Abstract
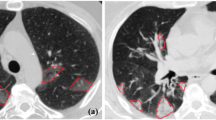
In the early 2020, the corona virus disease (COVID-19) has become a global epidemic, resulting in a profound impact on the lives of billions of people, from both of safety and economic perspective. Rapid screening is of great significance to control the spread of disease. In the clinic practice, computed tomography (CT) is widely utilized by the doctors to detect and evaluate novel coronavirus pneumonia and lung segmentation is a necessary initial step for lung image analysis. However, the segmentation task is still confronted with several challenges, such as high variations in intensity, indistinct edges and noise due to data acquisition process. To address aforementioned challenges, in this paper, we present a novel two-stage-based COVID-19 lung segmentation method. First, we design a coarse segmentation method combining threshold and rib outline, which can remove most background while retaining complete lung shapes. Then, a contour refinement algorithm was introduced to refine the coarse segmentation based on local information including intensity, shape and gradient. The proposed method was tested on 20 sets of COVID-19 CT cases. Quantitative evaluations are conducted with different methods (including the deep learning-based approach), and the results demonstrate that our method can provide superior performance with few-shot samples. Our method achieves an average symmetric surface distance (ASD) of \(0.0101 \pm 0.0147\)mm and dice similarity coefficient (DSC) of \(99.22 \pm 0.99\%\) on lung CT image segmentation compared with ground truths. To better promote the research in this field, we have released our code to facilitate the research community(https://github.com/qianjingw/Two-Stage-COVID-19-Lung-Segmentation).
Qianjing Wang is a graduate student.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai, T., et al.: Correlation of chest CT and RT-PCR testing for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: a report of 1014 cases. Radiology 296(2), E32–E40 (2020)
Chung, M., et al.: CT imaging features of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Radiology 295(1), 202–207 (2020)
Deng, Y., Lei, L., Chen, Y., Zhang, W.: The potential added value of FDG PET/CT for COVID-19 pneumonia. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 1–2 (2020)
Gerard, S.E., Herrmann, J., Kaczka, D.W., Musch, G., Fernandez-Bustamante, A., Reinhardt, J.M.: Multi-resolution convolutional neural networks for fully automated segmentation of acutely injured lungs in multiple species. Med. Image Anal. 60, 101592 (2020)
Gill, G., Beichel, R.R.: Segmentation of lungs with interstitial lung disease in CT scans: a TV-L1 based texture analysis approach. In: Bebis, G., et al. (eds.) ISVC 2014. LNCS, vol. 8887, pp. 511–520. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-14249-4_48
Kiaei, A.A., Khotanlou, H.: Segmentation of medical images using mean value guided contour. Med. Image Anal. 40, 111–132 (2017)
Li, Q., Deng, T., Xie, W.: Active contours driven by divergence of gradient vector flow. Sig. Process. 120, 185–199 (2016)
Liu, C., Pang, M.: Automatic lung segmentation based on image decomposition and wavelet transform. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 61, 102032 (2020)
Mansoor, A., et al.: Segmentation and image analysis of abnormal lungs at CT: current approaches, challenges, and future trends. Radiographics 35(4), 1056–1076 (2015)
Mansoor, A., Bagci, U., Mollura, D.J.: Near-optimal keypoint sampling for fast pathological lung segmentation. In: 2014 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp. 6032–6035. IEEE (2014)
Mesanovic, N., Grgic, M., Huseinagic, H., Males, M., Skejic, E., Smajlovic, M.: Automatic CT image segmentation of the lungs with region growing algorithm. In: 18th International Conference on Systems, Signals and Image Processing-IWSSIP, pp. 395–400 (2011)
Park, B., Park, H., Lee, S.M., Seo, J.B., Kim, N.: Lung segmentation on HRCT and volumetric CT for diffuse interstitial lung disease using deep convolutional neural networks. J. Digit. Imaging 32(6), 1019–1026 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-019-00254-8
Prasad, M.N., et al.: Automatic segmentation of lung parenchyma in the presence of diseases based on curvature of ribs. Acad. Radiol. 15(9), 1173–1180 (2008)
Pulagam, A.R., Kande, G.B., Ede, V.K.R., Inampudi, R.B.: Automated lung segmentation from HRCT scans with diffuse parenchymal lung diseases. J. Digit. Imaging 29(4), 507–519 (2016)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Shen, S., Bui, A.A., Cong, J., Hsu, W.: An automated lung segmentation approach using bidirectional chain codes to improve nodule detection accuracy. Comput. Biol. Med. 57, 139–149 (2015)
Sousa, A.M., Martins, S.B., Falcao, A.X., Reis, F., Bagatin, E., Irion, K.: ALTIS: A fast and automatic lung and trachea CT-image segmentation method. Med. Phys. 46(11), 4970–4982 (2019)
Sun, S., Bauer, C., Beichel, R.: Automated 3-D segmentation of lungs with lung cancer in CT data using a novel robust active shape model approach. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 31(2), 449–460 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, Q., Wang, C., Xu, K., Zhang, Ym. (2021). Two-Stage COVID-19 Lung Segmentation from CT Images by Integrating Rib Outlining and Contour Refinement. In: Ma, H., et al. Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision. PRCV 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13021. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-88010-1_27
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-88010-1_27
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-88009-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-88010-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)