Abstract
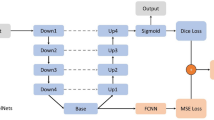
The rapid and accurate prediction of residual stresses in metal additive manufacturing (3D printing) processes is crucial to ensuring defect-free fabrication of parts used in critical industrial applications. This paper presents promising outcomes from applying attention-based neural architectures for predicting such 3D stress phenomena accurately, efficiently, and reliably. This capability is critical to drastically reducing the design maturation time for additively manufactured parts. High fidelity, physics-based numerical models of the additive melting process exist that can simulate the thermal gradients and consequent stresses produced during manufacturing, which can then be used to synthesize a 3D crack index field for the entire part volume, capturing the likelihood that a region in a part will crack upon heat treatment. However, these models are expensive and time-consuming to run. In response, a Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN) model is explored as a surrogate for the physics-based model, so that it can be used to time-efficiently estimate the crack index for a given part-design. This requires careful design of the training regime and dataset for a given design problem. Using the U-Net architecture as the baseline, we expand the standard 2D application of this architecture for segmentation to the estimation of the full 3D, continuous valued, stress field. We illustrate the primary challenge faced by the standard U-Net architecture with L2-loss arising from sparsity in critical values of the crack index and show how augmenting the architecture with attention mechanisms helps address the issue as well as improve the overall accuracy of estimation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DebRoy, T., et al.: Additive manufacturing of metallic components-process, structure and properties. Prog. Mater Sci. 92, 112–224 (2018)
Frazier, W.E.: Metal additive manufacturing: a review. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 23(6), 1917–1928 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-0958-z
Khairallah, S.A., Anderson, A.T., Rubenchik, A., King, W.E.: Laser powder-bed fusion additive manufacturing: physics of complex melt flow and formation mechanisms of pores, spatter, and denudation zones. Acta Mater. 108, 36–45 (2016)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Lin, T.Y., Goyal, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Dollár, P.: Focal loss for dense object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2980–2988 (2017)
Bahdanau, D., Cho, K., Bengio, Y.: Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.0473 (2014)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 5998–6008 (2017)
Guo, C., Szemenyei, M., Yi, Y., Wang, W., Chen, B., Fan, C.: SA-UNet: spatial attention U-Net for retinal vessel segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.03696 (2020)
Schlemper, J., et al.: Attention gated networks: learning to leverage salient regions in medical images. Med. Image Anal. 53, 197–207 (2019)
Çiçek, Ö., Abdulkadir, A., Lienkamp, S.S., Brox, T., Ronneberger, O.: 3D U-Net: learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. In: Ourselin, S., Joskowicz, L., Sabuncu, M.R., Unal, G., Wells, W. (eds.) MICCAI 2016. LNCS, vol. 9901, pp. 424–432. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46723-8_49
Milletari, F., Navab, N., Ahmadi, S.-A.: V-Net: fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In: IEEE International Conference on 3D Vision, pp. 565–571 (2016)
Lee, K., Zung, J., Li, P., Jain, V., Seung, H.S.: Superhuman accuracy on the SNEMI3D connectomics challenge. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.00120 (2017)
Yu, L., Yang, X., Chen, H., Qin, J., Heng, P.: Volumetric ConvNets with mixed residual connections for automated prostate segmentation from 3D MR images. In: AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 66–72 (2017)
Zhou, X., et al.: Performance evaluation of 2D and 3D deep learning approaches for automatic segmentation of multiple organs on CT images. In: Medical Imaging: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, vol. 10575, p. 105752C (2018)
Ghavami, N., et al.: Automatic segmentation of prostate MRI using convolutional neural networks: investigating the impact of network architecture on the accuracy of volume measurement and MRI-ultrasound registration. Med. Image Anal. 58, 101558 (2019)
Scime, L., Beuth, J.: A multi-scale convolutional neural network for autonomous anomaly detection and classification in a laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing process. Addit. Manuf. 24, 273–286 (2018)
Khadilkar, A., Wang, J., Rai, R.: Deep learning-based stress prediction for bottom-up SLA 3D printing process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 102, 2555–2569 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03363-4
Liang, L., Liu, M., Martin, C., Sun, W.: A deep learning approach to estimate stress distribution: a fast and accurate surrogate of finite-element analysis. J. Roy. Soc. Interface 15(138), 20170844 (2018)
Qi, X., Chen, G., Li, Y., Cheng, X., Li, C.: Applying neural-network-based machine learning to additive manufacturing: current applications, challenges, and future perspectives. Engineering 5(4), 721–729 (2019). ISSN: 2095-8099
Nie, Z., Jiang, H., Kara, L.B.: Stress field prediction in cantilevered structures using convolutional neural networks. ASME J. Comput. Inf. Sci. Eng. 20(1), 011002 (2020)
Acknowledgments
The information, data, or work presented herein was funded in part by the Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy (ARPA-E), U.S. Department of Energy, under Award Number DE-AR0001203. The views and opinions of authors expressed herein do not necessarily state or reflect those of the United States Government or any agency thereof.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Iyer, N., Raghavan, S., Zhang, Y., Jiao, Y., Robinson, D. (2021). Attention-Based 3D Neural Architectures for Predicting Cracks in Designs. In: Farkaš, I., Masulli, P., Otte, S., Wermter, S. (eds) Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning – ICANN 2021. ICANN 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12891. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-86362-3_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-86362-3_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-86361-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-86362-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)