Abstract
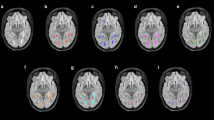
This work proposes and evaluates a semi-automated integrated segmentation system for multiple sclerosis (MS) lesions in fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) brain magnetic resonance images (MRI). The proposed system uses an adaptive two-dimensional (2D) full convolutional neural network (CNN) and is applied to each MRI brain slice separately. The system is based on a U-Net architecture and allows manual error corrections by the user. This task produces continuing additional improvements to the accuracy of the segmentation system, which can be adapted and reconfigured interactively based on the data entered by the user of the system. The system was evaluated based on the ISBI dataset, on 20 MRI brain images acquired from 5 MS subjects who repeated their examinations in four consecutive time points (TP1-TP4). Manual lesion delineations were provided by two different experts. A Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) of 0.76 was achieved using the proposed system which is the highest achieved also by another system. A higher DSC of 0.82 was achieved when the proposed system was evaluated on TP4 images only. A larger dataset will be analyzed in the future, and new measurement metrics will be suggested.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trip, S.A., Miller, D.H.: Imaging in multiple sclerosis. Neurol. Pract. 76(3), 11–19 (2005)
Gross, H.J., Watson, C.: Characteristics, burden of illness, and physical functioning of patients with relapsing-remitting and secondary progressive multiple sclerosis: a cross-sectional US survey. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 13, 1349–1357 (2017)
Loizou, C.P., Petroudi, S., Seimenis, I., Pantziaris, M., et al.: Quantitative texture analysis of brain white matter lesions derived from T2-weighted MR images in MS patients with clinically isolated syndrome. J Neuroradiol 42(2), 99–114 (2015)
Loizou, C.P., Pantzaris, M., Pattichis, C.S.: Normal appearing brain white matter changes in relapsing multiple sclerosis: texture image and classification analysis in serial MRI scans. Magn. Reson. Imaging 73(August), 192–202 (2020)
Wicks, D.A.G., Tofts, P.S., Miller, D.H., de Boulay, G.H., et al.: Volume measurement of multiple sclerosis lesions with magnetic resonance images - a preliminary study. Neuroradiology 34(6), 475–479 (1992)
Polman, C.H., Reingold, S.C., Banwell, B., Clanet, M., et al.: Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 revisions to the McDonald criteria. Ann Neurol 69(2), 292–302 (2011)
Cabezas, M., Oliver, A., Valverde, S., Beltran, B., et al.: BOOST: a supervised approach for multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation. J. Neurosci. Methods 237, 108–117 (2014)
Carass, A., Roy, S., Jog, A., Cuzzocreo, J.L., et al.: Longitudinal multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation: resource and challenge. Neuroimage 148, 77–102 (2017)
Jesson, A., Arbel, T.: Hierarchical MRF and random forest segmentation of MS lesions and healthy tissues in brain MRI (2015)
Maier, O., Handels, H.: MS lesion segmentation in MRI with random forests. In: Proc 2015 Longitudinal Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Segmentation Challenge, pp. 5–6 (2015)
Weng, W., Zhu, X.: INet: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. IEEE Access 9, 16591–16603 (2021)
Brosch, T., Tang, L.Y.W.W., Yoo, Y., Li, D.K.B.B., et al.: Deep 3D convolutional encoder networks with shortcuts for multiscale feature integration applied to multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 35(5), 1229–1239 (2016)
Aslani, S., Dayan, M., Storelli, L., Filippi, M., et al.: Multi-branch convolutional neural network for multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation. Neuroimage 196(March), 1–15 (2019)
Afzal, H.M.R., Luo, S., Ramadan, S., Lechner-Scott, J., et al.: Automatic and robust segmentation of multiple sclerosis lesions with convolutional neural networks. Comput. Mater. Contin. 66(1), 977–991 (2021)
Vaidya, S., Chunduru, A., Muthuganapathy, R., Krishnamurthi, G.: Longitudinal multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation using 3D convolutional neural networks (2015)
Narayana, P.A., Coronado, I., Sujit, S.J., Wolinsky, J.S., Lublin, F.D., Gabr, R.E.: Deep‐learning‐based neural tissue segmentation of MRI in multiple sclerosis: effect of training set size. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 51(5), 1487–1496 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.26959
Tustison, N.J., Avants, B.B., Cook, P.A., Zheng, Y., et al.: N4ITK: improved N3 bias correction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 29(6), 1310–1320 (2010)
Carass, A., Wheeler, M.B., Cuzzocreo, J., Bazin, P., et al.: Image analysis and communications laboratory, electrical and computer engineering. In: Division of Psychiatric Neuroimaging, Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, MedIC, Neuroradiology Division, Radiology and Radiological Science, The Johns Hopkins University Library (London), pp. 656–659 (2007)
Shiee, N., Bazin, P.-L.L., Cuzzocreo, J.L., Ye, C., et al.: Reconstruction of the human cerebral cortex robust to white matter lesions: method and validation. Hum. Brain Mapp 35(7), 3385–3401 (2014)
Rafael C. González, R.E.W.: Digital Image Processing. Prentice Hall (2007)
Wang, J., Perez, L.: The Effectiveness of data augmentation in image classification using deep learning (2017)
Sweeney, E.M., Shinohara, R.T., Reich, D.S., Crainiceanu, C.M., et al.: Automatic lesion incidence estimation and detection in multiple sclerosis using. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 34(1), 68–73 (2013)
Styner, M., Lee, J., Chin, B., Chin, M.S., et al.: 3D Segmentation in the clinic: a grand challenge II: MS lesion segmentation (2008)
Zijdenbos, A.P., Dawant, B.M., Margolin, R.A., Palmer, A.C.: Morphometric analysis of white matter lesions in MR images: method and validation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 13(4), 716–724 (1994)
Molyneux, P.D.: Precision and reliability for measurement of change in MRI lesion volume in multiple sclerosis: a comparison of two computer assisted techniques. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat. 65(1), 42–47 (1998)
Gregoriou C., Loizou, C.P., Georgiou A., Pantzaris M., Pattichis, C.S.: A Three-dimensional reconstruction integrated system for brain multiple sclerosis lesions. In: Proceedings of Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns, 19th International Conference, CAIP 2021, This volume (2021)
Nicolaou A., Loizou, C.P., Pantzaris M., Kakas A., Pattichis, C.S.: Rule extraction in the assessment of brain MRI lesions in multiple sclerosis: preliminary findings. In: Proceedings of Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns, 19th International Conference, CAIP 2021, This volume (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Georgiou, A., Loizou, C.P., Nicolaou, A., Pantzaris, M., Pattichis, C.S. (2021). An Adaptive Semi-automated Integrated System for Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Segmentation in Longitudinal MRI Scans Based on a Convolutional Neural Network. In: Tsapatsoulis, N., Panayides, A., Theocharides, T., Lanitis, A., Pattichis, C., Vento, M. (eds) Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns. CAIP 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13052. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-89128-2_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-89128-2_25
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-89127-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-89128-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)