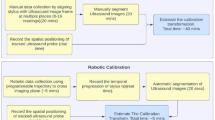
Abstract
The evolution of consumer-grade hardware components (e.g., trackers, portable ultrasound probes) has opened the door for the development of low cost systems. We evaluated different low-cost tracking alternatives on the accuracy of 3D freehand ultrasound reconstruction in the context of image-guided neurosurgery. Specifically, we compared two low-cost tracking options, an Intel RealSense depth camera setup and the OptiTrack camera to a standard commercial infrared optical tracking system, the Atracsys FusionTrack 500. In addition to the tracking systems, we investigated the impact of ultrasound imaging on 3D reconstruction. We compared two ultrasound systems: a low-cost handheld ultrasound system and a high-resolution ultrasound mobile station. Ten acquisitions were made with each tracker and probe pair. Our results showed no statistically significant difference between the two probes and no difference between high and low-end optical trackers. The findings suggest that low cost hardware may offer a solution in the operating room or environments where commercial hardware systems are not available without compromising on the accuracy and usability of US image-guidance.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asselin, M., Lasso, A., Ungi, T., Fichtinger, G.: Towards webcam-based tracking for interventional navigation. In: Fei, B., Webster III, R.J. (eds.) Medical Imaging 2018: Image-Guided Procedures, Robotic Interventions, and Modeling, vol. 10576, pp. 534–543. International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE (2018). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2293904
Carbajal, G., Lasso, A., Gómez, Á., Fichtinger, G.: Improving N-wire phantom-based freehand ultrasound calibration. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 8(6), 1063–1072 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-013-0904-9
Cenni, F., Monari, D., Desloovere, K., Aertbeliën, E., Schless, S.H., Bruyninckx, H.: The reliability and validity of a clinical 3D freehand ultrasound system. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 136, 179–187 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2016.09.001
Clatz, O., et al.: Robust nonrigid registration to capture brain shift from intraoperative MRI. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 24(11), 1417–1427 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2005.856734
Garrido-Jurado, S., Muñoz-Salinas, R., Madrid-Cuevas, F.J., Marín-Jiménez, M.J.: Automatic generation and detection of highly reliable fiducial markers under occlusion. Pattern Recogn. 47(6), 2280–2292 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2014.01.005
Lasso, A., Heffter, T., Rankin, A., Pinter, C., Ungi, T., Fichtinger, G.: PLUS: open-source toolkit for ultrasound-guided intervention systems. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 61(10), 2527–2537 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2014.2322864
Lemes, S.: Comparison of similar injection moulded parts by a coordinate measuring machine. SN Appl. Sci. 1(2), 1–8 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0191-3
Mercier, L., et al.: New prototype neuronavigation system based on preoperative imaging and intraoperative freehand ultrasound: system description and validation. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 6(4), 507–522 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-010-0535-3
Mercier, L., Langø, T., Lindseth, F., Collins, D.L.: A review of calibration techniques for freehand 3-D ultrasound systems. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 31(4), 449–471 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2004.11.015
Pieper, S., Halle, M., Kikinis, R.: 3D slicer. In: 2004 2nd IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: Macro to Nano 1, pp. 632–635 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/isbi.2004.1398617
Reinertsen, I., Lindseth, F., Askeland, C., Iversen, D.H., Unsgård, G.: Intra-operative correction of brain-shift. Acta Neurochir. 156(7), 1301–1310 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-014-2052-6
Riva, M., et al.: Intraoperative computed tomography and finite element modelling for multimodal image fusion in brain surgery. Operative Neurosurg. 18(5), 531–541 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1093/ons/opz196
Rohling, R., Gee, A., Berman, L.: A comparison of freehand three-dimensional ultrasound reconstruction techniques. Med. Image Anal. 3(4), 339–359 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1361-8415(99)80028-0
Solberg, O.V., Lindseth, F., Torp, H., Blake, R.E., Nagelhus Hernes, T.A.: Freehand 3D ultrasound reconstruction algorithms-a review. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 33(7), 991–1009 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2007.02.015
Unsgaard, G., et al.: Intra-operative 3D ultrasound in neurosurgery. Acta Neurochir. 148(3), 235–253 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-005-0688-y
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Léger, É., Gueziri, H.E., Collins, D.L., Popa, T., Kersten-Oertel, M. (2021). Evaluation of Low-Cost Hardware Alternatives for 3D Freehand Ultrasound Reconstruction in Image-Guided Neurosurgery. In: Noble, J.A., Aylward, S., Grimwood, A., Min, Z., Lee, SL., Hu, Y. (eds) Simplifying Medical Ultrasound. ASMUS 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12967. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87583-1_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87583-1_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-87582-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-87583-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)