Abstract
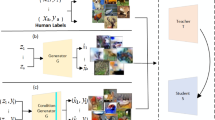
Iterative Knowledge Distillation (IKD) [20] is an iterative variant of Hinton’s knowledge distillation framework for deep neural network compression. IKD has shown promising model compression results for image classification tasks where a large amount of training data is available for training the teacher and student models. In this paper, we consider problems where training data is not available, making it impractical to use the usual IKD approach. We propose a variant of the IKD framework, called Data-Free IKD (or DF-IKD), that adopts recent results from data-free learning of deep models [2]. This exploits generative adversarial networks (GANs), in which a readily available pre-trained teacher model is regarded as a fixed discriminator, and a generator (a deep network) is used to generate training samples. The goal of the generator is to generate samples that can obtain a maximum predictive response from the discriminator. In DF-IKD, the student model at every IKD iteration is a compressed version of the original discriminator (‘teacher’). Our experiments suggest: (a) DF-IKD results in a student model that is significantly smaller in size than the original parent model; (b) the predictive performance of the compressed student model is comparable to that of the parent model.
H. Shah and A. Vaswani—Equal contribution.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, M., Gómez-Rodríguez, C.: Distilling neural networks for greener and faster dependency parsing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.00844 (2020)
Chen, H., et al.: Data-free learning of student networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), October 2019
Chen, W., Wilson, J.T., Tyree, S., Weinberger, K.Q., Chen, Y.: Compressing neural networks with the hashing trick. In: ICML (2015)
Denton, E.L., Zaremba, W., Bruna, J., LeCun, Y., Fergus, R.: Exploiting linear structure within convolutional networks for efficient evaluation. arXiv:1404.0736 (2014)
Gong, Y., Liu, L., Yang, M., Bourdev, L.D.: Compressing deep convolutional networks using vector quantization. arXiv:1412.6115 (2014)
Han, S., Mao, H., Dally, W.J.: Deep compression: compressing deep neural networks with pruning, trained quantization and Huffman coding (2016)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 770–778 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
Hinton, G., Vinyals, O., Dean, J.: Distilling the knowledge in a neural network (2015)
Koutini, K., Eghbal-zadeh, H., Widmer, G.: Iterative knowledge distillation in R-CNNs for weakly-labeled semi-supervised sound event detection. In: Proceedings of the Detection and Classification of Acoustic Scenes and Events (DCASE) (2018)
Krizhevsky, A.: Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images. University of Toronto (2012)
LeCun, Y., Cortes, C., Burges, C.: MNIST handwritten digit database. ATT Labs (2010). http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist
Lopes, R.G., Fenu, S., Starner, T.: Data-free knowledge distillation for deep neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.07535 (2017)
Nayak, G.K., Mopuri, K.R., Shaj, V., Babu, R.V., Chakraborty, A.: Zero-shot knowledge distillation in deep networks. In: ICML (2019)
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R.B., Sun, J.: Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39, 1137–1149 (2015)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. CoRR arxiv:1409.1556 (2015)
Srinivas, S., Babu, R.V.: Data-free parameter pruning for deep neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1507.06149 (2015)
Tran, D., Wang, H., Torresani, L., Feiszli, M.: Video classification with channel-separated convolutional networks. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 5551–5560 (2019)
Wang, H., Zhao, H., Li, X., Tan, X.: Progressive blockwise knowledge distillation for neural network acceleration. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI 2018), pp. 2769–2775. AAAI Press (2018)
Xiao, H., Rasul, K., Vollgraf, R.: Fashion-MNIST: a novel image dataset for benchmarking machine learning algorithms. CoRR arxiv:1708.07747 (2017)
Yalburgi, S., Dash, T., Hebbalaguppe, R., Hegde, S., Srinivasan, A.: An empirical study of iterative knowledge distillation for neural network compression. In: Proceedings of the European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Computational Intelligence and Machine Learning (2020)
Zhu, J., et al.: Incorporating BERT into neural machine translation. arXiv:2002.06823 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by “The DataLab” agreement between BITS Pilani, K. K. Birla Goa Campus and TCS Research, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Shah, H., Vaswani, A., Dash, T., Hebbalaguppe, R., Srinivasan, A. (2021). Empirical Study of Data-Free Iterative Knowledge Distillation. In: Farkaš, I., Masulli, P., Otte, S., Wermter, S. (eds) Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning – ICANN 2021. ICANN 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12893. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-86365-4_44
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-86365-4_44
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-86364-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-86365-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)