Abstract
A recent case study from AWS by Chong et al. proposes an effective methodology for Bounded Model Checking in industry. In this paper, we report on a followup case study that explores the methodology from the perspective of three research questions: (a) can proof artifacts be used across verification tools; (b) are there bugs in verified code; and (c) can specifications be improved. To study these questions, we port the verification tasks for aws-c-common library to SeaHorn and KLEE. We show the benefits of using compiler semantics and cross-checking specifications with different verification techniques, and call for standardizing proof library extensions to increase specification reuse. The verification tasks discussed are publicly available online.
This research was supported by grants from WHJIL and NSERC CRDPJ 543583-19.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
By continuous verification, we mean verification that is integrated with continuous integration (CI) and is checked during every commit.
- 2.
- 3.
In [7], these are called proof harnesses.
- 4.
- 5.
Similarly, we introduced
 to replace lines 2–5 in Fig. 1.
to replace lines 2–5 in Fig. 1. - 6.
An example is https://github.com/awslabs/aws-c-common/pull/686/commits.
References
Barnett, M., Fähndrich, M., Leino, K.R.M., Müller, P., Schulte, W., Venter, H.: Specification and verification: the Spec# experience. Commun. ACM 54(6), 81–91 (2011)
Bessey, A., et al.: A few billion lines of code later: using static analysis to find bugs in the real world. Commun. ACM 53(2), 66–75 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1145/1646353.1646374
Beyer, D.: Advances in automatic software verification: SV-COMP 2020. In: TACAS 2020. LNCS, vol. 12079, pp. 347–367. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-45237-7_21
Beyer, D., Keremoglu, M.E.: CPAchecker: a tool for configurable software verification. In: Gopalakrishnan, G., Qadeer, S. (eds.) CAV 2011. LNCS, vol. 6806, pp. 184–190. Springer, Heidelberg (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-22110-1_16
Kleine Büning, M., Sinz, C., Faragó, D.: QPR verify: a static analysis tool for embedded software based on bounded model checking. In: Christakis, M., Polikarpova, N., Duggirala, P.S., Schrammel, P. (eds.) NSV/VSTTE -2020. LNCS, vol. 12549, pp. 21–32. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-63618-0_2
Cadar, C., Dunbar, D., Engler, D.R.: KLEE: unassisted and automatic generation of high-coverage tests for complex systems programs. In: 8th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation, OSDI 2008, 8–10 December 2008, San Diego, California, USA, Proceedings, pp. 209–224. USENIX Association (2008)
Chong, N., et al.: Code-level model checking in the software development workflow. In: ICSE-SEIP 2020: 42nd International Conference on Software Engineering, Software Engineering in Practice, Seoul, South Korea, 27 June–19 July 2020, pp. 11–20. ACM (2020)
Chudnov, A., et al.: Continuous formal verification of Amazon s2n. In: Chockler, H., Weissenbacher, G. (eds.) CAV 2018. LNCS, vol. 10982, pp. 430–446. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-96142-2_26
Clarke, E., Kroening, D., Lerda, F.: A tool for checking ANSI-C programs. In: Jensen, K., Podelski, A. (eds.) TACAS 2004. LNCS, vol. 2988, pp. 168–176. Springer, Heidelberg (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-24730-2_15
Cook, B., et al.: Using model checking tools to triage the severity of security bugs in the Xen hypervisor. In: 2020 Formal Methods in Computer Aided Design, FMCAD 2020, Haifa, Israel, 21–24 September 2020, pp. 185–193. IEEE (2020). https://doi.org/10.34727/2020/isbn.978-3-85448-042-6_26
Cook, B., Khazem, K., Kroening, D., Tasiran, S., Tautschnig, M., Tuttle, M.R.: Model checking boot code from AWS data centers. In: Chockler, H., Weissenbacher, G. (eds.) CAV 2018. LNCS, vol. 10982, pp. 467–486. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-96142-2_28
Gadelha, M.Y.R., Monteiro, F.R., Morse, J., Cordeiro, L.C., Fischer, B., Nicole, D.A.: ESBMC 5.0: an industrial-strength C model checker. In: Proceedings of the 33rd ACM/IEEE International Conference on Automated Software Engineering, ASE 2018, Montpellier, France, 3–7 September 2018, pp. 888–891. ACM (2018)
Galois: Crux: A Tool for Improving the Assurance of Software Using Symbolic Testing. https://crux.galois.com/
Gurfinkel, A., Kahsai, T., Komuravelli, A., Navas, J.A.: The seahorn verification framework. In: Kroening, D., Păsăreanu, C.S. (eds.) CAV 2015. LNCS, vol. 9206, pp. 343–361. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-21690-4_20
Ivančić, F., Yang, Z., Ganai, M.K., Gupta, A., Shlyakhter, I., Ashar, P.: F-Soft: software verification platform. In: Etessami, K., Rajamani, S.K. (eds.) CAV 2005. LNCS, vol. 3576, pp. 301–306. Springer, Heidelberg (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/11513988_31
Kim, Y., Kim, M.: SAT-based bounded software model checking for embedded software: a case study. In: 21st Asia-Pacific Software Engineering Conference, APSEC 2014, Jeju, South Korea, 1–4 December 2014. Volume 1: Research Papers, pp. 55–62. IEEE Computer Society (2014)
Kocher, P., et al.: Spectre attacks: exploiting speculative execution (2018). http://meltdownattack.com/
Kupferman, O.: Sanity checks in formal verification. In: Baier, C., Hermanns, H. (eds.) CONCUR 2006. LNCS, vol. 4137, pp. 37–51. Springer, Heidelberg (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/11817949_3
Lal, A., Qadeer, S.: Powering the static driver verifier using Corral. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGSOFT International Symposium on Foundations of Software Engineering, (FSE-22), Hong Kong, China, 16–22 November 2014, pp. 202–212. ACM (2014)
Lattner, C., Adve, V.S.: LLVM: a compilation framework for lifelong program analysis & transformation. In: 2nd IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Code Generation and Optimization (CGO 2004), 20–24 March 2004, San Jose, CA, USA, pp. 75–88. IEEE Computer Society (2004)
Memarian, K., et al.: Into the depths of C: elaborating the de facto standards. In: Proceedings of the 37th ACM SIGPLAN Conference on Programming Language Design and Implementation, PLDI 2016, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 13–17 June 2016, pp. 1–15. ACM (2016)
Moy, Y., Wallenburg, A.: Tokeneer: beyond formal program verification. Embed. Real Time Softw. Syst. 24 (2010)
Osherove, R.: The Art of Unit Testing: With Examples in .Net. Manning PublicationsCo., Shelter Island (2009)
Rakamarić, Z., Emmi, M.: SMACK: decoupling source language details from verifier implementations. In: Biere, A., Bloem, R. (eds.) CAV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8559, pp. 106–113. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-08867-9_7
Serebryany, K.: libFuzzer: a library for coverage-guided fuzz testing. https://llvm.org/docs/LibFuzzer.html
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Priya, S., Zhou, X., Su, Y., Vizel, Y., Bao, Y., Gurfinkel, A. (2021). Verifying Verified Code. In: Hou, Z., Ganesh, V. (eds) Automated Technology for Verification and Analysis. ATVA 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12971. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-88885-5_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-88885-5_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-88884-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-88885-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)


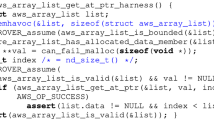


 to replace lines 2–5 in Fig.
to replace lines 2–5 in Fig.