Abstract
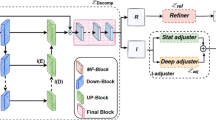
Images captured in low light conditions usually suffer from color distortion and poor visibility. Although remarkable success has been made, existing methods are still unstable when applied to various scenes. Therefore, we propose a robust deep multi-scale network for underexposure image correction. We construct Gaussian pyramid to explore the complementary and redundant information in different scales, and further extract, fuse illuminations with progressive fusion strategy across scales. This process not only boosts the end-to-end training but also promotes the cooperative representation. Moreover, fine-fused illuminations in multi-scales bridge the gap between the restoration knowledge of underexposure images and the perceptual quality preference to normal light images. Extensive experiments with advanced methods and ablation studies demonstrate our method outperforms others under a variety of metrics in terms of qualitative and quantitative comparison.
This work was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grant 61906029, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shen, L., Yue, Z., Feng, F., et al.: MSR-net: low-light image enhancement using deep convolutional network. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.02488 (2017)
Guo, C., Li, C., Guo, J., et al.: Zero-reference deep curve estimation for low-light image enhancement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1780–1789 (2020)
Wang, R., Zhang, Q., Fu, C.W., et al.: Underexposed photo enhancement using deep illumination estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6849–6857 (2019)
Pizer, S.M., Amburn, E.P., Austin, J.D., et al.: Adaptive histogram equalization and its variations. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 39(3), 355–368 (1987)
Ibrahim, H., Kong, N.S.P.: Brightness preserving dynamic histogram equalization for image contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 53(4), 1752–1758 (2007)
Coltuc, D., Bolon, P., Chassery, J.M.: Exact histogram specification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(5), 1143–1152 (2006)
Pisano, E.D., Zong, S., Hemminger, B.M., et al.: Contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization image processing to improve the detection of simulated spiculations in dense mammograms. J. Digit. Imaging 11(4), 193 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03178082
Land, E.H.: The retinex theory of color vision. Sci. Am. 237(6), 108–129 (1977)
Jobson, D.J., Rahman, Z., Woodell, G.A.: Properties and performance of a center/surround retinex. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 6(3), 451–462 (1997)
Fu, X., Zeng, D., Huang, Y., et al.: A weighted variational model for simultaneous reflectance and illumination estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2782–2790 (2016)
Cai, B., Xu, X., Guo, K., et al.: A joint intrinsic-extrinsic prior model for retinex. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4000–4009 (2017)
Lore, K.G., Akintayo, A., Sarkar, S.: LLNet: a deep autoencoder approach to natural low-light image enhancement. Pattern Recogn. 61, 650–662 (2017)
Yan, Z., Zhang, H., Wang, B., et al.: Automatic photo adjustment using deep neural networks. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 35(2), 1–15 (2016)
Gharbi, M., Chen, J., Barron, J.T., et al.: Deep bilateral learning for real-time image enhancement. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 36(4), 1–12 (2017)
Cai, J., Gu, S., Zhang, L.: Learning a deep single image contrast enhancer from multi-exposure images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 27(4), 2049–2062 (2018)
Jiang, Y., Gong, X., Liu, D., et al.: EnlightenGAN: deep light enhancement without paired supervision. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 2340–2349 (2021)
Wang, Z., Bovik, A.C., Sheikh, H.R., et al.: Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13(4), 600–612 (2004)
Bychkovsky, V., Paris, S., Chan, E., et al.: Learning photographic global tonal adjustment with a database of input/output image pairs. In: CVPR 2011, pp. 97–104. IEEE (2011)
Li, C., Guo, J., Porikli, F., et al.: LightenNet: a convolutional neural network for weakly illuminated image enhancement. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 104, 15–22 (2018)
Zhang, Y., Zhang, J., Guo, X.: Kindling the darkness: a practical low-light image enhancer. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 1632–1640 (2019)
Guo, X., Li, Y., Ling, H.: LIME: low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(2), 982–993 (2016)
Ma, K., Zeng, K., Wang, Z.: Perceptual quality assessment for multi-exposure image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 24(11), 3345–3356 (2015)
Wang, S., Zheng, J., Hu, H.M., et al.: Naturalness preserved enhancement algorithm for non-uniform illumination images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 22(9), 3538–3548 (2013)
Mittal, A., Soundararajan, R., Bovik, A.C.: Making a “completely blind’’ image quality analyzer. IEEE Sig. Process. Lett. 20(3), 209–212 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhong, W., Zhang, X., Ma, L., Liu, R., Fan, X., Luo, Z. (2021). Learning Multi-scale Underexposure Image Correction. In: Fang, L., Chen, Y., Zhai, G., Wang, J., