Abstract
This paper introduces a novel commonsense generation task ExperienceGen 1.0, which is used to test whether the current models have deduction and induction capabilities. It includes two subtasks, both are used to generate commonsense knowledge expressed in natural language. The difference is that the first task is to generate commonsense using causal sentences that contain causal relationships, the second is to generate commonsense with the sentence which is the major premise of the syllogism reconstructed from the original causal sentence. ExperienceGen 1.0 is challenging because it essentially requires the model to have 1) abundant commonsense knowledge, 2) the ability of deduction and induction, and 3) relational reasoning with commonsense. We selected webtext 2019 (https://github.com/brightmart/nlp_chinese_corpus) as the data source, filtered causal sentences and got major premise of the syllogism with manual annotations. ExperienceGen 1.0 contains 2000 items which include causal sentence, major premise of the syllogism and their corresponding commonsense. It is worth noting that the ExperienceGen 1.0 is the product of deduction and induction based on commonsense knowledge from people, which is different from existed commonsense knowledge base. Experiments have shown that even the current best-performing generative models still performs poorly. We are currently releasing an initial version which is publicly available at https://github.com/NLUSoCo/ExperienceGen to inspire work in the field along with feedback gathered from the research community.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
References
Cambria, E., Song, Y., Wang, H., Hussain, A.: Isanette: a common and common sense knowledge base for opinion mining. In: 2011 IEEE 11th International Conference on Data Mining Workshops, pp. 315–322. IEEE (2011)
Chen, M., D’Arcy, M., Liu, A., Fernandez, J., Downey, D.: CODAH: an adversarially authored question-answer dataset for common sense. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.04365 (2019)
Huang, L., Bras, R.L., Bhagavatula, C., Choi, Y.: Cosmos QA: machine reading comprehension with contextual commonsense reasoning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.00277 (2019)
Li, X., Taheri, A., Tu, L., Gimpel, K.: Commonsense knowledge base completion. In: Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pp. 1445–1455 (2016)
Lin, B.Y., Xu, F.F., Zhu, K., Hwang, S.w.: Mining cross-cultural differences and similarities in social media. In: Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pp. 709–719 (2018)
Lin, B.Y., et al.: CommonGen: a constrained text generation challenge for generative commonsense reasoning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1911.03705 (2019)
Lin, C.Y.: ROUGE: a package for automatic evaluation of summaries. In: Text Summarization Branches Out, pp. 74–81 (2004)
Lu, J., Yang, J., Batra, D., Parikh, D.: Neural baby talk. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7219–7228 (2018)
Ming-Chen, L.V., Ding, X.F., University, J.: A contrastive study of the causal and causation relationship from the perspective of logic reasoning and semantic category. J. Northeast Normal Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci.) (2019)
Nunberg, G.: Position paper on common-sense and formal semantics. In: Theoretical Issues in Natural Language Processing 3 (1987)
Papineni, K., Roukos, S., Ward, T., Zhu, W.J.: BLEU: a method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 311–318 (2002)
Peng, S., Liu, L., Liu, C., Yu, D.: Exploring reasoning schemes: a dataset for syllogism figure identification. In: Liu, M., Kit, C., Su, Q. (eds.) CLSW 2020. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 12278, pp. 445–451. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-81197-6_37
Poliak, A., Naradowsky, J., Haldar, A., Rudinger, R., Van Durme, B.: Hypothesis only baselines in natural language inference. arXiv preprint arXiv:1805.01042 (2018)
Sakaguchi, K., Le Bras, R., Bhagavatula, C., Choi, Y.: WinoGrande: an adversarial Winograd schema challenge at scale. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34, pp. 8732–8740 (2020)
Sap, M., et al.: ATOMIC: an Atlas of machine commonsense for if-then reasoning. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 33, pp. 3027–3035 (2019)
Sap, M., Rashkin, H., Chen, D., LeBras, R., Choi, Y.: SocialIQA: commonsense reasoning about social interactions. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.09728 (2019)
Speer, R., Havasi, C., Lieberman, H.: AnalogySpace: reducing the dimensionality of common sense knowledge. In: AAAI, vol. 8, pp. 548–553 (2008)
Talmor, A., Herzig, J., Lourie, N., Berant, J.: CommonsenseQA: a question answering challenge targeting commonsense knowledge. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.00937 (2018)
Tincoff, R., Jusczyk, P.W.: Some beginnings of word comprehension in 6-month-olds. Psychol. Sci. 10(2), 172–175 (1999)
Wang, C., Liang, S., Zhang, Y., Li, X., Gao, T.: Does it make sense? And why? A pilot study for sense making and explanation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.00363 (2019)
Xu, F.F., Lin, B.Y., Zhu, K.Q.: Automatic extraction of commonsense located near knowledge. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.04204 (2017)
Yang, P., Li, L., Luo, F., Liu, T., Sun, X.: Enhancing topic-to-essay generation with external commonsense knowledge. In: Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 2002–2012 (2019)
Yang, P., et al.: Knowledgeable storyteller: a commonsense-driven generative model for visual storytelling. In: IJCAI, pp. 5356–5362 (2019)
Zang, L.J., Cao, C., Cao, Y.N., Wu, Y.M., Cun-Gen, C.: A survey of commonsense knowledge acquisition. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 28(4), 689–719 (2013)
Zellers, R., Bisk, Y., Farhadi, A., Choi, Y.: From recognition to cognition: visual commonsense reasoning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6720–6731 (2019)
Zellers, R., Bisk, Y., Schwartz, R., Choi, Y.: SWAG: a large-scale adversarial dataset for grounded commonsense inference. arXiv preprint arXiv:1808.05326 (2018)
Zellers, R., Holtzman, A., Bisk, Y., Farhadi, A., Choi, Y.: HellaSwag: can a machine really finish your sentence? arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.07830 (2019)
Zhang, H., Liu, Z., Xiong, C., Liu, Z.: Grounded conversation generation as guided traverses in commonsense knowledge graphs. arXiv preprint arXiv:1911.02707 (2019)
 . 2(10) (1982)
. 2(10) (1982)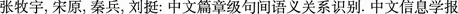 . 27(6), 51–58 (2013)
. 27(6), 51–58 (2013)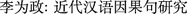 . Ph.D. thesis
. Ph.D. thesis
 (2013)
(2013)
Acknowledgments
The research is supported by Beijing Natural Science Foundation (4192057) and Science Foundation of Beijing Language and Culture University (the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities: 21YJ040005). We thank anonymous reviewers for their helpful feedback and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, H., Liu, P., Yu, D., Zhang, S. (2021). ExperienceGen 1.0: A Text Generation Challenge Which Requires Deduction and Induction Ability. In: Wang, L., Feng, Y., Hong, Y., He, R. (eds) Natural Language Processing and Chinese Computing. NLPCC 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13029. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-88483-3_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-88483-3_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-88482-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-88483-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)


 . 2(10) (1982)
. 2(10) (1982)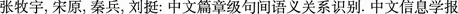 . 27(6), 51–58 (2013)
. 27(6), 51–58 (2013)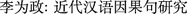 . Ph.D. thesis
. Ph.D. thesis
 (2013)
(2013)