Abstract
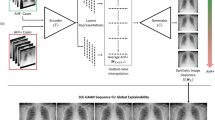
We present a novel framework for explainable labeling and interpretation of medical images. Medical images require specialized professionals for interpretation, and are explained (typically) via elaborate textual reports. Different from prior methods that focus on medical report generation from images or vice-versa, we novelly generate congruent image–report pairs employing a cyclic-Generative Adversarial Network (cycleGAN); thereby, the generated report will adequately explain a medical image, while a report-generated image that effectively characterizes the text visually should (sufficiently) resemble the original. The aim of the work is to generate trustworthy and faithful explanations for the outputs of a model diagnosing chest X-ray images by pointing a human user to similar cases in support of a diagnostic decision. Apart from enabling transparent medical image labeling and interpretation, we achieve report and image-based labeling comparable to prior methods, including state-of-the-art performance in some cases as evidenced by experiments on the Indiana Chest X-ray dataset.
A. Pandey and B. Paliwal—contributed equally.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jing, B., Xie, P., Xing, E.: On the automatic generation of medical imaging reports. In: Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (2018)
Girshicka, R., Donahuea, J., Darrell, T., Malik, J.: Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In: CVPR (2014)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: NIPS (2012)
Selvaraju, R.R., Das, A., Vedantam, R., Cogswell, M., Parikh, D., Batra, D.: Grad-CAM: why did you say that? visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. CoRR, abs/1610.02391 (2016). http://arxiv.org/abs/1610.02391
Paszke, A., et al.: Pytorch: an imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In: Wallach, H., Larochelle, H., Beygelzimer, A., dAlche-Buc, F., Fox, E., Garnett, R. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 32, pp. 8024–8035. Curran Associates Inc, (2019). http://papers.neurips.cc/paper/9015-pytorch:an-imperative-style-high-performance-deep-learning-library.pdf
Cortez, P., Embrechts, M.J.: Using sensitivity analysis and visualization techniques to open black box data mining models. Inf. Sci. 225, 1–17 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2012.10.039
Chattopadhay, A., Sarkar, A., Howlader, P., Balasubramanian, V.N.: Grad-cam++: generalized gradient based visual explanations for deep convolutional networks. IN: 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), March 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV.2018.00097
Reed, S.E., Akata, Z., Yan, X., Logeswaran, L., Schiele, B., Lee, H.: Generative adversarial text to image synthesis. CoRR, abs/1605.05396, (2016). http://arxiv.org/abs/1605.05396
Xu, T., et al.: Attngan: fine-grained text to image generation with attentional generative adversarial networks. CoRR, abs/1711.10485 (2017). http://arxiv.org/abs/1711.10485
Zhang, H., et al.: Stackgan: text to photo-realistic image synthesis with stacked generative adversarial networks. CoRR, vol. abs/1612.03242 (2016). http://arxiv.org/abs/1612.03242
Liu, G., et al.: Clinically accurate chest x-ray report generation. CoRR, abs/1904.02633 (2019). http://arxiv.org/abs/1904.02633
Adebayo, J., Gilmer, J., Muelly, M., Goodfellow, I., Hardt, M., Kim, B.: Sanity checks for saliency maps (2020)
Ribeiro, M.T., Singh, S., Guestrin, C.: Why should i trust you?: Explaining the predictions of any classifier (2016)
Zhu, J.Y., Park, T., Isola, P., Efros, A.A.: Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks (2020)
Chen, Z., Song, Y., Chang, T.H., Wan, X.: Generating radiology reports via memory-driven transformer (2020). In: Mahapatra, D., Poellinger, A., Shao, L., Reyes, M. (eds.) @articleMahapatraTMI2021, Interpretability-Driven Sample Selection Using Self Supervised Learning For Disease Classification And Segmentation, pp. 1–15. IEEE (2021)
Mahapatra, D., Poellinger, A., Shao, L., Reyes, M.: A interpretability-driven sample selection using self supervised learning for disease classification and segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. (2021)
Krause, J., Johnson, J., Krishna, R., Fei-Fei, L.: A hierarchical approach for generating descriptive image paragraphs. In: Computer Vision and Patterm Recognition (CVPR) (2017)
Chen, C., Li, D., Barnett, A., Su, J., Rudin, C.: This looks like that: deep learning for interpretable image recognition. CoRR, abs/1806.10574 (2018). http://arxiv.org/abs/1806.10574
Rajpurkar, P., et al.: Chexnet: radiologist-level pneumonia detection on chest x-rays with deep learning. CoRR, abs/1711.05225 (2017). http://arxiv.org/abs/1711.05225
Demner-Fushman, D., et al.: Preparing a collection of radiology examinations for distribution and retrieval. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 23(2), 304–310. https://doi.org/10.1093/jamia/ocv080
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. CoRR, abs/1512.03385 (2015). http://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385
Simonyan, K.: Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition (2015)
Papineni, K., Roukos, S., Ward, T., Zhu, W.: Bleu: a method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 311–318. Association for Computational Linguistics (2012)
Lin, C.-Y.: Rouge: a package for automatic evaluation of summaries. In: Proceedings of the ACL-04 Workshop on Text Summarization Branches Out, vol. 8. Barcelona, Spain (2004)
Xue, Y., et al.: Multimodal recurrent model with attention for automated radiology report generation. In: Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2018) (2018)
Olah, C.M., Ludwig, A.S.: Feature visualization. Distill (2017)
Lipton, Z.C.: The mythos of model interpretability. In: Workshop on Human Interpretability in Machine Learning (WHI 2016) (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Pandey, A., Paliwal, B., Dhall, A., Subramanian, R., Mahapatra, D. (2021). This Explains That: Congruent Image–Report Generation for Explainable Medical Image Analysis with Cyclic Generative Adversarial Networks. In: Reyes, M., et al. Interpretability of Machine Intelligence in Medical Image Computing, and Topological Data Analysis and Its Applications for Medical Data. IMIMIC TDA4MedicalData 2021 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12929. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87444-5_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87444-5_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-87443-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-87444-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)