Abstract
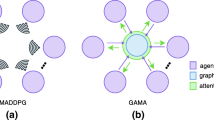
The collaboration between agents has gradually become an important topic in multi-agent systems. The key is how to efficiently solve the credit assignment problems. This paper introduces MGAN for collaborative multi-agent reinforcement learning, a new algorithm that combines graph convolutional networks and value-decomposition methods. MGAN learns the representation of agents from different perspectives through multiple graph networks, and realizes the proper allocation of attention between all agents. We show the amazing ability of the graph network in representation learning by visualizing the output of the graph network, and therefore improve interpretability for the actions of each agent in the multi-agent system.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Böhmer, W., Kurin, V., Whiteson, S.: Deep coordination graphs. arXiv arXiv:1910.00091 (2020)
Comaniciu, D., Meer, P.: Mean shift: a robust approach toward feature space analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 24, 603–619 (2002)
Defferrard, M., Bresson, X., Vandergheynst, P.: Convolutional neural networks on graphs with fast localized spectral filtering. In: NIPS (2016)
Foerster, J.N., Farquhar, G., Afouras, T., Nardelli, N., Whiteson, S.: Counterfactual multi-agent policy gradients. In: AAAI (2018)
Ha, D., Dai, A.M., Le, Q.V.: Hypernetworks. arXiv arXiv:1609.09106 (2017)
Hamilton, W.L., Ying, Z., Leskovec, J.: Inductive representation learning on large graphs. In: NIPS (2017)
Hausknecht, M.J., Stone, P.: Deep recurrent Q-learning for partially observable MDPs. In: AAAI Fall Symposia (2015)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 770–778 (2016)
Lowe, R., Wu, Y., Tamar, A., Harb, J., Abbeel, P., Mordatch, I.: Multi-agent actor-critic for mixed cooperative-competitive environments. In: NIPS (2017)
Maaten, L.V.D., Hinton, G.E.: Visualizing data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 9, 2579–2605 (2008)
Oliehoek, F.A., Amato, C.: A Concise Introduction to Decentralized POMDPs. SpringerBriefs in Intelligent Systems. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-28929-8
Peng, P., et al.: Multiagent Bidirectionally-Coordinated Nets: emergence of human-level coordination in learning to play StarCraft combat games. arXiv: Artificial Intelligence (2017)
Perozzi, B., Al-Rfou, R., Skiena, S.: DeepWalk: online learning of social representations. In: Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (2014)
Rashid, T., Samvelyan, M., Witt, C.S., Farquhar, G., Foerster, J.N., Whiteson, S.: QMIX: monotonic value function factorisation for deep multi-agent reinforcement learning. arXiv arXiv:1803.11485 (2018)
Samvelyan, M., et al.: The StarCraft multi-agent challenge. arXiv arXiv:1902.04043 (2019)
Son, K., Kim, D., Kang, W., Hostallero, D., Yi, Y.: QTRAN: learning to factorize with transformation for cooperative multi-agent reinforcement learning. arXiv arXiv:1905.05408 (2019)
Sukhbaatar, S., Szlam, A., Fergus, R.: Learning multiagent communication with backpropagation. In: NIPS (2016)
Sunehag, P., et al.: Value-decomposition networks for cooperative multi-agent learning. arXiv arXiv:1706.05296 (2018)
Sutton, R., Barto, A.: Reinforcement learning: an introduction. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 16, 285–286 (2005)
Tampuu, A., et al.: Multiagent cooperation and competition with deep reinforcement learning. PLOS ONE 12, e0172395 (2017)
Thekumparampil, K.K., Wang, C., Oh, S., Li, L.: Attention-based graph neural network for semi-supervised learning. arXiv arXiv:1803.03735 (2018)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. arXiv arXiv:1706.03762 (2017)
Velickovic, P., Cucurull, G., Casanova, A., Romero, A., Liò, P., Bengio, Y.: Graph attention networks. arXiv arXiv:1710.10903 (2018)
Xu, K., Hu, W., Leskovec, J., Jegelka, S.: How powerful are graph neural networks? arXiv arXiv:1810.00826 (2019)
Xu, K., Li, C., Tian, Y., Sonobe, T., Kawarabayashi, K., Jegelka, S.: Representation learning on graphs with jumping knowledge networks. In: ICML (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xu, Z., Zhang, B., Bai, Y., Li, D., Fan, G. (2021). Learning to Coordinate via Multiple Graph Neural Networks. In: Mantoro, T., Lee, M., Ayu, M.A., Wong, K.W., Hidayanto, A.N. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13110. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92238-2_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92238-2_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-92237-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-92238-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)