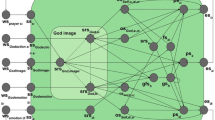
Abstract
Religion is an important aspect of many individuals’ lives. A central element of it is a mental God-model. Such a mental God-model can have different forms and depending on that it has a specific influence on human behaviour. This has been extensively studied from different perspectives. The current study uses a number of these perspectives as a basis for an integrative adaptive network model for formation and use of a mental God-model. It describes the mental states involved, their mutual relations, and the adaptation of some of these relations over time due to learning. Based on the obtained network model, simulations can be done for almost any kind of religion and person, showing different behaviours for persons with different religious backgrounds and characters. The focus here was mainly on the very relevant topic of the influence of religion on human empathy and disempathy. The developed adaptive network model can be valuable for many uses, involving support for a better understanding, and even prediction, of the behaviour of religious individuals and its underlying mechanisms. It is illustrated for a number of different scenarios for different types of persons and religions.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, J.G.: Mentalizing in practice. In: Handbook of Mentalization-Based Treatment, pp. 3–30 (2006)
Allen, J.G., Fonagy, P., Bateman, A.W.: Mentalizing in Clinical Practice. American Psychiatric Publishing, Washington/London (2008)
Atran, S.: In Gods We Trust: The Evolutionary Landscape of Religion. Oxford University Press, New York (2002).
Bamford, C., Lagattuta, K.H.: A new look at children’s understanding of mind and emotion: the case of prayer. Dev. Psychol. 46(1), 78 (2010)
Bateman, A., Fonagy, P. (eds.): Handbook of Mentalizing in Mental Health Practice. American Psychiatric Association, Washington (2012)
Beauregard, M., Paquette, V.: Neural correlates of a mystical experience in Carmelite nuns. Neurosci. Lett. 405(3), 186–190 (2006)
Beste, C., Dinse, H.R.: Learning without training. Curr. Biol. 23(11), R489–R499 (2013)
Bi, G.Q., Poo, M.M.: Synaptic modification by correlated activity: Hebb’s postulate revisited. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24(1), 139–166 (2001)
Blogowska, J., Saroglou, V.: For better or worse: fundamentalists’ attitudes toward outgroups as a function of exposure to authoritative religious texts. Int. J. Psychol. Relig. 23(2), 103–125 (2013)
Bowlby, J.: Attachment and Loss. Vol. 3. Loss. Basic Books, New York (1980)
Boyer, P.: Religious thought and behaviour as by-products of brain function. Trends Cogn. Sci. 7(3), 119–124 (2003)
Bremner, R.H., Koole, S.L., Bushman, B.J.: “Pray for those who mistreat you”: effects of prayer on anger and aggression. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 37(6), 830–837 (2011)
Bulbulia, J.: The cognitive and evolutionary psychology of religion. Biol. Philos. 19(5), 655–686 (2004)
Cooke, P., Elcoro, M.: Neurotheology: neuroscience of the soul. J. Young Investigators 25(3), 1–6 (2013)
Counted, V.: God as an attachment figure: a case study of the god attachment language and god concepts of anxiously attached Christian youths in South Africa. J. Spirituality Mental Health 18(4), 316–346 (2016)
Damasio, A.R.: Descartes’ Error: Emotion, Reason and the Human Brain. Papermac (1994)
Damasio, A.R.: Self Comes to Mind: Constructing the Conscious Brain. Pantheon Books (2010)
Ellison, C.G., Bradshaw, M., Kuyel, N., Marcum, J.P.: Attachment to God, stressful life events, and changes in psychological distress. Rev. Relig. Res. 53(4), 493–511 (2012)
Emmons, R.A.: Striving for the sacred: personal goals, life meaning, and religion. J. Soc. Issues 61(4), 731–745 (2005)
Escher, D.: How does religion promote forgiveness? Linking beliefs, orientations, and practices. J. Sci. Study Relig. 52(1), 100–119 (2013)
Fishman, I., Keown, C.L., Lincoln, A.J., Pineda, J.A., Müller, R.A.: Atypical cross talk between mentalizing and mirror neuron networks in autism spectrum disorder. JAMA Psychiat. 71(7), 751–760 (2014)
Fonagy, P.: The mentalization-focused approach to social development. In: Busch, F.N. (ed.) Mentalization: Theoretical Considerations, Research Findings and Clinical Implications, pp. 3–56. The Analytic Press, New York/London (2008)
Fonagy, P., Luyten, P.: A developmental, mentalization-based approach to the understanding and treatment of borderline personality disorder. Dev. Psychopathol. 21, 1355–1381 (2009)
Geertz, A.W., Jensen, J.S.: Religious Narrative, Cognition and Culture: Image and Word in the Mind of Narrative. Routledge (2014)
Gerstner, W., Kistler, W.M.: Mathematical formulations of Hebbian learning. Biol. Cybern. 87, 404–415 (2002)
Grafman, J., Cristofori, I., Zhong, W., Bulbulia, J.: The neural basis of religious cognition. Curr Dir Psychol Sci 29, 126–133 (2020)
Granqvist, P.: (2016). Attachment, emotion, and religion. In: Issues in Science and Theology: Do Emotions Shape the World?, pp. 9–26. Springer International Publishing (2014)
Granqvist, P., Hagekull, B.: Longitudinal predictions of religious change in adolescence: contributions from the interaction of attachment and relationship status. J. Soc. Pers. Relat. 20, 793–817 (2003)
Granqvist, P., Kirkpatrick, L.A.: Attachment and religious representations and behavior. In: Cassidy, J., Shaver, P.R. (eds.) Handbook of Attachment: Theory, Research, and Clinical Applications (2nd ed., pp. 906–933). Guilford, New York (2008)
Granqvist, P., Kirkpatrick, L.A.: Religion, spirituality, and attachment. In: Pargament, K.I., Exline, J.J., Jones, J.W. (eds.) APA Handbook of Psychology, Religion, and Spirituality Vol. 1: Context, Theory, and Research, pp. 139–155. American Psychological Association (2013)
Granqvist, P., Mikulincer, M., Shaver, P.R.: Religion as attachment: normative processes and individual differences. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Rev. 14(1), 49–59 (2010)
Granqvist, P., Broberg, A.G., Hagekull, B.: Attachment, religiousness, and distress among the religious and spiritual: links between religious syncretism and compensation. Ment. Health Relig. Cult. 17(7), 726–740 (2014)
Hebb, D.O.: The Organisation of Behavior. Wiley (1949)
James, W.: What is an emotion. Mind 9, 188–205 (1884)
Johnson, K.A., Li, Y.J., Cohen, A.B., Okun, M.A.: Friends in high places: The influence of authoritarian and benevolent god-concepts on social attitudes and behaviors. Psychol. Relig. Spiritual. 5(1), 15 (2013)
Kapogiannis, D., Barbey, A.K., Su, M., Zamboni, G., Krueger, F., Grafman, J.: Cognitive and neural foundations of religious belief. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 106(12), 4876–4881 (2009)
Kapogiannis, D., Deshpande, G., Krueger, F., Thornburg, M.P., Grafman, J.H.: Brain networks shaping religious belief. Brain Connectivity 4(1), 70–79 (2014)
Keysers, C., Gazzola, V.: Hebbian learning and predictive mirror neurons for actions, sensations and emotions. Philos. Trans. Royal Soc. London B: Biol. Sci. 369(1644), 20130175 (2014)
Keysers, C., Gazzola, V.: From vicarious actions to moral behavior. In: Issues in Science and Theology: Do Emotions Shape the World?, pp. 99–118. Springer International Publishing (2016)
Kirkpatrick, L.A.: Attachment, Evolution, and the Psychology of Religion. Guilford Press, New York (2005)
Koole, S.L., McCullough, M.E., Kuhl, J., Roelofsma, P.H.: Why religion’s burdens are light: from religiosity to implicit self-regulation. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Rev. 14(1), 95–107 (2010)
Lindeman, M., Heywood, B., Riekki, T., Makkonen, T.: Atheists become emotionally aroused when daring God to do terrible things. Int. J. Psychol. Relig. 24(2), 124–132 (2014)
Main, M., Goldwyn, R., Hesse, E.: Adult attachment scoring and classification systems. Unpublished manuscript, University of California, Berkeley (2003)
McKay, R., Whitehouse, H.: Religion and morality. Psychol. Bull. 141(2), 447–473 (2015)
Memon, Z.A., Treur, J.: An agent model for cognitive and affective empathic understanding of other agents. In: Transactions on Computational Collective Intelligence VI, pp. 56–83. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2012)
Mencken, F.C., Fitz, B.: Image of God and community volunteering among religious adherents in the United States. Rev. Relig. Res. 55(3), 491–508 (2013)
Metzger, B.M., Coogan, M.D. (eds.): The Oxford Companion to the Bible. Oxford University Press (1993)
Norenzayan, A., Gervais, W.M., Trzesniewski, K.H.: Mentalizing deficits constrain belief in a personal God. PloS One 7(5), e36880 (2012)
Poe, J.M.: Closer to God: An ERP Investigation into the Role of God as an Attachment Figure. Doctoral dissertation, University of Colorado Colorado Springs. Kraemer Family Library (2016)
Popp, C.A., Luborsky, L., Andrusyna, T.P., Cotsonis, G., Seligman, D.: Relationships between God and people in the Bible: a core conflictual relationship theme study of the Pentateuch/Torah. Psychiatry 65(3), 179–196 (2002)
Purzycki, B.G., Apicella, C., Atkinson, Q.D., Cohen, E., McNamara, R.A., Willard, A.K., Xygalatas, D., Norenzayan, A., Henrich, J.: Moralistic gods, supernatural punishment and the expansion of human sociality. Nature 530, 327–330 (2016)
Randolph-Seng, B., Nielsen, M.E.: Honesty: one effect of primed religious representations. Int. J. Psychol. Relig. 17(4), 303–315 (2007)
Saroglou, V., Buxant, C., Tilquin, J.: Positive emotions as leading to religion and spirituality. J. Posit. Psychol. 3(3), 165–173 (2008)
