Abstract
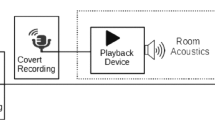
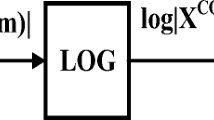
In this paper, authors propose spectral root cepstral coefficients (SRCC) feature set to develop the effective countermeasure system for replay attacks on voice assistants (VAs). Experiments are performed on ReMASC dataset, which is specifically designed for the replay attack detection task. Logarithm operation in MFCC extraction is replaced by power-law nonlinearity (i.e. \((\cdot )^\gamma \)) to derive SRCC feature set. The proper choice of the \(\gamma \) helps to capture the system information of the speech signal, with a minimum number of cepstral coefficients. We investigated two approaches for proper choice of \(\gamma \)-value, in particular, by estimating the energy concentration in cepstral coefficients and by visualizing the spectrogram w.r.t. \(\gamma \)-value. This system representation of the speech signal, is the discriminative cue for the replay spoof speech detection (SSD) task as replay speech signal consists of additional transmission channel effects convolved with the genuine signal. The performance of the proposed feature set is validated using Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM), and Light Convolutional Neural Network (LCNN). Our primary system shows relative improvement of 47.49% over the baseline system (Constant-Q Cepstral Coefficients (CQCC)-GMM) on the evaluation set. The EER is further reduced to 11.84% on evaluation set by classifier-level fusion.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alegre, F., Janicki, A., Evans, N.: Re-assessing the threat of replay spoofing attacks against automatic speaker verification. In: 2014 International Conference of the Biometrics Special Interest Group (BIOSIG), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2014)
Cai, W., Wu, H., Cai, D., Li, M.: The DKU replay detection system for the ASVspoof 2019 challenge: on data augmentation, feature representation, classification, and fusion. In: INTERSPEECH, pp. 1023–1027, Graz, Austria, September 2019
Carlini, N., et al.: Hidden voice commands. In: 25th USENIX Security Symposium, pp. 513–530, Austin, USA, August 2016
Carlini, N., Wagner, D.: Audio adversarial examples: targeted attacks on speech-to-text. In: IEEE Security and Privacy Workshops (SPW), pp. 1–7, San Francisco, USA, May 2018
Delgado, H., et al.: ASVspoof 2017 version 2.0: meta-data analysis and baseline enhancements. In: Odyssey 2018: The Speaker and Language Recognition Workshop, pp. 296–303, Les Sables d’Olonne, France, June 2018
Diao, W., Liu, X., Zhou, Z., Zhang, K.: Your voice assistant is mine: how to abuse speakers to steal information and control your phone. In: 4th ACM Workshop on SPSM, pp. 63–74, Scottsdale, USA, November 2014
Gong, Y., Poellabauer, C.: An overview of vulnerabilities of voice controlled systems. In: \(1^{st}\) International Workshop on Security and Privacy for Internet-of-Things, Orlando, United States, April 2018
Gong, Y., Yang, J., Huber, J., MacKnight, M., Poellabauer, C.: ReMASC: realistic replay attack corpus for voice controlled systems. In: INTERSPEECH, pp. 2355–2359, Graz, Austria, September 2019
Goodfellow, I.J., Warde-Farley, D., Mirza, M., Courville, A., Bengio, Y.: Maxout networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1319–1327, Atlanta, USA, June 2013
Hermansky, H.: Perceptual linear predictive (PLP) analysis of speech. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 87(4), 1738–1752 (1990)
Hermansky, H., Morgan, N.: RASTA processing of speech. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 2(4), 578–589 (1994)
Kim, C., Stern, R.M.: Power-normalized cepstral coefficients (PNCC) for robust speech recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 24(7), 1315–1329 (2016)
Lai, C.I., Chen, N., Villalba, J., Dehak, N.: ASSERT: anti-spoofing with squeeze-excitation and residual networks. In: INTERSPEECH, pp. 1013–1017, Graz, Austria, September 2019
Lavrentyeva, G., Novoselov, S., Malykh, E., Kozlov, A., Kudashev, O., Shchemelinin, V.: Audio replay attack detection with deep learning frameworks. In: INTERSPEECH, pp. 82–86. Stockholm, Sweden, August 2017
