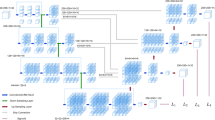
Abstract
Stroke is one of the leading causes of death around the world. Segmenting atherosclerotic plaques in carotid arteries from ultrasound images is of great value for preventing and treating ischemic stroke, yet still challenging due to the ambiguous boundary of plaque and intense noise in ultrasound. In this paper, we introduce a new approach for carotid plaque segmentation, namely Multi-Branch Feature Fusion Network (MBFF-Net). Inspired by the prior knowledge that carotid plaques generally grow in carotid artery walls (CAWs), we design a Multi-Branch Feature Fusion (MBFF) module with three branches. Specifically, the first two branches are well-designed to extract plaque features of multiple scales and different contexts, and the other branch is to exploit the prior information of CAWs. In addition, a boundary preserving structure is applied to alleviate the ambiguity of plaque boundary. With the proposed MBFF and the novel structure, our model is capable of extracting discriminative features of plaques and integrating the location information of CAWs for better segmentation. Experiments on the clinical dataset demonstrate that our model outperforms state-of-the-art methods. Code is available at https://github.com/mishiyu/MBFF.
S. Mi and Q. Bao—These authors contributed equally to this work.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feigin, V.L., Nguyen, G., Cercy, K., et al.: Global, regional, and country-specific lifetime risks of stroke, 1990 and 2016. N. Engl. J. Med. 379(25), 2429–2437 (2018)
Johnson, C.O., Nguyen, M., Roth, G.A.: Global, regional, and national burden of stroke, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 18(5), 439–458 (2019)
Touboul, P.J., Hennerici, M.G., Meairs, S., et al.: Mannheim carotid intima-media thickness and plaque consensus (2004-2006-2011). Cerebrovasc. Dis. 34(4), 290–296 (2012)
Sifakis, E.G., Golemati, S.: Robust carotid artery recognition in longitudinal b-mode ultrasound images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 23(9), 3762–3772 (2014)
Golemati, S., Stoitsis, J., Sifakis, E.G., et al.: Using the Hough transform to segment ultrasound images of longitudinal and transverse sections of the carotid artery. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 33(12), 1918–1932 (2008)
Zhang, J., Teng, Z., Guan, Q., et al.: Automatic segmentation of MR depicted carotid arterial boundary based on local priors and constrained global optimisation. IET Image Proc. 13(3), 506–514 (2019)
China, D., Nag, M.K., Mandana, K.M., et al.: Automated in vivo delineation of lumen wall using intravascular ultrasound imaging. In: 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp. 4125–4128 (2016)
Samber, D.D., Ramachandran, S., Sahota, A., et al.: Segmentation of carotid arterial walls using neural networks. World J. Radiol. 12, 1–9 (2020)
Destrempes, F., Soulez G., Giroux, M.F., et al.: Segmentation of plaques in sequences of ultrasonic B-mode images of carotid arteries based on motion estimation and Nakagami distributions. In: IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium, pp. 2480–2483 (2010)
Yoneyama, T., et al.: In vivo semi-automatic segmentation of multicontrast cardiovascular magnetic resonance for prospective cohort studies on plaque tissue composition: initial experience. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 32(1), 73–81 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-015-0704-0
Wei, M., Ran, Z., Yuan, Z., et al.: Plaque recognition of carotid ultrasound images based on deep residual network. In: IEEE 8th Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference, pp. 931–934 (2019)
Van’t, K.R., Naggara, O., Marsico, R., et al.: Automated versus manual in vivo segmentation of carotid plaque MRI. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 33(8), 1621–1627 (2012)
Bonanno, L., Sottile, F., Ciurleo, R., et al.: Automatic algorithm for segmentation of atherosclerotic carotid plaque. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 26(2), 411–416 (2017)
Zhao, H., Shi, J., Qi, X., et al.: Pyramid scene parsing network. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2881–2890 (2017)
Zhang, Z., Liu, Q., Wang, Y.: Road extraction by deep residual U-Net. IEEE Geo-sci. Remote Sens. Lett. 15(5), 749–753 (2018)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing & Computer Assisted Intervention, pp. 234–241 (2015)
Badrinarayanan, V., Kendall, A., Cipolla, R.: SegNet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(12), 2481–2495 (2019)
Li, X., Chen, H., Qi, X., et al.: H-DenseUNet: hybrid densely connected UNet for liver and tumor segmentation from CT volumes. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 37(12), 2663–2674 (2018)
Wang, Y., Deng, Z., Hu, X., et al.: Deep attentional features for prostate segmentation in ultrasound. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing & Computer Assisted Intervention (2018)
Azzopardi, C., Hicks, Y.A., Camilleri, K.P.: Automatic carotid ultrasound segmentation using deep convolutional Neural Networks and phase congruency maps. In: IEEE 14th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (2017)
Meshram, N.H., Mitchell, C.C., Wilbrand, S., et al.: Deep learning for carotid plaque segmentation using a dilated U-Net architecture. Ultrason. Imaging 42(4–5), 221–230 (2020)
Xie, S., Girshick, R., Dollár, P., et al.: Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5987–5995 (2017)
Mi, S., Wei, Z., Xu, J., et al.: Detecting carotid intima-media from small-sample ultrasound images. In: Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society, pp. 2129–2132 (2020)
Wang, X., Yu, K., Dong, C., et al.: Recovering realistic texture in image super-resolution by deep spatial feature transform. In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 606–615 (2018)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. 2020A1515010711) and the Special Foundation for the Development of Strategic Emerging Industries of Shenzhen (Nos. JCYJ20170818161845824, JCYJ20200109143010272 and JCYJ20200109143035495).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mi, S., Bao, Q., Wei, Z., Xu, F., Yang, W. (2021). MBFF-Net: Multi-Branch Feature Fusion Network for Carotid Plaque Segmentation in Ultrasound. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2021. MICCAI 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12905. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87240-3_30
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87240-3_30
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-87239-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-87240-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)