Sayadmansour, A.: Neurotheology: the relationship between brain and religion. Iran. J. Neurol. 13(1), 52–55 (2014)
Schaap-Jonker, H., Corveleyn, J.M.: Mentalizing and religion. Arch. Psychol. Relig. 36(3), 303–322 (2014)
Schaap-Jonker, H., Sizoo, B., van Schothorst-van Roekel, J., Corveleyn, J.: Autism spectrum disorders and the image of God as a core aspect of religiousness. Int. J. Psychol. Relig. 23(2), 145–160 (2013)
Schjoedt, U., Stodkilde-Jorgensen, H., Geerts, A.W., Roepstorff, A.: Highly religious participants recruit areas of social cognition in personal prayer. SocCog Affect Neurosci. 4, 199–207 (2009)
Schnitker, S.A., Emmons, R.A.: Spiritual striving and seeking the sacred: religion as meaningful goal-directed behavior. Int. J. Psychol. Relig. 23(4), 315–324 (2013)
Shariff, A.F., Norenzayan, A.: God is watching you priming God concepts increases prosocial behavior in an anonymous economic game. Psychol. Sci. 18(9), 803–809 (2007)
Shariff, A.F., Piazza, J., Kramer, S.R.: Morality and the religious mind: why theists and nontheists differ. Trends Cogn. Sci. 18(9), 439–441 (2014)
Shatz, C.J.: The developing brain. Sci. Am. 267, 60–67 (1992)
Sosis, R., Ruffle, B.J.: Religious ritual and cooperation: testing for a relationship on Israeli religious and secular Kibbutzim1. Curr. Anthropol. 44(5), 713–722 (2003)
Treur, J.: Modelling joint decision making processes involving emotion-related valuing and empathic understanding. In: Agents in Principle, Agents in Practice, Proceedings of PRIMA’11. Lecture Notes in AI, vol. 7047, pp. 410–423. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2011a)
Treur, J.: From mirroring to the emergence of shared understanding and collective power. In Computational Collective Intelligence. Technologies and Applications, Lecture Notes in Artifical Intelligence, vol. 6922, pp. 1–16. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2011b)
Treur, J.: A cognitive agent model incorporating prior and retrospective ownership states for actions. In: Walsh, T. (ed.) Proceedings of the Twenty-Second International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI’11, pp. 1743–1749. AAAI Press (2011c)
Treur, J.: A cognitive agent model displaying and regulating different social response patterns. In: Walsh, T. (ed.) Proceedings of the Twenty-Second International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI’11, pp. 1743–1749. AAAI Press (2011d)
Treur, J.: Displaying and regulating different social response patterns: a computational agent model. Cogn. Comput. J. 6, 182–199 (2014)
Treur, J.: Network-Oriented Modeling: Addressing Complexity of Cognitive, Affective and Social Interactions. Springer International Publishers (2016)
Treur, J.: Network-Oriented Modeling for Adaptive Networks: Designing Higher-Order Adaptive Biological, Mental and Social Network Models. Springer Nature (2020)
Van Ments, L., Treur, J., Roelofsma, P.H.M.P.: Modelling the effect of religion on human empathy based on an adaptive temporal–causal network model. Comput. Soc. Netw. 5(1) (2018)
Van Ments, L., Treur, J.: Reflections on dynamics, adaptation and control: toward a cognitive architecture for mental models. Cogn. Syst. Res. 70, 1–9 (2021)
Visala, A.: Cognition, brain, and religious experience: a critical analysis. In: Handbook of Neuroethics, pp. 1553–1568. Springer (2015)
Vishkin, A., Bigman, Y., Tamir, M.: Religion, emotion regulation, and well-being. In: Religion and Spirituality Across Cultures (pp. 247–269). Springer, The Netherlands (2014)
Weingarten, C.P., Luborsky, L., Descôteaux, J., Diguer, L., Andrusyna, T.P., Kirk, D., Cotsonis, G.: Relationships between God and people in the Bible, part III: when the other is an outsider. Psychiatry 67(1), 26–37 (2004)
Weingarten, C.P., Luborsky, L., Andrusyna, T., Diguer, L., Descôteaux, J.: Relationships between god and people: an interpersonal study of scriptures. Int. J. Psychol. Relig. 24(2), 133–150 (2014)
White, S.J., Frith, U., Rellecke, J., Al-Noor, Z., Gilbert, S.J.: Autistic adolescents show atypical activation of the brain’s mentalizing system even without a prior history of mentalizing problems. Neuropsychologia 56, 17–25 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
van Ments, L., Roelofsma, P.H., Treur, J. (2022). How Empathic is Your God: An Adaptive Network Model for Formation and Use of a Mental God-Model and Its Effect on Human Empathy. In: Treur, J., Van Ments, L. (eds) Mental Models and Their Dynamics, Adaptation, and Control. Studies in Systems, Decision and Control, vol 394. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85821-6_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85821-6_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-85820-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-85821-6
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)