Abstract
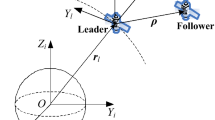
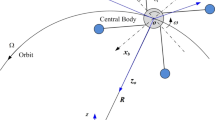
Evolutionary optimization methods have proven efficient in optimal transfer and orbit determination. This paper investigates the suitability of a Quantum Particle Swarm Optimization (QPSO) scheme for finding optimal transfer trajectories required for a fuel-efficient formation reconfiguration. It achieves this by comparing the search results for optimal transfer trajectories using QPSO, with traditional PSO. Given an initially clustered formation, a configuration, based on satellite coverage requirements, is set as the final configuration which the cluster aims to achieve, with minimal fuel consumption. Results show that QPSO had a better performance compared to traditional PSO, yielding faster convergence, higher accuracy, as well as better reliability to evade local minima by exploring a wider search spread.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
dos Santos, D.P.S., Formiga, J.K.S.: Application of a genetic algorithm in orbital maneuvers. Computat. Appl. Math. 34(2), 437–450 (2014)
Soyinka, O.K., Duan, H.: Optimal impulsive thrust trajectories for satellite formation via improved brainstorm optimization. In: Tan, Y., Shi, Y., Li, Li. (eds.) ICSI 2016. LNCS, vol. 9713. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-41009-8
Jiashi, G., Lei, L., Yongji, W.: Spacecraft orbit design based on intelligent optimization. In: 2017 2nd International Conference on Advanced Robotics and Mechatronics (ICARM), Hefei, China. IEEE (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICARM.2017.8273244
Mauro, P., Bruce, A.C.: Particle swarm optimization applied to space trajectories. J. Guidance Control Dynam. (2010). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.48475
Meireles, L., Rocco, E.M.: Study of orbital transfers with time constraint and fuel optimization. In: XVIII Brazilian Colloquium on Orbital Dynamics, 2016. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Águas de Lindoia (2014). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/911/1/012014
Jun, S., Choi-Hong, L., Xiao-Jun, W.: Particle Swarm Optimisation: Classical and Quantum Perspectives. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, London (2012)
Bagheri, A., Hamed, M., Mohsen, A.: Financial forecasting using ANFIS networks with quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 41(14), 6235–6250 (2014)
Fang, W., Sun, J., Wu, X.: Adaptive web QoS controller based on online system identification using quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization. Soft. Comput. 19(6), 1715–1725 (2015)
Liu, L., Sun, J., Zhang, D., Guocheng, D., Chen, J., Wenbo, X.: Culture conditions optimization of hyaluronic acid production by Streptococcus zooepidemicus based on radial basis function neural network and quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization algorithm. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 44(1), 24–32 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2008.09.015
Li, S., Wang, R., Weiwei, H., Sun, J.: A new QPSO based BP neural network for face detection. In: Cao, B.-Y. (ed.) Fuzzy information and engineering, pp. 355–363. Springer, Heidelberg (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-71441-5_40
Kun, Y., Weiming, F., Gang, L., Junfeng, Z., Piaoyi, S.: Quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization for far-distance rapid cooperative rendezvous between two spacecraft. Adv. Space Res. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2018.08.006
Qing, Z., Jianxin, Z., Junjie, T.: On-orbit servicing mission planning for multi-spacecraft using improved QPSO algorithm. Int. Core J. Eng. 3, 2414–1895 (2017)
Curtis, H.: Lambert’s Problem. In Orbital Mechanics for Engineering Students. Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford (2005)
Curtis, H.: Orbital Mechanics for Engineering Students. Elsevier, Burlington (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Soyinka Olukunle, K., Nwanze, N., Akoma Henry, E.C.A. (2021). Time Dependent Fuel Optimal Satellite Formation Reconfiguration Using Quantum Particle Swarm Optimization. In: Rutkowski, L., Scherer, R., Korytkowski, M., Pedrycz, W., Tadeusiewicz, R., Zurada, J.M. (eds) Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing. ICAISC 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12855. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87897-9_34
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87897-9_34
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-87896-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-87897-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)