Abstract
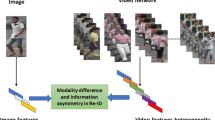
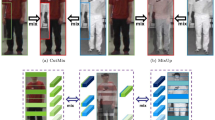
The extensive Re-ID progress in the RGB modality has obtained encouraging performance. However, in practice, the usual surveillance system is automatically switched from visible modality to infrared modality at night. The task of infrared-visible modality-based cross-modal person Re-ID (IV-Re-ID) is required. However, the existing substantial semantic gap between the visible images and the infrared images results in the IV-Re-ID still challenging. In this paper, a Cross-modal Channel Exchange Network (CmCEN) is proposed. In the CmCEN, a channel exchange network is first designed. The magnitude of Batch-Normalization (BN) is calculated to adaptively and dynamically exchange discriminative information between two different modalities sub-networks. Then, a discriminator with adversarial loss is designed to guide the network to learn the similarity distribution in the latent domain space. The evaluation results on two popular benchmark datasets demonstrated the effectiveness of our proposed CmCEN, and it obtained higher performance than state-of-the-art methods on the task of IV-Re-ID. The source code of the proposed CmCEN is available at: https://github.com/SWU-CS-MediaLab/CmCEN.
Supported by organization Southwest University.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Visible thermal person re-identification via dual-constrained top-ranking. In: Twenty-Seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence IJCAI-18 (2018)
Baltrušaitis, T., Ahuja, C., Morency, L.-P.: Multimodal machine learning: a survey and taxonomy. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 41(2), 423–443 (2019)
Chen, S., Wu, S., Wang, L.: Hierarchical semantic interaction-based deep hashing network for cross-modal retrieval. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 7(2), e552 (2020)
Choi, S., Lee, S., Kim, Y., Kim, T., Kim, C.: Hi-CMD: hierarchical cross-modality disentanglement for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2020, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020, pp. 10254–10263. IEEE (2020)
Dai, P., Ji, R., Wang, H., Wu, Q., Huang, Y.: Cross-modality person re-identification with generative adversarial training. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI-18, pp. 677–683. International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence Organization, July 2018
Dat, N., Hong, H., Ki, K., Kang, P.: Person recognition system based on a combination of body images from visible light and thermal cameras. Sensors 17(3), 605 (2017)
Feng, Z.-X., Lai, J., Xie, X.: Learning modality-specific representations for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 579–590 (2020)
Ioffe, S., Szegedy, C.: Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. JMLR.org (2015)
Li, D., Wei, X., Hong, X., Gong, Y.: Infrared-visible cross-modal person re-identification with an x modality. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34, pp. 4610–4617, April 2020
Li, W., Ke, Q., Chen, W., Zhou, Y.: Bridging the distribution gap of visible-infrared person re-identification with modality batch batch normalization (2021)
Liao, S., Yang, H., Zhu, X., Li, S.Z.: Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning. In: 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2015)
Liao, S., Li, S.Z.: Efficient PSD constrained asymmetric metric learning for person re-identification. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 3685–3693 (2015)
Lu, Y., et al.: Cross-modality person re-identification with shared-specific feature transfer. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR2020, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020, pp. 13376–13386. IEEE (2020)
Mao, X., Li, Q., Xie, H.: AlignGAN: learning to align cross-domain images with conditional generative adversarial networks (2017)
Peng, Y., Qi, J., Yuan, Y.: CM-GANs: cross-modal generative adversarial networks for common representation learning. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 15(1), 1–24 (2017)
Shi, Z., Hospedales, T.M., Tao, X.: Transferring a semantic representation for person re-identification and search. IEEE (2015)
Wang, G., Yuan, Y., Chen, X., Li, J., Zhou, X.: Learning discriminative features with multiple granularities for person re-identification. ACM (2018)
Wang, G., Zhang, T., Cheng, J., Liu, S., Yang, Y., Hou, Z.: RGB-infrared cross-modality person re-identification via joint pixel and feature alignment. In2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2019, Seoul, Korea (South), 27 October–2 November 2019, pp. 3622–3631. IEEE (2019)
Wang, X., Zou, X., Bakker, E.M., Wu, S.: Self-constraining and attention-based hashing network for bit-scalable cross-modal retrieval. Neurocomputing 400, 255–271 (2020)
Wang, Z., Wang, Z., Zheng, Y., Chuang, Y.Y., Satoh, S.: Learning to reduce dual-level discrepancy for infrared-visible person re-identification. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2019)
Wang, Z., Wang, Z., Zheng, Y., Chuang, Y.-Y., Satoh, S.: Learning to reduce dual-level discrepancy for infrared-visible person re-identification. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2019, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019, pp. 618–626. Computer Vision Foundation/IEEE (2019)
Wu, A., Zheng, W.-S., Yu, H.-X., Gong, S., Lai, J.: RGB-infrared cross-modality person re-identification. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 5390–5399 (2017)
Wu, S., Oerlemans, A., Bakker, E.M., Lew, M.S.: Deep binary codes for large scale image retrieval. Neurocomputing 257(sep.27), 5–15 (2017)
Xzab, D., Xw, A., Emb, C., Song, W.A.: Multi-label semantics preserving based deep cross-modal hashing. Signal Process.: Image Commun. 93, 116131 (2021)
Ye, J., Xin, L., Zhe, L., Wang, J.Z.: Rethinking the smaller-norm-less-informative assumption in channel pruning of convolution layers (2018)
Ye, M., Lan, X., Leng, Q.: Modality-aware collaborative learning for visible thermal person re-identification. In: Amsaleg, L., et al. (eds.) Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, MM 2019, Nice, France, 21–25 October 2019, pp. 347–355. ACM (2019)
Ye, M., Shen, J., J. Crandall, D., Shao, L., Luo, J.: Dynamic dual-attentive aggregation learning for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12362, pp. 229–247. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58520-4_14
Ye, M., Shen, J., Shao, L.: Visible-infrared person re-identification via homogeneous augmented tri-modal learning. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 16, 728–739 (2021)
Chen, Y.-C., Zhu, X., Zheng, W.-S., Lai, J.-H.: Person re-identification by camera correlation aware feature augmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40, 392–408 (2017)
Zheng, L., Shen, L., Tian, L., Wang, S., Wang, J., Tian, Q.: Scalable personre-identification: a benchmark. IEEE (2016)
Zhuang, L., Li, J., Shen, Z., Gao, H., Zhang, C.: Learning efficient convolutional networks through network slimming. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2017)
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61806168), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (SWU117059), and Venture and Innovation Support Program for Chongqing Overseas Returnees (CX2018075).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xu, X., Wu, S., Liu, S., Xiao, G. (2021). Cross-Modal Based Person Re-identification via Channel Exchange and Adversarial Learning. In: Mantoro, T., Lee, M., Ayu, M.A., Wong, K.W., Hidayanto, A.N. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13108. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92185-9_41
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92185-9_41
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-92184-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-92185-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)