Abstract
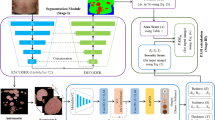
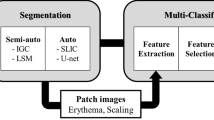
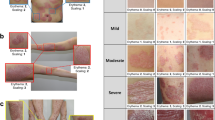
Psoriasis is a chronic skin disease which occurs to 2%–3% of the world’s entire population. If treated properly, patients can still maintain a relatively high quality of life. Otherwise, Psoriasis could cause severe complications or even threat to life. Therefore, continuous tracking of severity degree is critical in Psoriasis treatment. However, due to the shortage of dermatologists, it’s hard for patients to receive regular severity evaluation. Furthermore, evaluating the severity degree of Psoriasis is both time-consuming and error-prone which poses a heavy burden for dermatologists. To address this problem, we propose an automatic rating model which measures the severity degree quantitatively based on skin lesion pictures. The proposed rating model applies coarse to fine grained neural networks to evaluate skin lesions from multiple perspectives. According to experimental results, the proposed model outperforms experienced dermatologists.
X. Wu, Y. Yan, S. Zhao and Y. Kuang—Equal contribution.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmand, M., Ihtatho, D.: Objective assessment of psoriasis erythema for PASI scoring. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 33, 514–516 (2009)
Alcón, J.F., et al.: Automatic imaging system with decision support for inspection of pigmented skin lesions and melanoma diagnosis. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 3(1), 14–25 (2009)
Berth-Jones, J., et al.: A study examining inter-and intrarater reliability of three scales for measuring severity of psoriasis: psoriasis area and severity index, physician’s global assessment and lattice system physician’s global assessment. Br. J. Dermatol. 155(4), 707–713 (2006)
Blum, A., Luedtke, H., Ellwanger, U., Schwabe, R., Rassner, G., Garbe, C.: Digital image analysis for diagnosis of cutaneous melanoma. development of a highly effective computer algorithm based on analysis of 837 melanocytic lesions. Br. J. Dermatol. 151(5), 1029–1038 (2004)
Chauhan, G., et al.: Joint modeling of chest radiographs and radiology reports for pulmonary edema assessment. In: Martel, A.L., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2020. LNCS, vol. 12262, pp. 529–539. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59713-9_51
Denmark, D.D.: An image based system to automatically and objectively score the degree of redness and scaling in psoriasis lesions. In: Proceedings FRA den 13. Danske Konference i, p. 130 (2004)
Berth-Jones, A., et al.: Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 542(7639), 115–118 (2017)
Fink, C., Fuchs, T., Enk, A., Haenssle, H.A.: Design of an algorithm for automated, computer-guided PASI measurements by digital image analysis. J. Med. Syst. 42, 248 (2018)
George, Y., Aldeen, M., Garnavi, R.: Automatic psoriasis lesion segmentation in two-dimensional skin images using multiscale superpixel clustering. J. Med. Imaging 4, 044004 (2017)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7132–7141 (2018)
Li, Y., et al.: PseNet: psoriasis severity evaluation network. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34, pp. 800–807 (2020)
Liu, Y., et al.: A deep learning system for differential diagnosis of skin diseases. Nature Med. 26, 900–908 (2020)
Lu, J., Manton, J.H., Kazmierczak, E., Sinclair, R.: Erythema detection in digital skin images. In: 2010 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, pp. 2545–2548. IEEE (2010)
Pal, A., Chaturvedi, A., Garain, U., Chandra, A., Chatterjee, R.: Severity grading of psoriatic plaques using deep CNN based multi-task learning. In: 2016 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), pp. 1478–1483. IEEE (2016)
Pal, A., Chaturvedi, A., Garain, U., Chandra, A., Chatterjee, R., Senapati, S.: Severity assessment of psoriatic plaques using deep CNN based ordinal classification. In: Stoyanov, D., et al. (eds.) CARE/CLIP/OR 2.0/ISIC -2018. LNCS, vol. 11041, pp. 252–259. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01201-4_27
Rajpara, S., Botello, A., Townend, J., Ormerod, A.: Systematic review of dermoscopy and digital dermoscopy/artificial intelligence for the diagnosis of melanoma. Br. J. Dermatol. 161(3), 591–604 (2009)
Szegedy, C., Vanhoucke, V., Ioffe, S., Shlens, J., Wojna, Z.: Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2818–2826 (2016)
Wang, X., Girshick, R., Gupta, A., He, K.: Non-local neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7794–7803 (2018)
Zhou, Y., Sheng, Y., Gao, J., Zhang, X.: Dermatology in China. In: Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings, vol. 17, pp. 12–14. Elsevier (2015)
Zhu, X., Hu, H., Lin, S., Dai, J.: Deformable convnets V2: more deformable, better results. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 9308–9316 (2019)
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank all the anonymous reviewers and chairs for their constructive comments and suggestions that substantially improved this paper. This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China, No. 2018YFC0117000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wu, X. et al. (2021). Automatic Severity Rating for Improved Psoriasis Treatment. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2021. MICCAI 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12907. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87234-2_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87234-2_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-87233-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-87234-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)