Abstract
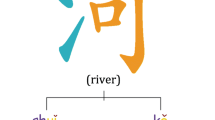
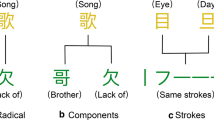
With the increasing demands of high-quality Chinese word embeddings for natural language processing, Chinese word embedding learning has attracted wide attention in recent years. Most of the existing research focused on capturing word semantics on large-scaled datasets. However, these methods are difficult to obtain effective word embeddings with limited data used for some specific fields. Observing the rich semantic information of Chinese fine-grained structures, we develop a model to fully fuse Chinese fine-grained structures as auxiliary information for word embedding learning. The proposed model views the word context information as a combination of word, character, pronunciation, and component. Besides, it adds the semantic relationship between pronunciations and components as a constraint to exploit auxiliary information comprehensively. Based on the decomposition of shifted positive pointwise mutual information matrix, our model could effectively generate Chinese word embeddings on small-scaled data. The results of word analogy, word similarity, and name entity recognition conducted on two public datasets show the effectiveness of our proposed model for capturing Chinese word semantics with limited data.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ailem, M., Salah, A., Nadif, M.: Non-negative matrix factorization meets word embedding. In: SIGIR, pp. 1081–1084 (2017)
Altszyler, E., Sigman, M., Slezak, D.F.: Comparative study of LSA vs word2vec embeddings in small corpora: a case study in dreams database. CoRR abs/1610.01520 (2016)
Avraham, O., Goldberg, Y.: The interplay of semantics and morphology in word embeddings. In: EACL, pp. 422–426 (2017)
Bengio, Y., Ducharme, R., Vincent, P., Jauvin, C.: A neural probabilistic language model. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 3, 1137–1155 (2003)
Cao, S., Lu, W., Zhou, J., Li, X.: cw2vec: learning Chinese word embeddings with stroke n-gram information. In: AAAI, pp. 5053–5061 (2018)
Chen, X., Xu, L., Liu, Z., Sun, M., Luan, H.: Joint learning of character and word embeddings. In: IJCAI, pp. 1236–1242 (2015)
Deerwester, S., Dumais, S.T., Furnas, G.W., Landauer, T.K., Harshman, R.: Indexing by latent semantic analysis. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 41(6), 391–407 (1990)
Devlin, J., Chang, M., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In: NAACL-HLT, pp. 4171–4186 (2019)
Ding, C., Li, T., Peng, W.: On the equivalence between non-negative matrix factorization and probabilistic latent semantic indexing. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 52(8), 3913–3927 (2008)
Hofmann, T.: Probabilistic latent semantic analysis. In: UAI, pp. 289–296 (1999)
Huang, Z., Xu, W., Yu, K.: Bidirectional LSTM-CRF models for sequence tagging. CoRR abs/1508.01991 (2015)
Levy, O., Goldberg, Y.: Neural word embedding as implicit matrix factorization. In: NIPS, pp. 2177–2185 (2014)
Li, Y., Xu, L., Tian, F., Jiang, L., Zhong, X., Chen, E.: Word embedding revisited: a new representation learning and explicit matrix factorization perspective. In: IJCAI, pp. 3650–3656 (2015)
Luong, M.T., Socher, R., Manning, C.D.: Better word representations with recursive neural networks for morphology. In: CoNLL, pp. 104–113 (2013)
Mikolov, T., Chen, K., Corrado, G., Dean, J.: Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. In: ICLR Workshop (2013)
Mikolov, T., Sutskever, I., Chen, K., Corrado, G.S., Dean, J.: Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In: NIPS, pp. 3111–3119 (2013)
Peng, Y., Jiang, H.: Leverage financial news to predict stock price movements using word embeddings and deep neural networks. In: NAACL-HLT, pp. 374–379 (2016)
Pennington, J., Socher, R., Manning, C.D.: Glove: global vectors for word representation. In: EMNLP, pp. 1532–1543 (2014)
Peters, M.E., et al.: Deep contextualized word representations. arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.05365 (2018)
Salah, A., Ailem, M., Nadif, M.: Word co-occurrence regularized non-negative matrix tri-factorization for text data co-clustering. In: AAAI, pp. 3992–3999 (2018)
Salle, A., Idiart, M., Villavicencio, A.: Matrix factorization using window sampling and negative sampling for improved word representations. arXiv preprint arXiv:1606.00819 (2016)
Su, T.R., Lee, H.Y.: Learning Chinese word representations from glyphs of characters. arXiv preprint arXiv:1708.04755 (2017)
Sun, Y., et al.: ERNIE 2.0: a continual pre-training framework for language understanding. In: AAAI, pp. 8968–8975 (2020)
Tang, D., Wei, F., Yang, N., Zhou, M., Liu, T., Qin, B.: Learning sentiment-specific word embedding for twitter sentiment classification. In: ACL, pp. 1555–1565 (2014)
Xu, J., Liu, J., Zhang, L., Li, Z., Chen, H.: Improve Chinese word embeddings by exploiting internal structure. In: NAACL-HLT, pp. 1041–1050 (2016)
Xun, G., Li, Y., Gao, J., Zhang, A.: Collaboratively improving topic discovery and word embeddings by coordinating global and local contexts. In: SIGKDD, pp. 535–543 (2017)
Yang, Q., Xie, H., Cheng, G., Wang, F.L., Rao, Y.: Pronunciation-enhanced Chinese word embedding. Cogn. Comput. 13(3), 688–697 (2021)
Yu, J., Jian, X., Xin, H., Song, Y.: Joint embeddings of Chinese words, characters, and fine-grained subcharacter components. In: EMNLP, pp. 286–291 (2017)
Zhang, Y., et al.: Learning Chinese word embeddings from stroke, structure and pinyin of characters. In: CIKM, pp. 1011–1020 (2019)
Acknowledgment
We are grateful to the reviewers for their valuable comments. This work has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61972426) and Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2020A1515010536).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chen, S., Chen, Y., Lu, Y., Rao, Y., Xie, H., Li, Q. (2021). Chinese Word Embedding Learning with Limited Data. In: U, L.H., Spaniol, M., Sakurai, Y., Chen, J. (eds) Web and Big Data. APWeb-WAIM 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12858. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85896-4_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85896-4_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-85895-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-85896-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)