Abstract
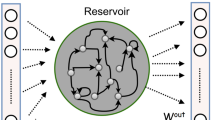
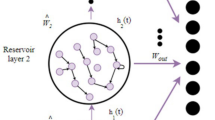
Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) has become a popular research topic due to having a significant role in many practical applications and is considered a key effort in Human-Computer Interaction (HCI). Previous works in this field have mostly focused on global features or time series feature representation with deep learning models. However, the main focus of this work is to design a simple model for SER by adopting multivariate time series feature representation. This work also used the Echo State Network (ESN) including parallel reservoir layers as a special case of the Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) and applied Principal Component Analysis (PCA) to reduce the high dimension output from reservoir layers. The late grouped fusion has been applied to capture additional information independently of the two reservoirs. Additionally, hyperparameters have been optimized by using the Bayesian approach. The high performance of the proposed SER model is proved when adopting the speaker-independent experiments on the SAVEE dataset and FAU Aibo emotion Corpus. The experimental results show that the designed model is superior to the state-of-the-art results.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Talabani, A., Sellahewa, H., Jassim, S.: Excitation source and low level descriptor features fusion for emotion recognition using SVM and ANN. In: 2013 5th Computer Science and Electronic Engineering Conference (CEEC), pp. 156–161 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/CEEC.2013.6659464
Al-Talabani, A., Sellahewa, H., Jassim, S.A.: Emotion recognition from speech: tools and challenges. In: Agaian, S.S., Jassim, S.A., Du, E.Y. (eds.) Mobile Multimedia/Image Processing, Security, and Applications 2015, vol. 9497, pp. 193–200. International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE (2015). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2191623
Bianchi, F.M., Scardapane, S., Løkse, S., Jenssen, R.: Bidirectional deep-readout echo state networks. In: ESANN (2018)
Bianchi, F.M., Livi, L., Alippi, C.: Investigating echo-state networks dynamics by means of recurrence analysis. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 29(2), 427–439 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2630802
Bianchi, F.M., Scardapane, S., Løkse, S., Jenssen, R.: Reservoir computing approaches for representation and classification of multivariate time series. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 32(5), 2169–2179 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3001377
Cerina, L., Santambrogio, M.D., Franco, G., Gallicchio, C., Micheli, A.: EchoBay: design and optimization of echo state networks under memory and time constraints. ACM Trans. Archit. Code Optim. 17(3), 1–24 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1145/3404993
Chen, L., Mao, X., Xue, Y., Cheng, L.L.: Speech emotion recognition: features and classification models. Digit. Signal Process. 22(6), 1154–1160 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsp.2012.05.007. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1051200412001133
Daneshfar, F., Kabudian, S.J., Neekabadi, A.: Speech emotion recognition using hybrid spectral-prosodic features of speech signal/glottal waveform, metaheuristic-based dimensionality reduction, and Gaussian elliptical basis function network classifier. Appl. Acoust. 166, 107360 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2020.107360. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0003682X1931117X
Deb, S., Dandapat, S.: Multiscale amplitude feature and significance of enhanced vocal tract information for emotion classification. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 49(3), 802–815 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2017.2787717
Degottex, G., Kane, J., Drugman, T., Raitio, T., Scherer, S.: COVAREP - a collaborative voice analysis repository for speech technologies. In: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 960–964 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2014.6853739
Eyben, F., Wöllmer, M., Schuller, B.: OpenSMILE: the munich versatile and fast open-source audio feature extractor. In: Proceedings of the 18th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, MM 2010, pp. 1459–1462. Association for Computing Machinery, New York (2010). https://doi.org/10.1145/1873951.1874246
Gallicchio, C., Micheli, A.: A preliminary application of echo state networks to emotion recognition (2014)
Gallicchio, C., Micheli, A.: Reservoir topology in deep echo state networks. In: Tetko, I.V., Kůrková, V., Karpov, P., Theis, F. (eds.) ICANN 2019. LNCS, vol. 11731, pp. 62–75. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-30493-5_6
Haq, S., Jackson, P.: Multimodal emotion recognition. In: Machine Audition: Principles, Algorithms and Systems, pp. 398–423. IGI Global, Hershey, August 2010
