Abstract
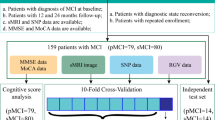
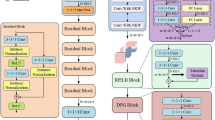
Imaging genomics is an effective tool in the detection and causative factor analysis of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Based on single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data, we propose a novel AD analysis model using multi-modal data fusion and multi-detection model fusion. Firstly, based on the characteristics of SNP data, we fully extract highly representative features. Secondly, the fused data are used to construct fusion features. Finally, according to the characteristics of the fused data, we design a fused prediction model with multiple machine learning models. The model integrates four machine learning models and feeds them into the final XGBoost model for AD prediction. The experimental results show that the data fusion method and the fusion model of multiple machine learning models proposed in this paper can effectively improve the prediction accuracy. Our model can identify AD patients and detect abnormal brain regions and risk SNPs associated with AD, which can perform the association of risk SNPs with abnormal brain regions.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kucmanski, L.S., Zenevicz, L., Geremia, D.S., Madureira, V.S.F., Silva, T.G.d., Souza, S.S.D.: Alzheimer’s desease: challenges faced by family caregivers. J. Revista Brasileira de Geriatria e Gerontologia. 196, 1022–1029 (2016)
Khachaturian, Z.S.: Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Arch. Neurol. 4211, 1097–1105 (1985)
Mucke, L.: Alzheimer's disease. J. Nat. 4617266, 895–897 (2009)
Association, A.S.: 2021 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. J. Alzheimer's Dementia 173, 327–406 (2021)
Marchitelli, R., et al.: Simultaneous resting-state FDG-PET/fMRI in Alzheimer disease: relationship between glucose metabolism and intrinsic activity. J. Neuroimage. 176, 246–258 (2018)
McEvoy, L.K., et al.: Alzheimer disease: quantitative structural neuroimaging for detection and prediction of clinical and structural changes in mild cognitive impairment. J. Radiol. 2511, 195–205 (2009)
Vemuri, P., Jack, C.R.: Role of structural MRI in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer Res. Therapy 24, 1–10 (2010)
Feulner, T., Laws, S., Friedrich, P., Wagenpfeil, S., Wurst, S., Riehle, C., et al.: Examination of the current top candidate genes for AD in a genome-wide association study. J. Mole. Psychiatr. 157, 756–766 (2010)
Hariri, A.R., Drabant, E.M., Weinberger, D.R.: Imaging genetics: perspectives from studies of genetically driven variation in serotonin function and corticolimbic affective processing. J. Biol. Psychiatr. 5910, 888–897 (2006)
Huang, M., Chen, X., Yu, Y., Lai, H., Feng, Q.: Imaging genetics study based on a temporal group sparse regression and additive model for biomarker detection of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 40, 1461–1473 (2021)
Bi, X.-A., Hu, X., Wu, H., Wang, Y.: Multimodal data analysis of Alzheimer's disease based on clustering evolutionary random forest. J. IEEE Biomed. Health Inform. 2410, 2973–2983 (2020)
Kang, E., Jang, J., Choi, C.H., Kang, S.B., Bang, K.B., Kim, T.O., et al.: Development of a clinical and genetic prediction model for early intestinal resection in patients with Crohn’s disease: results from the IMPACT study. J. J. Clin. Med. 104, 633 (2021)
Gray, K.R., Aljabar, P., Heckemann, R.A., Hammers, A., Rueckert, D., Initiative, A.S.D.N.: Random forest-based similarity measures for multi-modal classification of Alzheimer's disease. J. NeuroImage 65, 167–175 (2013)
Marchetti-Bowick, M., Yin, J., Howrylak, J.A., Xing, E.P.: A time-varying group sparse additive model for genome-wide association studies of dynamic complex traits. J. Bioinform. 3219, 2903–2910 (2016)
Du, L., Liu, K., Zhu, L., Yao, X., Risacher, S.L., Guo, L., et al.: Identifying progressive imaging genetic patterns via multi-task sparse canonical correlation analysis: a longitudinal study of the ADNI cohort. J. Bioinform. 3514, i474–i483 (2019)
Bi, X.-A., Hu, X., Xie, Y., Wu, H.: A novel CERNNE approach for predicting Parkinson’s Disease-associated genes and brain regions based on multimodal imaging genetics data. J. Med. Image Anal. 67, 101830 (2021)
Huang, Z., Lei, H., Chen, G., Frangi, A.F., Xu, Y., Elazab, A., et al.: Parkinson's disease classification and clinical score regression via united embedding and sparse learning from longitudinal data. J. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (2021)
Purcell, S., Neale, B., Todd-Brown, K., Thomas, L., Ferreira, M.A., Bender, D., et al.: PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. J. Am. Hum. Gene. 813, 559–575 (2007)
Marees, A.T., de Kluiver, H., Stringer, S., Vorspan, F., Curis, E., Marie-Claire, C., et al.: A tutorial on conducting genome-wide association studies: quality control and statistical analysis. J. Int. Methods Psychiatr. Res. 272, e1608 (2018)
Kulminski, A.M., Shu, L., Loika, Y., He, L., Nazarian, A., Arbeev, K., et al.: Genetic and regulatory architecture of Alzheimer's disease in the APOE region. J. Alzheimer's Dementia Diag. Assess. Dis. Monit. 121, e12008 (2020)
Zhao, T., Hu, Y., Zang, T., Wang, Y.: Integrate GWAS, eQTL, and mQTL data to identify Alzheimer’s disease-related genes. J. Front, Gene. 10, 1021 (2019)
Killiany, R., Hyman, B., Gomez-Isla, T., Moss, M., Kikinis, R., Jolesz, F., et al.: MRI measures of entorhinal cortex vs hippocampus in preclinical AD. J. Neurol. 588, 1188–1196 (2002)
Echávarri, C., Aalten, P., Uylings, H.B., Jacobs, H., Visser, P.J., Gronenschild, E., et al.: Atrophy in the parahippocampal gyrus as an early biomarker of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Brain Struct. Funct. 215(3–4), 265–271 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Li, Y., Liu, Y., Wang, T., Lei, B. (2021). Alzheimer's Disease Prediction via the Association of Single Nucleotide Polymorphism with Brain Regions. In: Feng, J., Zhang, J., Liu, M., Fang, Y. (eds) Biometric Recognition. CCBR 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12878. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-86608-2_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-86608-2_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-86607-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-86608-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)