Abstract
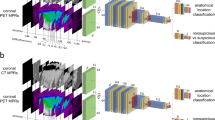
Clinical decision support systems (CDSSs) have gained critical importance in clinical practice and research. Machine learning (ML) and deep learning methods are widely applied in CDSSs to provide diagnostic and prognostic assistance in oncological studies. Taking prostate cancer (PCa) as an example, true segmentation of pathological uptake and prediction of treatment outcome taking advantage of radiomics features extracted from prostate-specific membrane antigen-positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PSMA-PET/CT) were the main objectives of this study. Thus, we aimed at providing an automated clinical decision support tool to assist physicians. To this end, a multi-channel deep neural network inspired by U-Net architecture is trained and fit to automatically segment pathological uptake in multimodal whole-body baseline \(^{68}\)Ga-PSMA-PET/CT scans. Moreover, state-of-the-art ML methods are applied to radiomics features extracted from the predicted U-Net masks to identify responders to \(^{177}\)Lu-PSMA treatment. To investigate the performance of the methods, 2067 pathological hotspots annotated in a retrospective cohort of 100 PCa patients are applied after subdividing to train and test cohorts. For the automated segmentation task, we achieved 0.88 test precision, 0.77 recall, and 0.82 Dice. For predicting responders, we achieved 0.73 area under the curve (AUC), 0.81 sensitivity, and 0.58 specificity on the test cohort. As a result, the facilitated automated decision support tool has shown its potential to serve as an assistant for patient screening for \(^{177}\)Lu-PSMA therapy.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Data and Code Availability
Due to German regulations on medical data availability, we cannot disclose the data, however all the data would be available for review on-site. The in-house developed code is available online at https://gitlab.com/Moazemi/pet-ct-u-net.
References
Ferlay, J., et al.: Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon. https://gco.iarc.fr/today. Accessed 30 June 2021
Jin, S., Li, D., Wang, H., Yin, Y.: Registration of PET and CT images based on multiresolution gradient of mutual information demons algorithm for positioning esophageal cancer patients. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 14(1), 55–61 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1120/jacmp.v14i1.3931
Bundschuh, R.A., et al.: Textural parameters of tumor heterogeneity in 18F-FDG PET/CT for therapy response assessment and prognosis in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 55(6), 891–897 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.113.127340
Bang, J.-I., et al.: Prediction of neoadjuvant radiation chemotherapy response and survival using pretreatment [18F]FDG PET/CT scans in locally advanced rectal cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 43(3), 422–431 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-015-3180-9
Ypsilantis, P.P., et al.: Predicting response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with PET imaging using convolutional neural networks. PLoS One 10(9) (2015). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0137036
Gorgi Zadeh, S., et al.: CNNs enable accurate and fast segmentation of Drusen in optical coherence tomography. In: Cardoso, M.J. (ed.) DLMIA/ML-CDS -2017. LNCS, vol. 10553, pp. 65–73. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67558-9_8
Selvaganesan, K., et al.: Robust, atlas-free, automatic segmentation of brain MRI in health and disease. Heliyon. 5(2), e01226 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01226
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Hatt, M., et al.: The first MICCAI challenge on PET tumor segmentation. Med. Image Ana. 44, 177–195 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2017.12.007. ISSN 1361–8415
Li, L., Zhao, X., Lu, W., Tan, S.: Deep learning for variational multimodality tumor segmentation in PET/CT. Neurocomputing 392, 277–295 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.10.099. ISSN 0925–2312
Liu, L., Cheng, J., Quan, Q., Wu, F.X., Wang, Y. P., Wang, J.: A survey on U-shaped networks in medical image segmentations. Neurocomputing 409, 244–258 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2020.05.070. ISSN 0925–2312
Beukinga, R.J., et al.: Predicting response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in esophageal cancer with textural features derived from pretreatment 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 58(5), 723–729 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.116.180299
Cheng, J.Z., et al.: Computer-aided diagnosis with deep learning architecture: applications to breast lesions in US images and pulmonary nodules in CT scans. Scientific reports, vol. 6 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep24454
Moazemi, S., et al.: Decision-support for treatment with 177Lu-PSMA: machine learning predicts response with high accuracy based on PSMA-PET/CT and clinical parameters. Ann. Transl. Med. 9,9, 818 (2021). https://doi.org/10.21037/atm-20-6446
Parisot, C.: The DICOM standard. Int. J. Cardiac. Imag. 11, 171–177 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01143137
Abadi, M., et al.: TensorFlow: large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous systems. tensorflow.org (2015). https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4724125
Chollet, F.: Keras. GitHub repository (2015). https://github.com/fchollet/keras
Dice, L.R.: Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 26(3), 297–302 (1945). https://doi.org/10.2307/1932409
van Griethuysen, J.J.M., et al.: Computational radiomics system to decode the radiographic phenotype. Cancer Res. 77(21), e104–e107 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0339
Guyon, I., Weston, J., Barnhill, S., Vapnik, V.: Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machines. Mach. Learn. 46, 389–422 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012487302797
Official Company Website for the InterView FUSION: Software. https://www.mediso.de/Interview-fusion.html. Accessed 30 June 2021
Tomar, N.K.: Polyp Segmentation using UNET in TensorFlow 2.0. https://idiotdeveloper.com/polyp-segmentation-using-unet-in-tensorflow-2/. Accessed 30 June 2021
Wright, R.E.: Logistic regression. In: Grimm, L.G., Yarnold, P.R.: (eds.) Reading and Understanding Multivariate Statistics, pp. 217–244. American Psychological Association (1995)
Hearst, M.A., Dumais, S.T., Osuna, E., Platt, J., Scholkopf, B.: Support vector machines. IEEE Intell. Syst. Appl. 13(4), 18–28 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1109/5254.708428
Simm, J., de Abril, I., Sugiyama, M.: Tree-based ensemble multi-task learning method for classification and regression 97(6) (2014). http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=extraTrees
Breiman, L.: Random forests. Mach. Learn. 45, 5–32 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010933404324
Moazemi, S., et al.: Machine learning facilitates hotspot classification in PSMA-PET/CT with nuclear medicine specialist accuracy. Diagnostics (Basel, Switzerland) 10(9), 622 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10090622
Erle, A., Moazemi, S., Lütje, S., Essler, M., Schultz, T., Bundschuh, R.A.: Evaluating a machine learning tool for the classification of pathological uptake in whole-body PSMA-PET-CT scans. Tomography 7, 301–312 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7030027
Vallieres, M., et al.: Radiomics strategies for risk assessment of tumour failure in head-and-neck cancer. Sci. Rep. 7(1), e10117 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10371-5
Moazemi, S., Erle, A., Lütje, S., Gaertner, F.C., Essler, M., Bundschuh, R.A.: Estimating the potential of radiomics features and radiomics signature from pretherapeutic PSMA-PET-CT scans and clinical data for prediction of overall survival when treated with 177Lu-PSMA. Diagnostics 11(2), 186 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020186
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Moazemi, S., Essler, M., Schultz, T., Bundschuh, R.A. (2021). Predicting Treatment Response in Prostate Cancer Patients Based on Multimodal PET/CT for Clinical Decision Support. In: Syeda-Mahmood, T., et al. Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support. ML-CDS 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13050. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-89847-2_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-89847-2_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-89846-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-89847-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)