Jaeger, H., Haas, H.: Harnessing nonlinearity: predicting chaotic systems and saving energy in wireless communication. Science 304(5667), 78–80 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1091277. https://science.sciencemag.org/content/304/5667/78
Kathiresan, T., Dellwo, V.: Cepstral derivatives in MFCCS for emotion recognition. In: 2019 IEEE 4th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing (ICSIP), pp. 56–60 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/SIPROCESS.2019.8868573
Lee, J., Tashev, I.: High-level feature representation using recurrent neural network for speech emotion recognition. In: INTERSPEECH (2015)
Lemaître, G., Nogueira, F., Aridas, C.K.: Imbalanced-learn: a python toolbox to tackle the curse of imbalanced datasets in machine learning. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 18(17), 1–5 (2017). http://jmlr.org/papers/v18/16-365.html
Lukoševičius, M.: A practical guide to applying echo state networks. In: Montavon, G., Orr, G.B., Müller, K.-R. (eds.) Neural Networks: Tricks of the Trade. LNCS, vol. 7700, pp. 659–686. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-35289-8_36
Lukoševičius, M., Jaeger, H.: Reservoir computing approaches to recurrent neural network training. Comput. Sci. Rev. 3(3), 127–149 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosrev.2009.03.005. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1574013709000173
Maat, J.R., Gianniotis, N., Protopapas, P.: Efficient optimization of echo state networks for time series datasets. In: 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1–7 (2018)
Mao, Q., Dong, M., Huang, Z., Zhan, Y.: Learning salient features for speech emotion recognition using convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 16(8), 2203–2213 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2014.2360798
Mustaqeem, Sajjad, M., Kwon, S.: Clustering-based speech emotion recognition by incorporating learned features and deep BiLSTM. IEEE Access 8, 79861–79875 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2990405
Nogueira, F.: Bayesian optimization: open source constrained global optimization tool for Python (2014). https://github.com/fmfn/BayesianOptimization
Özseven, T.: A novel feature selection method for speech emotion recognition. Appl. Acoust. 146, 320–326 (2019)
Saleh, Q., Merkel, C., Kudithipudi, D., Wysocki, B.: Memristive computational architecture of an echo state network for real-time speech-emotion recognition. In: 2015 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence for Security and Defense Applications (CISDA), pp. 1–5 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/CISDA.2015.7208624
Scherer, S., Oubbati, M., Schwenker, F., Palm, G.: Real-time emotion recognition using echo state networks. In: André, E., Dybkjær, L., Minker, W., Neumann, H., Pieraccini, R., Weber, M. (eds.) PIT 2008. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 5078, pp. 200–204. Springer, Heidelberg (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-69369-7_22
Schuller, B., Steidl, S., Batliner, A.: The interspeech 2009 emotion challenge. In: Tenth Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (2009)
Snoek, J., Larochelle, H., Adams, R.P.: Practical Bayesian optimization of machine learning algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 2, NIPS 2012, pp. 2951–2959. Curran Associates Inc., Red Hook (2012)
Steidl, S.: Automatic Classification of Emotion Related User States in Spontaneous Children’s Speech. Logos-Verlag (2009)
Triantafyllopoulos, A., Liu, S., Schuller, B.W.: Deep speaker conditioning for speech emotion recognition. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), pp. 1–6 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICME51207.2021.9428217
Wen, G., Li, H., Huang, J., Li, D., Xun, E.: Random deep belief networks for recognizing emotions from speech signals. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2017 (2017)
Wu, Q., Fokoue, E., Kudithipudi, D.: On the statistical challenges of echo state networks and some potential remedies (2018)
Zhao, Z., et al.: Exploring deep spectrum representations via attention-based recurrent and convolutional neural networks for speech emotion recognition. IEEE Access 7, 97515–97525 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2928625
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Covid-19 Special Research Grant under Project CSRG008-2020ST, Impact Oriented Interdisciplinary Research Grant Programme (IIRG), IIRG002C-19HWB from University of Malaya, and the AUA-UAEU Joint Research Grant 31R188.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ibrahim, H., Loo, C.K., Alnajjar, F. (2021). Grouped Echo State Network with Late Fusion for Speech Emotion Recognition. In: Mantoro, T., Lee, M., Ayu, M.A., Wong, K.W., Hidayanto, A.N. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13110. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92238-2_36
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92238-2_36
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-92237-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-92238-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)