Abstract
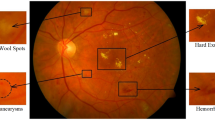
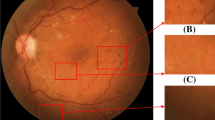
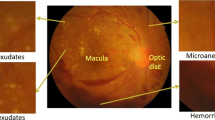
Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is a very common retinal disease in the world, which can affect vision and even cause blindness. Early diagnosis can effectively prevent the disease, or at least delay the progression of DR. However, most methods are based on regular single-view images, which would lack complete information of lesions. In this paper, a novel method is proposed to achieve DR classification using ultra-widefield images (UWF). The proposed network includes a dual-branch network, an efficient channel attention (ECA) module, a spatial attention (SA) module, and an atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP) module. Specifically, the dual-branch network uses ResNet-34 model as the backbone. The ASPP module enlarges the receptive field to extract rich feature information by setting different dilated rates. To emphasize the useful information and suppress the useless information, the ECA and SA modules are utilized to extract important channel information and spatial information respectively. To reduce the parameters of the network, we use a global average pooling (GAP) layer to compress the features. The experimental results on the UWF images collected by a local hospital show that our model performs very well.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yau, J.W., et al.: Global prevalence and major risk factors of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 35(3), 556–564 (2012)
Webb, R.H., Hughes, G.W.: Scanning laser ophthalmoscope. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 7, 488–492 (1981)
Haleem, M.S., Han, L., van Hemert, J., Li, B., Fleming, A.: Retinal area detector from scanning laser ophthalmoscope (SLO) images for diagnosing retinal diseases. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 19(4), 1472–1482 (2014)
Ashok, V., Murugesan, G.: Detection of retinal area from scanning laser ophthalmoscope images (SLO) using deep neural network. Int. J. Biomed. Eng. Technol. 23(2–4), 303–314 (2017)
Nagasato, D., et al.: Deep neural network-based method for detecting central retinal vein occlusion using ultrawide-field fundus ophthalmoscopy. Ophthalmology 2018 (2018)
Pellegrini, E., et al.: A graph cut approach to artery/vein classification in ultra-widefield scanning laser ophthalmoscopy. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 37(2), 516–526 (2017)
Brown, J.M., et al.: Automated diagnosis of plus disease in retinopathy of prematurity using deep convolutional neural networks. JAMA Ophthalmol. 136(7), 803–810 (2018)
Li, F., et al.: Deep learning-based automated detection for diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular oedema in retinal fundus photographs. Eye, 1–9 (2021)
Diaz-Pinto, A., et al.: Retinal image synthesis and semi-supervised learning for glaucoma assessment. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 38(9), 2211–2218 (2019)
Xie, H., et al.: Cross-attention multi-branch network for fundus diseases classification using SLO images. Med. Image Anal. 71, 102031 (2021)
Hamwood, J., et al.: Automatic detection of cone photoreceptors with fully convolutional networks. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 8(6), 10 (2019)
Ruan, Y., et al.: MB-FSGAN: joint segmentation and quantification of kidney tumor on CT by the multi-branch feature sharing generative adversarial network. Med. Image Anal. 64, 101721 (2020)
Mou, L., et al.: CS-Net: Channel and Spatial Attention Network for Curvilinear Structure Segmentation. In: Shen, D., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2019. LNCS, vol. 11764, pp. 721–730. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32239-7_80
Nie, D., Wang, L., Xiang, L., Zhou, S., Adeli, E., Shen, D.: Difficulty-aware attention network with confidence learning for medical image segmentation. In: AAAI, pp. 1085–1092 (2019)
Shaikh, M., Kollerathu, V.A., Krishnamurthi, G.: Recurrent attention mechanism networks for enhanced classification of biomedical images. In: IEEE ISBI, pp. 1260–1264 (2019)
Zhang, J., Xie, Y., Xia, Y., Shen, C.: Attention residual learning for skin lesion classification. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 38(9), 2092–2103 (2019)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Gu, Z., et al.: DeepDisc: optic disc segmentation based on atrous convolution and spatial pyramid pooling. In: Stoyanov, D., et al. (eds.) OMIA/COMPAY 2018, LNCS, vol. 11039, pp. 253–260. Springer, Cham (2018)
Schlemper, J., et al.: Attention gated networks: learning to leverage salient regions in medical images. Med. Image Anal. 53, 197–207 (2019)
Xu, K., et al.: Show, attend and tell: neural image caption generation with visual attention. In: Bach, F.R., Blei, D.M. (eds.) International Conference on Machine Learning 2015, PMLR, vol. 37, pp. 2048–2057. PMLR, Lille (2015)
Wang, Q., et al.: ECA-Net: efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In: CVPR (2020)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: ICLR (2015)
Szegedy, C., Vanhoucke, V., Ioffe, S., Shlens, J., Wojna, Z.: Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In: CVPR, pp. 2818–2826 (2016)
Huang, G., et al.: Densely connected convolutional networks. In: CVPR, pp. 4700–4708 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported partly by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61871274, 61801305 and 81571758), National Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. 2020A1515010649 and No. 2019A1515111205), Guangdong Province Key Laboratory of Popular High Performance Computers (No. 2017B030314073), Guangdong Laboratory of Artificial-Intelligence and Cyber-Economics (SZ), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021M692196), Shenzhen Peacock Plan (Nos. KQTD2016053112051497 and KQTD2015033016104926), Shenzhen Key Basic Research Project (Nos. JCYJ20190808165209410, 20190808145011259, JCYJ20180507184647636, GJHZ20190822095414576 and JCYJ20170302153337765, JCYJ20170302150411789, JCYJ20170302142515949, GCZX2017040715180580, GJHZ20180418190529516, and JSGG20180507183215520), NTUT-SZU Joint Research Program (No. 2020003), Special Project in Key Areas of Ordinary Universities of Guangdong Province (No. 2019KZDZX1015), Shenzhen Key Medical Discipline Construction Fund (No. SZXK038), Shenzhen Fund for Guangdong Provincial High-level Clinical Key Speciaties (No. SZGSP014), Shenzhen-Hong Kong Co-financing Project (No. SGDX20190920110403741).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tian, Z. et al. (2021). Dual-Branch Attention Network and Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling for Diabetic Retinopathy Classification Using Ultra-Widefield Images. In: Fu, H., Garvin, M.K., MacGillivray, T., Xu, Y., Zheng, Y. (eds) Ophthalmic Medical Image Analysis. OMIA 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12970. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87000-3_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87000-3_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-86999-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-87000-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)