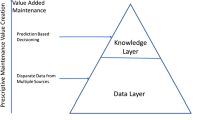
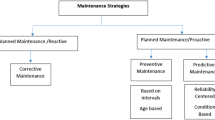
Abstract
Maintenance service delivery constitutes one of the most problematic tasks for companies offering such service. Besides dealing with customers expecting to be served as soon as possible, companies must consider the penalties they are incurring if the service is delivered later than the deadline, especially if the service suppliers want to establish long and lasting relationships with customers. Despite being advisable to use appropriate tools to schedule such activity, in many companies, planners rely only on simple tools (e.g., Excel sheets) to schedule maintenance interventions. Frequently, this results in a suboptimal allocation of the interventions, which causes customer satisfaction problems. This paper, contextualised in the Balance Systems case study, proposes an optimisation model that can be used by planners to perform the intervention allocation. The optimisation model has been developed in the context of the Dual-perspective, Data-based, Decision-making process for Maintenance service delivery (D3M) framework, which aims to improve the maintenance service delivery by making a proper use of real-time and historical data related to the asset status and the service resources available. The proposed model tries to cope with the current problems present in the company’s service delivery process by proposing the introduction of a mathematical instrument in support of the planner. Being strongly influenced by the contextual setting, the model discussed in this paper originates from the D3M framework logic and is adapted to the company necessities.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rahman, A.R.A., Husen, C.V., Pallot, M., Richir, S.: Innovation by service prototyping design dimensions & attributes, key design aspects, & toolbox Abdul. In: 23rd ICE/IEEE International Technology Management Conference, pp. 587–592 (2017)
Potes Ruiz, P.A., Kamsu-Foguem, B., Noyes, D.: Knowledge reuse integrating the collaboration from experts in industrial maintenance management. Knowl. Based Syst. 50, 171–186 (2013)
Ardolino, M., Rapaccini, M., Saccani, N., Gaiardelli, P., Crespi, G., Ruggeri, C.: The role of digital technologies for the service transformation of industrial companies. Int. J. Prod. Res. 1–17 (2017)
Gopalakrishnan, M., Bokrantz, J., Ylipää, T., Skoogh, A.: Planning of maintenance activities - a current state mapping in industry. Procedia CIRP 30, 480–485 (2015)
Bumblauskas, D., Gemmill, D., Igou, A., Anzengruber, J.: Smart maintenance decision support systems (SMDSS) based on corporate big data analytics. Expert Syst. Appl. 90, 303–317 (2017)
Karim, R., Westerberg, J., Galar, D., Kumar, U., Karim, R.: Maintenance analytics – the new know in maintenance. IFAC-PapersOnLine. 49, 214–219 (2016)
Mathieu, V.: Service strategies within the manufacturing sector: benefits, costs and partnership. Int. J. Serv. Ind. Manage. 12, 451–475 (2001)
Kuo, T.C., Wang, M.L.: The optimisation of maintenance service levels to support the product service system. Int. J. Prod. Res. 50, 6691–6708 (2012)
Rondini, A., Tornese, F., Gnoni, M.G., Pezzotta, G., Pinto, R.: Hybrid simulation modelling as a supporting tool for sustainable product service systems: a critical analysis. Int. J. Prod. Res. 55, 6932–6945 (2017)
Afshar-Nadjafi, B.: Multi-skilling in scheduling problems: a review on models, methods and applications. Comput. Ind. Eng. 107004 (2020)
Agnihothri, S.R., Mishra, A.K.: Cross-training decisions in field services with three job types and server-job mismatch*. Decis. Sci. 35, 239–257 (2004)
Pal, D., Vain, J., Srinivasan, S., Ramaswamy, S.: Model-based maintenance scheduling in flexible modular automation systems. In: IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation, ETFA, pp. 1–6. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc. (2017)
Xu, Z., Ming, X.G., Zheng, M., Li, M., He, L., Song, W.: Cross-trained workers scheduling for field service using improved NSGA-II cross-trained workers scheduling for field service using improved NSGA-II. Int. J. Prod. Res. 53, 1255–1272 (2014)
Sala, R., Bertoni, M., Pirola, F., Pezzotta, G.: Data-based decision-making in maintenance service delivery: the D3M framework. J. Manuf. Technol. Manage. 32, 122–141 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by MADE Competence Center in the project “PRocessi, strumEnti e dAti a supporto delle deciSiOni di MaNutenzione 4.0 (REASON4.0)”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 IFIP International Federation for Information Processing
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sala, R., Pirola, F., Pezzotta, G., Vernieri, M. (2021). Improving Maintenance Service Delivery Through Data and Skill-Based Task Allocation. In: Dolgui, A., Bernard, A., Lemoine, D., von Cieminski, G., Romero, D. (eds) Advances in Production Management Systems. Artificial Intelligence for Sustainable and Resilient Production Systems. APMS 2021. IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology, vol 631. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85902-2_22
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85902-2_22
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-85901-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-85902-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)