Abstract
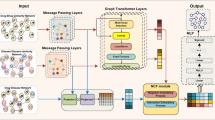
Computational drug repositioning is essential in drug discovery and development. The previous methods basically utilized matrix calculation. Although they had certain effects, they failed to treat drug-disease associations as a graph structure and could not find out more in-depth features of drugs and diseases. In this paper, we propose a model based on multi-graph deep learning to predict unknown drug-disease associations. More specifically, the known relationships between drugs and diseases are learned by two graph deep learning methods. Graph attention network is applied to learn the local structure information of nodes and graph embedding is exploited to learn the global structure information of nodes. Finally, Gradient Boosting Decision Tree is used to combine the two characteristics for training. The experiment results reveal that the AUC is 0.9625 under the ten-fold cross-validation. The proposed model has excellent classification and prediction ability.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jarada, T.N., Rokne, J.G., Alhajj, R.: A review of computational drug repositioning: strategies, approaches, opportunities, challenges, and directions. J. Cheminf. 12(1), 1–23 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13321-020-00450-7
Paul, S.M., et al.: How to improve R&D productivity: the pharmaceutical industry’s grand challenge. Nat. Rev. Drug Disc. 9, 203–214 (2010)
Adams, C.P., Brantner, V.V.: Estimating the cost of new drug development: is it really $802 million? Health Aff. 25, 420–428 (2006)
DiMasi, J.A., Hansen, R.W., Grabowski, H.G.: The price of innovation: new estimates of drug development costs. J. Health Econ. 22, 151–185 (2003)
Luo, H., Li, M., Yang, M., Wu, F.-X., Li, Y., Wang, J.: Biomedical data and computational models for drug repositioning: a comprehensive review. Brief. Bioinf. 22, 1604 (2019)
Luo, H., Li, M., Wang, S., Liu, Q., Li, Y., Wang, J.: Computational drug repositioning using low-rank matrix approximation and randomized algorithms. Bioinformatics 34, 1904–1912 (2018)
Chen, Z.-H., You, Z.-H., Guo, Z.-H., Yi, H.-C., Luo, G.-X., Wang, Y.-B.: Prediction of drug-target interactions from multi-molecular network based on deep walk embedding model. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 8, 338 (2020)
Chen, Z.-H., You, Z.-H., Li, L.-P., Wang, Y.-B., Qiu, Y., Hu, P.-W.: Identification of self-interacting proteins by integrating random projection classifier and finite impulse response filter. BMC Genomics 20, 1–10 (2019)
Ji, B.-Y., You, Z.-H., Jiang, H.-J., Guo, Z.-H., Zheng, K.: Prediction of drug-target interactions from multi-molecular network based on LINE network representation method. J. Transl. Med. 18, 1–11 (2020)
Jiang, H.-J., Huang, Y.-A., You, Z.-H.: SAEROF: an ensemble approach for large-scale drug-disease association prediction by incorporating rotation forest and sparse autoencoder deep neural network. Sci. Rep. 10, 1–11 (2020)
Jiang, H.-J., Huang, Y.-A., You, Z.-H.: Predicting drug-disease associations via using gaussian interaction profile and kernel-based autoencoder. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 1–11 (2019)
Jiang, H.-J., You, Z.-H., Huang, Y.-A.: Predicting drug− disease associations via sigmoid kernel-based convolutional neural networks. J. Transl. Med. 17, 382 (2019)
Hu, L., Wang, X., Huang, Y.-A., Hu, P., You, Z.-H.: A survey on computational models for predicting protein–protein interactions. Brief. Bioinf. (2021)
Hu, L., Pan, X., Yan, H., Hu, P., He, T.: Exploiting higher-order patterns for community detection in attributed graphs. Integr. Comput.-Aided Eng. 28, 1–12 (2020)
Hu, L., Yang, S.: A fast algorithm to identify coevolutionary patterns from protein sequences based on tree-based data structure. In: 2019 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (SMC), pp. 2273–2278. IEEE (2019)
Zhao, B.-W., Zhang, P., You, Z.-H., Zhou, J.-R., Li, X.: Predicting LncRNA-miRNA interactions via network embedding with integrated structure and attribute information. In: Huang, D.-S., Jo, K.-H. (eds.) ICIC 2020. LNCS, vol. 12464, pp. 493–501. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60802-6_43
