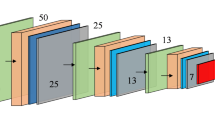
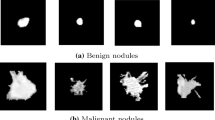
Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers in the world, and the detection and classification of benign-malignant lung nodules are critical during the diagnosis and treatment for lung cancer. In this paper, a multi-view improved dense convolutional network is proposed for the classification of benign-malignant pulmonary nodules, where more information of input multi-scale features can be extracted from 2D views of nine different directions. The improved dense block and other layers are linked by shortcuts, which optimizes the feature extraction. The proposed network model is trained in the LIDC-IDRI dataset, and the results show that the average classification accuracy and AUC are 86.52% and 97.23% respectively, which means that the network model has significantly improved the performance of benign-malignant pulmonary nodules classification.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay, J., et al.: Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 136(5), E359–E386 (2015)
Bach, P.B., Silvestri, G.A., Hanger, M., Jett, J.R.: Screening for lung cancer: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guide-lines. Chest 132, 69S-77S (2007)
Larici, A.R., Farchione, A., Franchi, P., Ciliberto, M., Cicchetti, G., Calandriello, L., del Ciello, A., Bonomo, L.: Lung nodules: Size still matters. Eur. Respir. Rev. 26, 170025 (2017)
Siegel, R.L., Miller, K.D., Jemal, A.: Cancer statistics, 2018, CA. Cancer J. Clin. 68(1), 7–30 (2018)
Zhao, X., Liu, L., Qi, S., Teng, Y., Li, J., Qian, W.: Agile convolutional neural network for pulmonary nodule classification using CT images. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 13(4), 585–595 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-017-1696-0
Filho, P.P.R., Sarmento, R.M., Holanda, G.B., de AlencarLima, D.: ‘New approach to detect and classify stroke in skull CT images via analysis of brain tissue densities.’ Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 148, 27–43 (2017)
Chen, S., et al.: ‘Automatic scoring of multiple semantic attributes with multi-task feature leverage: a study on pulmonary nodules in CT images.’ IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 36(3), 802–814 (2017)
Srensen, L., Shaker, S.B., de Bruijne, M.: ‘Quantitative analysis of pulmonary emphysema using local binary patterns.’ IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 29(2), 559–569 (2010)
Zhang, F., et al.: A ranking-based lung nodule image classification method using unlabeled image knowledge. In: Proceedings of the ISBI, pp. 1356–1359, April 2014
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Hua, K.-L., Hsu, C.H., Hidayati, S.C., Cheng, W., Chen, Y.: Computer-aided classification of lung nodules on computed tomography images via deep learning technique. Onco-Targets Terapy 8, 2015–2022 (2015)
EI-Baza, S., Gimel'farbg, et al.: Elastic phantoms generated by microfluidics technology: validation of an imaged-based approach for accurate measurement of the growth rate of lung nodules. Biotechnol. J. 6(2), 195–203 (2011)
Xie, Y., et al.: Knowledge-based collaborative deep learning for benign-malignant lung nodule classification on chest CT. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 38(4), 991–1004 (2019)
Dey, R., Lu, Z., Hong, Y.: Diagnostic classification of lung nodules using 3D neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018), Washington, DC, USA, 4–7 April 2018, pp. 774–778 (2018)
Yan, X., et al.: Classification of lung nodule malignancy risk on computed tomography images using convolutional neural network: a comparison between 2D and 3D strategies. In: Chen, C.-S., Lu, J., Ma, K.-K. (eds.) ACCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 10118, pp. 91–101. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-54526-4_7
Dey, R., Lu, Z., Hong, Y.: Diagnostic classification of lung nodules using 3D neural networks. In: Proceedings of the ISBI, pp. 774–778, April 2018
El-Regaily, S.A., Salem, M.A.M., Aziz, M.H.A., Roushdy, M.I.: Multi-view Convolutional Neural Network for lung nodule false positive reduction. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 113017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2019.113017
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Shen, LH., Wang, XH., Gao, MX., Li, B. (2021). Classification of Benign-Malignant Pulmonary Nodules Based on Multi-view Improved Dense Network. In: Huang, DS., Jo, KH., Li, J., Gribova, V., Bevilacqua, V. (eds) Intelligent Computing Theories and Application. ICIC 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12836. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-84522-3_48
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-84522-3_48
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-84521-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-84522-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)