Abstract
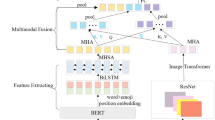
Emojis are widely used in online social networks to express emotions, attitudes, and opinions. As emotional-oriented characters, emojis can be modeled as important features of emotions towards the recipient or subject for sentiment analysis. However, existing methods mainly take emojis as heuristic information that fails to resolve the problem of ambiguity noise. Recent researches have utilized emojis as an independent input to classify text sentiment but they ignore the emotional impact of the interaction between text and emojis. It results that the emotional semantics of emojis cannot be fully explored. In this paper, we propose an emoji-based co-attention network that learns the mutual emotional semantics between text and emojis on microblogs. Our model adopts the co-attention mechanism based on bidirectional long short-term memory incorporating the text and emojis, and integrates a squeeze-and-excitation block in a convolutional neural network classifier to increase its sensitivity to emotional semantic features. Experimental results show that the proposed method can significantly outperform several baselines for sentiment analysis on short texts of social media.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cramer, H., de Juan, P., Tetreault, J.: Sender-intended functions of emojis in us messaging. In: Proceeding of MobileHCI, pp. 504–509. ACM (2016)
Davidov, D., Tsur, O., Rappoport, A.: Enhanced sentiment learning using twitter hashtags and smileys. In: Proceeding of CICLing, pp. 241–249. ACL (2010)
Go, A., Bhayani, R., Huang, L.: Twitter sentiment classification using distant supervision. CS224150 (2009)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Albanie, S., Sun, G., Wu, E.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. IEEE TPAMI 42(8), 2011–2023 (2020)
Hu, T., Guo, H., Sun, H., Thi Nguyen, T.v., Luo, J.: Spice up your chat: the intentions and sentiment effects of using emoji. In: ICWSM, pp. 102–111 (2017)
Hu, X., Tang, J., Gao, H., Liu, H.: Unsupervised sentiment analysis with emotional signals. In: Proceeding of WWW, pp. 607–618. ACM (2013)
Jiang, F., Cui, A., Liu, Y., Zhang, M., Ma, S.: Every term has sentiment: learning from emoticon evidences for chinese microblog sentiment analysis. In: Zhou, G., Li, J., Zhao, D., Feng, Y. (eds.) NLPCC 2013. CCIS, vol. 400, pp. 224–235. Springer, Heidelberg (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-41644-6_21
Kim, Y.: Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification. In: Proceedings of EMNLP, pp. 1746–1751. ACL (2014)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. In: The 3rd International Conference for Learning Representations (2014)
Korenek, P., Simko, M.: Sentiment analysis on microblog utilizing appraisal theory. In: World Wide Web, pp. 847–867 (2014)
Lai, S., Xu, L., Liu, K., Zhao, J.: Recurrent convolutional neural networks for text classification. In: Proceeding of AAAI, pp. 2267–2273 (2015)
Li, M., Ch’ng, E., Chong, A., See, S.: Multi-class twitter sentiment classification with emojis. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 118 (2018)
Lou, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, F., Qian, T., Ji, D.: Emoji-based sentiment analysis using attention networks. In: Proceeding of TALLIP (2020)
Pang, B., Lee, L.: Opinion mining and sentiment analysis. Found. Trends Inf. Retr., 1–125 (2008)
Ptacek, T., Habernal, I., Hong, J.: Sarcasm detection on Czech and English twitter. In: Proceedings of COLING, pp. 213–223 (2014)
dos Santos, C., Gatti, M.: Deep convolutional neural networks for sentiment analysis of short texts. In: Proceeding of COLING, pp. 69–78. ACL (2014)
Socher, R., et al.: Recursive deep models for semantic compositionality over a sentiment treebank. In: EMNLP, pp. 1631–1642 (2013)
Walther, J.B., D’Addario, K.P.: The impacts of emoticons on message interpretation in computer-mediated communication. In: SSCR, pp. 324–347 (2001)
Yao, L., Mao, C., Luo, Y.: Graph convolutional networks for text classification. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2019)
Zhao, J., Dong, L., Wu, J., Xu, K.: Moodlens: an emoticon-based sentiment analysis system for Chinese tweets. In: Proceeding of KDD, pp. 1528–1531. ACM (2012)
Zhou, P., et al.: Attention-based bidirectional long short-term memory networks for relation classification. In: Proceedings of ACL, pp. 207–212. ACL (2016)
Acknowledgement
The research is supported in part by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Grant No. XDC02060400.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yuan, X., Hu, J., Zhang, X., Lv, H., Liu, H. (2021). Emoji-Based Co-Attention Network for Microblog Sentiment Analysis. In: Mantoro, T., Lee, M., Ayu, M.A., Wong, K.W., Hidayanto, A.N. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2021. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1516. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92307-5_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92307-5_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-92306-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-92307-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)