Jiang, H.-J., You, Z.-H., Hu, L., Guo, Z.-H., Ji, B.-Y., Wong, L.: A highly efficient biomolecular network representation model for predicting drug-disease associations. In: Huang, D.-S., Premaratne, P. (eds.) ICIC 2020. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 12465, pp. 271–279. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60796-8_23
Wang, L., You, Z.-H., Li, L.-P., Yan, X., Zhang, W.: Incorporating chemical sub-structures and protein evolutionary information for inferring drug-target interactions. Sci. Rep. 10, 1–11 (2020)
Wang, L., You, Z.-H., Chen, X., Yan, X., Liu, G., Zhang, W.: Rfdt: a rotation forest-based predictor for predicting drug-target interactions using drug structure and protein sequence information. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 19, 445–454 (2018)
Wang, L., et al.: A computational-based method for predicting drug–target interactions by using stacked autoencoder deep neural network. J. Comput. Biol. 25, 361–373 (2018)
Zhang, P., Zhao, B.-W., Wong, L., You, Z.-H., Guo, Z.-H., Yi, H.-C.: A novel computational method for predicting LncRNA-disease associations from heterogeneous information network with SDNE embedding model. In: Huang, D.-S., Jo, K.-H. (eds.) ICIC 2020. LNCS, vol. 12464, pp. 505–513. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60802-6_44
Gottlieb, A., Stein, G.Y., Ruppin, E., Sharan, R.: PREDICT: a method for inferring novel drug indications with application to personalized medicine. Mol. Syst. Biol. 7, 496 (2011)
Wang, Y., Chen, S., Deng, N., Wang, Y.: Drug repositioning by kernel-based integration of molecular structure, molecular activity, and phenotype data. PloS one 8, e78518 (2013)
Dai, W., et al.: Matrix factorization-based prediction of novel drug indications by integrating genomic space. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2015, 1–9 (2015)
Yang, J., Li, Z., Fan, X., Cheng, Y.: Drug–disease association and drug-repositioning predictions in complex diseases using causal inference–probabilistic matrix factorization. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 54, 2562–2569 (2014)
Zeng, X., Zhu, S., Liu, X., Zhou, Y., Nussinov, R., Cheng, F.: deepDR: a network-based deep learning approach to in silico drug repositioning. Bioinformatics 35, 5191–5198 (2019)
Wang, L., You, Z.-H., Li, Y.-M., Zheng, K., Huang, Y.-A.: GCNCDA: a new method for predicting circRNA-disease associations based on Graph Convolutional Network Algorithm. PLOS Comput. Biol. 16, e1007568 (2020)
Li, J., Zhang, S., Liu, T., Ning, C., Zhang, Z., Zhou, W.: Neural inductive matrix completion with graph convolutional networks for miRNA-disease association prediction. Bioinformatics 36, 2538–2546 (2020)
Jiang, M., et al.: Drug–target affinity prediction using graph neural network and contact maps. RSC Adv. 10, 20701–20712 (2020)
Wang, B., Lyu, X., Qu, J., Sun, H., Pan, Z., Tang, Z.: GNDD: a graph neural network-based method for drug-disease association prediction. In: 2019 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), pp. 1253–1255. IEEE (2019)
Sun, M., Zhao, S., Gilvary, C., Elemento, O., Zhou, J., Wang, F.: Graph convolutional networks for computational drug development and discovery. Brief. Bioinf. 21, 919–935 (2020)
Zhao, T., Hu, Y., Valsdottir, L.R., Zang, T., Peng, J.: Identifying drug–target interactions based on graph convolutional network and deep neural network. Briefings in Bioinformatics (2020)
Torng, W., Altman, R.B.: Graph convolutional neural networks for predicting drug-target interactions. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 59, 4131–4149 (2019)
Hu, L., Chan, K.C., Yuan, X., Xiong, S.: A variational Bayesian framework for cluster analysis in a complex network. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 32, 2115–2128 (2019)
Guo, Z.-H., You, Z.-H., Wang, Y.-B., Huang, D.-S., Yi, H.-C., Chen, Z.-H.: Bioentity2vec: attribute-and behavior-driven representation for predicting multi-type relationships between bioentities. GigaScience 9, giaa032 (2020)
Yi, H.-C., You, Z.-H., Huang, D.-S., Guo, Z.-H., Chan, K.C., Li, Y.: Learning representations to predict intermolecular interactions on large-scale heterogeneous molecular association network. Iscience 23, 101261 (2020)
Wong, L., You, Z.-H., Guo, Z.-H., Yi, H.-C., Chen, Z.-H., Cao, M.-Y.: MIPDH: a novel computational model for predicting microRNA–mRNA interactions by DeepWalk on a heterogeneous network. ACS Omega 5, 17022–17032 (2020)
