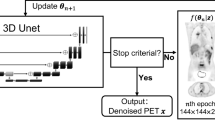
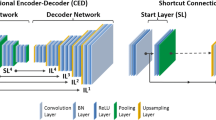
Abstract
As an important tool for cancer diagnosis and brain function imaging, PET is widely used in clinical fields where quantitative accuracy takes an important role. Several methods have been suggested to improve the quantification performance of PET by introducing quantitative coefficients, taking advantages of the time-of-flight (TOF) information, or modeling the point spread function (PSF). However, some physical effects such as photon attenuation limit the quantification potential, which should be focused on. In this paper, we proposed a novel method based on the combination of the expectation maximization (EM) and the learning ability of neural networks, achieving the quantification of PET reconstruction from raw sinogram data without attenuation correction (AC). The EM module was utilized to recover less-accurate PET images without the consideration of attenuation. And these rough images were finely adjusted by the network module which has strong nonlinearity to improve the quantitative performance. The proposed method was evaluated on simulated phantom data and compared to several existing reconstruction methods. It turns out that our method has great potential of high-quality PET image reconstruction.
Supported in part by the National Key Technology Research and Development Program of China (No: 2016YFC1300302, 2017YFE0104000), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No: U1809204, 61701436), and by the Key Research and Development Program of Zhejiang Province (No: 2021C03029).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zaidi, H., Karakatsanis, N.: Towards enhanced PET quantification in clinical oncology. Br. J. Radiol. 91, 20170508 (2017)
De Pierro, A.R.: A modified expectation maximization algorithm for penalized likelihood estimation in emission tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 14(1), 132–137 (1995)
Zhang, Z., Liu, H.: Nonlocal total variation based dynamic PET image reconstruction with low-rank constraints. Phys. Scr. 94(6), 065202 (2019)
Xie, N., et al.: Penalized-likelihood PET image reconstruction using 3D structural convolutional sparse coding. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2020.3042907
Cui, J., Yu, H., Chen, S., Chen, Y., Liu, H.: Simultaneous estimation and segmentation from projection data in dynamic PET. Med. Phys. 46, 1245–1259 (2019)
Cui, J., Qin, Z., Chen, S., Chen, Y., Liu, H.: Structure and tracer kinetics-driven dynamic PET reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 4, 400–409 (2020)
Tozaki, T., Senda, M., Sakamoto, S., Matsumoto, K.: Computer assisted diagnosis method of whole body cancer using FDG-PET images. In: Proceedings 2003 International Conference on Image Processing (Cat. No. 03CH37429), vol. 2, pp. II–1085 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2003.1246874
Emond, E.C., Groves, A.M., Hutton, B.F., Thielemans, K.: Effect of positron range on PET quantification in diseased and normal lungs. Phys. Med. Biol. 64(20), 205010 (2019)
Miederer, M., Pektor, S., Miederer, I., Bausbacher, N., Diken, M.: Iodine-124 PET quantification of organ-specific delivery and expression of NIS-encoding RNA. EJNMMI Res. 11(1), 1–8 (2021)
Seo, Y.: Quantification of SPECT and PET for drug development. Curr. Radiopharm. 1(1), 17–21 (2008)
Madsen, M.T.: Emission tomography: the fundamentals of PET and SPECT. Shock 23(11), 5341–9 (2005)
Karp, J.S., Surti, S., Daube-Witherspoon, M.E., Muehllehner, G.: Benefit of time-of-flight in PET: experimental and clinical results. J. Nucl. Med. 49(3), 462 (2008)
Alessio, A.M., Kinahan, P.E., Lewellen, T.K.: Modeling and incorporation of system response functions in 3-D whole body PET. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 25(7), 828–837 (2006)
Panin, V.Y., Kehren, F., Michel, C., Casey, M.: Fully 3-D PET reconstruction with system matrix derived from point source measurements. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 25(7), 907–921 (2006)
García-Pérez, P., Espaa, S.: Simultaneous emission and attenuation reconstruction in time-of-flight PET using a reference object. EJNMMI Phys. 7(1), 3 (2020)
Alessio, A.M., Kohlmyer, S., Branch, K., Chen, G., Kinahan, P.: Cine CT for attenuation correction in cardiac PET/CT. J. Nucl. Med. 48(5), 794–801 (2007)
Fei, B., et al.: MR/PET quantification tools: registration, segmentation, classification, and MR-based attenuation correction. Med. Phys. 39(10), 6443–6454 (2012)
Bortolin, K., Arabi, H., Zaidi, H.: Deep learning-guided attenuation and scatter correction without using anatomical images in brain PET/MRI. In: 2019 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC), pp. 1–3. IEEE (2019)
Lim, H., Chun, I.Y., Dewaraja, Y.K., Fessler, J.A.: Improved low-count quantitative PET reconstruction with an iterative neural network. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 39(11), 3512–3522 (2020)
Zhang, J., Ghanem, B.: ISTA-Net: interpretable optimization-inspired deep network for image compressive sensing. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1828–1837. IEEE (2018)
Zubal, I.G.: Computerized three-dimensional segmented human anatomy. Med. Phys. 21(2), 299 (1999)
Muzic, R.F., Cornelius, S.: Comkat: compartment model kinetic analysis tool. J. Nucl. Med. 42(4), 636–645 (2001)
Fessler, J.A.: Penalized weighted least-squares image reconstruction for positron emission tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 13(2), 290–300 (1994)
Häggström, I., Schmidtlein, C.R., Campanella, G., Fuchs, T.J.: Deeppet: a deep encoder-decoder network for directly solving the PET image reconstruction inverse problem. Med. Image Anal. 54, 253–262 (2019)
Horé, A., Ziou, D.: Image quality metrics: PSNR vs. SSIM. In: 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, pp. 2366–2369 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPR.2010.579
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhao, L., Liu, H. (2021). EMISTA-Based Quantitative PET Reconstruction. In: Peng, Y., Hu, SM., Gabbouj, M., Zhou, K., Elad, M., Xu, K. (eds) Image and Graphics. ICIG 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12889. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87358-5_56
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87358-5_56
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-87357-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-87358-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)