Lim, J.: Spectral root homomorphic deconvolution system. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 27(3), 223–233 (1979)
Makhoul, J.: Linear prediction: a tutorial review. Proc. IEEE 63(4), 561–580 (1975)
Marcel, S., Nixon, M.S., Li, S.Z. (eds.): Handbook of Biometric Anti-Spoofing. ACVPR, Springer, London (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4471-6524-8
Markel, J.D., Gray, A.J.: Linear Prediction of Speech, vol. 12. Springer, Heidelberg (2013)
Oppenheim, A., Schafer, R.: Homomorphic analysis of speech. IEEE Trans. Audio Electroacoust. 16(2), 221–226 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1109/TAU.1968.1161965
Oppenheim, A.V.: Superposition in a class of nonlinear systems. MIT Research Laboratory of Electronics (1965)
Oppenheim, A.V.: Speech analysis-synthesis system based on homomorphic filtering. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. (JASA) 45(2), 458–465 (1969)
Oppenheim, A.V., Schafer, R.W., Stockham, T.: Nonlinear filtering of multiplied and convolved signals. IEEE Trans. Audio Electroacoust. 16(3), 437–466 (1968)
Patel, T.B., Patil, H.A.: Combining evidences from Mel cepstral, cochlear filter cepstral and instantaneous frequency features for detection of natural vs. spoofed speech. In: INTERSPEECH, pp. 2062–2066, Dresden, Germany (Sept 2015)
Quatieri, T.F.: Discrete-Time Speech Signal Processing: Principles and Practice. \(1^{st}\) edition, Pearson Education India, New Delhi (2015)
Schafer, R.W.: Echo Removal by Discrete Generalized Linear Filtering. MIT Research Laboratory of Electronics, Cambridge (1969)
Shiota, S., Villavicencio, F., Yamagishi, J., Ono, N., Echizen, I., Matsui, T.: Voice liveness detection for speaker verification based on a tandem single/double-channel pop noise detector. In: Odyssey, vol. 2016, pp. 259–263, Bilbao, Spain, June 2016
Tapkir, P.A., Patil, A.T., Shah, N., Patil, H.A.: Novel spectral root cepstral features for replay spoof detection. In: APSIPA-ASC, pp. 1945–1950, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, November 2018
Todisco, M., Delgado, H., Evans, N.: Constant Q cepstral coefficients: a spoofing countermeasure for automatic speaker verification. Comput. Speech Lang. 45, 516–535 (2017)
Todisco, M., et al.: ASVspoof 2019: future horizons in spoofed and fake audio detection. In: INTERSPEECH, pp. 1008–1012, Graz, Austria, September 2019
Tom, F., Jain, M., Dey, P.: End-to-end audio replay attack detection using deep convolutional networks with attention. In: INTERSPEECH, pp. 681–685, Hyderabad, India, September 2018
Vaidya, T., Zhang, Y., Sherr, M., Shields, C.: Cocaine noodles: exploiting the gap between human and machine speech recognition. In: 9th USENIX Workshop on Offensive Technologies (WOOT-2015), Washington, DC, USA, August 2015
Wickramasinghe, B., Irtza, S., Ambikairajah, E., Epps, J.: Frequency domain linear prediction features for replay spoofing attack detection. In: INTERSPEECH, pp. 661–665, Hyderabad, India, September 2018
Wu, X., He, R., Sun, Z., Tan, T.: A light CNN for deep face representation with noisy labels. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 13(11), 2884–2896 (2018)
Wu, Z., et al.: ASVspoof 2015: the first automatic speaker verification spoofing and countermeasures challenge. In: INTERSPEECH, pp. 2037–2041, Dresden, Germany, September 2015
Zhang, G., Yan, C., Ji, X., Zhang, T., Zhang, T., Xu, W.: Dolphinattack: inaudible voice commands. In: Proceedings of the 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, pp. 103–117. ACM, Dallas, TX, USA, October 2017
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Patil, A.T., Kotta, H., Acharya, R., Patil, H.A. (2021). Spectral Root Features for Replay Spoof Detection in Voice Assistants. In: Karpov, A., Potapova, R. (eds) Speech and Computer. SPECOM 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12997. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87802-3_46
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87802-3_46
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-87801-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-87802-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)