Huang, Y.-A., Hu, P., Chan, K.C., You, Z.-H.: Graph convolution for predicting associations between miRNA and drug resistance. Bioinformatics 36, 851–858 (2020)
Yu, Z., Huang, F., Zhao, X., Xiao, W., Zhang, W.: Predicting drug–disease associations through layer attention graph convolutional network. Brief. Bioinf. (2020)
Guo, Z.-H., Yi, H.-C., You, Z.-H.: Construction and comprehensive analysis of a molecular association network via lncRNA–miRNA–disease–drug–protein graph. Cells 8, 866 (2019)
Yue, X., et al.: Graph embedding on biomedical networks: methods, applications and evaluations. Bioinformatics 36, 1241–1251 (2020)
Guo, Z.-H., You, Z.-H., Huang, D.-S., Yi, H.-C., Chen, Z.-H., Wang, Y.-B.: A learning based framework for diverse biomolecule relationship prediction in molecular association network. Commun. Biol. 3, 1–9 (2020)
Zhao, B.-W., et al.: A novel method to predict drug-target interactions based on large-scale graph representation learning. Cancers 13, 2111 (2021)
Guo, Z.-H., et al.: MeSHHeading2vec: a new method for representing MeSH headings as vectors based on graph embedding algorithm. Brief. Bioinform. 22, 2085–2095 (2021)
Guo, Z.-H., You, Z.-H., Yi, H.-C.: Integrative construction and analysis of molecular association network in human cells by fusing node attribute and behavior information. Molec. Therapy-Nucleic Acids 19, 498–506 (2020)
Zhao, B.-W., You, Z.-H., Wong, L., Zhang, P., Li, H.-Y., Wang, L.: MGRL: predicting drug-disease associations based on multi-graph representation learning. Front. Genet. 12, 491 (2021)
Wishart, D.S., et al.: DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucl. Acids Res. 46, D1074-D1082 (2017)
Hamosh, A., Scott, A.F., Amberger, J., Bocchini, C., Valle, D., McKusick, V.A.: Online mendelian inheritance in man (OMIM), a knowledgebase of human genes and genetic disorders. Nucl. Acids Res. 30, 52–55 (2002)
Van Der Maaten, L., Postma, E., Van den Herik, J.: Dimensionality reduction: a comparative. J Mach. Learn. Res. 10, 13 (2009)
Wang, Y., Yao, H., Zhao, S.: Auto-encoder based dimensionality reduction. Neurocomputing 184, 232–242 (2016)
Veličković, P., Cucurull, G., Casanova, A., Romero, A., Lio, P., Bengio, Y.: Graph attention networks (2017). arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.10903
Grover, A., Leskovec, J.: node2vec: scalable feature learning for networks. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 855–864 (2016)
Manoochehri, H.E., Nourani, M.: Drug-target interaction prediction using semi-bipartite graph model and deep learning. BMC Bioinf. 21, 1–16 (2020)
Zhang, Y., Qiao, S., Lu, R., Han, N., Liu, D., Zhou, J.: How to balance the bioinformatics data: pseudo-negative sampling. BMC Bioinf. 20, 1–13 (2019)
Yang, M., Luo, H., Li, Y., Wang, J.: Drug repositioning based on bounded nuclear norm regularization. Bioinformatics 35, i455–i463 (2019)
Luo, H., et al.: Drug repositioning based on comprehensive similarity measures and bi-random walk algorithm. Bioinformatics 32, 2664–2671 (2016)
Martinez, V., Navarro, C., Cano, C., Fajardo, W., Blanco, A.: DrugNet: network-based drug–disease prioritization by integrating heterogeneous data. Artif. Intell. Med. 63, 41–49 (2015)
Wang, W., Yang, S., Li, J.: Drug target predictions based on heterogeneous graph inference. In: Biocomputing 2013, pp. 53–64. World Scientific (2013)
Acknowledgement
This work is supported in part by the major science and technology projects in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, under Grant 2020A03004–4, The authors would like to thank all the guest editors and anonymous reviewers for their constructive advices.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhao, BW., You, ZH., Hu, L., Wong, L., Ji, BY., Zhang, P. (2021). A Multi-graph Deep Learning Model for Predicting Drug-Disease Associations. In: Huang, DS., Jo, KH., Li, J., Gribova, V., Premaratne, P. (eds) Intelligent Computing Theories and Application. ICIC 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12838. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-84532-2_52
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-84532-2_52
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-84531-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-84532-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)