Abstract
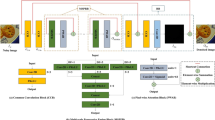
In this work, we address the problem of image denoising using deep neural networks. Recent developments in convolutional neural networks provide a very potent alternative for image restoration applications and in particular for image denoising. A particularly popular deep network structure for image processing are the auto-encoders which include the U-Net as an important example. U-Nets contract and expand feature maps repeatedly, which leads to extraction of multi scale information as well as an increase in the effective receptive field when compared to conventional convolutional nets. In this paper, we propose the integration of a multi scale channel attention module through a U-Net structure as a novelty for the image denoising problem. The introduced network structure also utilizes multi scale inputs in the various substages of the encoder module in a novel manner. Simulation results demonstrate competitive and mostly superior performance when compared to some state of the art deep learning based image denoising methodologies. Qualitative results also indicate that the developed deep network framework has powerful detail preserving capability.
This work is supported by TUBITAK (The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey) under project no. 119E248.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anwar, S., Barnes, N.: Real image denoising with feature attention. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 3155–3164 (2019)
Colak, O., Eksioglu, E.M.: Image denoising using patch ordering and 3D transformation of patches. IET Image Process. 13(13), 2636–2646 (2019)
Corbetta, M., Shulman, G.: Control of goal-directed and stimulus-driven attention in the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3, 201–15 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn755
Dabov, K., Foi, A., Katkovnik, V., Egiazarian, K.: Image denoising by sparse 3-D transform-domain collaborative filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 16(8), 2080–2095 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2007.901238
Franzén., R.: Kodak lossless true color image suite, vol. 4 (1999). http://r0k.us/graphics/kodak.
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 770–778 (2016)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7132–7141 (2018)
Huang, G., Liu, Z., Weinberger, K.Q.: Densely connected convolutional networks. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2261–2269 (2017)
Huang, Q., Yang, D., Wu, P., Qu, H., Yi, J., Metaxas, D.: MRI reconstruction via cascaded channel-wise attention network. In: 2019 IEEE 16th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2019), pp. 1622–1626 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISBI.2019.8759423
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. CoRR abs/1412.6980 (2015)
Liu, P., Zhang, H., Zhang, K., Lin, L., Zuo, W.: Multi-level Wavelet-CNN for Image Restoration, pp. 886–88609 (2018)
Martin, D., Fowlkes, C., Tal, D., Malik, J.: A database of human segmented natural images and its application to evaluating segmentation algorithms and measuring ecological statistics. In: Proceedings Eighth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2001, vol. 2, pp. 416–423 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2001.937655
Mei, Y., et al.: Pyramid attention networks for image restoration. ArXiv abs/2004.13824 (2020)
Oktay, O., et al.: Attention U-Net: Learning where to look for the pancreas. ArXiv abs/1804.03999 (2018)
Park, B., Yu, S., Jeong, J.: Densely connected hierarchical network for image denoising. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), pp. 2104–2113 (2019)
Peng, Y., Cao, Y., Liu, S., Yang, J., Zuo, W.: Progressive training of multi-level wavelet residual networks for image denoising. ArXiv abs/2010.12422 (2020)
Tai, Y., Yang, J., Liu, X., Xu, C.: MemNet: a persistent memory network for image restoration (2017)
Timofte, R., et al.: NTIRE 2017 challenge on single image super-resolution: methods and results. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), pp. 1110–1121 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2017.149
Wang, X., Girshick, R.B., Gupta, A., He, K.: Non-local neural networks. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7794–7803 (2018)
Yu, S., Park, B., Jeong, J.: Deep iterative down-up cnn for image denoising. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops (2019)
Zhang, K., Zuo, W., Chen, Y., Meng, D., Zhang, L.: Beyond a Gaussian denoiser: residual learning of deep CNN for image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26, 3142–3155 (2017)
Zhang, K., Zuo, W., Zhang, L.: FFDNet: toward a fast and flexible solution for CNN-based image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 27(9), 4608–4622 (2018)
Zhang, K., Zuo, W., Gu, S., Zhang, L.: Learning deep CNN denoiser prior for image restoration. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2808–2817 (2017)
Acknowledgment
This work is supported by TUBITAK (The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey) under project no. 119E248.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Acar, V., Eksioglu, E.M. (2021). Scale Input Adapted Attention for Image Denoising Using a Densely Connected U-Net: SADE-Net. In: Nguyen, N.T., Iliadis, L., Maglogiannis, I., Trawiński, B. (eds) Computational Collective Intelligence. ICCCI 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12876. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-88081-1_60
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-88081-1_60
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-88080-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-88081-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)