Abstract
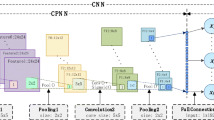
The deep neural network achieves superior performance in various tasks. However, it is notoriously known that its training needs a considerable time cost to refine a large number of parameters. We proposed a deep wavelet network to tackle the issue. The proposed network is built by processing blocks with various decomposition levels which named Discrete Wavelet Transformation Decomposition Convolution (DWTDC). The DWTDC aims to fulfill the task of feature map discrete wavelet transformation decomposition and subbands differential fusion. We employ the DWTDC block to act as the convolution layer so that the parameters are estimated within the frequency domain space. Because of the merits of economic representation in the wavelet domain, the training parameters are greatly reduced, only requiring \(33\%\) of the parameters of the popular networks. Extensive experiments by comparing with benchmark models show that the proposed DWTDC dramatically reduced the number of parameters and achieved light training without sacrificing the classification performance.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Candès, E.J., Recht, B.: Exact matrix completion via convex optimization. Found. Comput. Math. 9(6), 717 (2009)
Chen, W., Wilson, J., Tyree, S., Weinberger, K., Chen, Y.: Compressing neural networks with the hashing trick. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 2285–2294 (2015)
Chollet, F.: Xception: deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1251–1258 (2017)
Cotter, F., Kingsbury, N.: Deep learning in the wavelet domain. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.06115 (2018)
Courbariaux, M., Hubara, I., Soudry, D., El-Yaniv, R., Bengio, Y.: Binarized neural networks: training deep neural networks with weights and activations constrained to +1 or \(-\)1. arXiv preprint arXiv:1602.02830 (2016)
Daubechies, I.: The wavelet transform, time-frequency localization and signal analysis. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 36(5), 961–1005 (1990)
Denton, E.L., Zaremba, W., Bruna, J., LeCun, Y., Fergus, R.: Exploiting linear structure within convolutional networks for efficient evaluation. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1269–1277 (2014)
Gong, Y., Liu, L., Yang, M., Bourdev, L.: Compressing deep convolutional networks using vector quantization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6115 (2014)
Kim, Y.D., Park, E., Yoo, S., Choi, T., Yang, L., Shin, D.: Compression of deep convolutional neural networks for fast and low power mobile applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.06530 (2015)
Krizhevsky, A., Hinton, G., et al.: Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images. Tech. rep. Citeseer (2009)
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., Hinton, G.: Deep learning. Nature 521(7553), 436–444 (2015)
Mahanta, D.D.D.L.B.: Childhood medulloblastoma microscopic images (IEEE Dataport (2020). https://dxdoi.org/1021227/w0m0-mw21. https://doi.org/10.21227/w0m0-mw21
Mallat, S.: A Wavelet Tour of Signal Processing. Elsevier (1999)
Nene, S.A., Nayar, S.K., Murase, H.: Columbia object image library (coil-20. Tech. rep. (1996)
Nene, S.A., Nayar, S.K., Murase, H.: object image library (coil-100). Tech. rep. (1996)
Rastegari, M., Ordonez, V., Redmon, J., Farhadi, A.: XNOR-Net: ImageNet classification using binary convolutional neural networks. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9908, pp. 525–542. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46493-0_32
Sandler, M., Howard, A., Zhu, M., Zhmoginov, A., Chen, L.C.: Mobilenetv 2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4510–4520 (2018)
Shrestha, A., Mahmood, A.: Review of deep learning algorithms and architectures. IEEE Access 7, 53040–53065 (2019)
Subhashini, A., Victor, S.: A new approach on denoising for 1D, 2D and 3D images based on discrete wavelet transformation and thresholding. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comp. Sci. 9(1), 708–710 (2018)
Wen, W., Wu, C., Wang, Y., Chen, Y., Li, H.: Learning structured sparsity in deep neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1608.03665 (2016)
Yang, L., Yang, P., Ni, R., Zhao, Y.: Xception-based general forensic method on small-size images. In: Pan, J.-S., Li, J., Tsai, P.-W., Jain, L.C. (eds.) Advances in Intelligent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing. SIST, vol. 157, pp. 361–369. Springer, Singapore (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-9710-3_38
Zhang, Y.: DNN classifier of wide-angle retinal images in computer-aided screening for ROP (IEEE Dataport 2018). https://dxdoi.org/1021227/q5jw-t682. https://doi.org/10.21227/q5jw-t682
Zhao, J., Zhang, Y., He, X., Xie, P.: COVID-CT-dataset: a CT scan dataset about COVID-19. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.13865 (2020)
Acknowledgment
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61771007), Key-Area Research and Development of Guangdong Province (2020B010166002, 2020B111119001), Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province (2017B020226004), and the Health & Medical Collaborative Innovation Project of Guangzhou City (202002020049).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tao, G., Rong, W., Weng, W., Dan, T., Zhang, B., Cai, H. (2021). Incorporating Discrete Wavelet Transformation Decomposition Convolution into Deep Network to Achieve Light Training. In: Farkaš, I., Masulli, P., Otte, S., Wermter, S. (eds) Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning – ICANN 2021. ICANN 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12892. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-86340-1_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-86340-1_25
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-86339-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-86340-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)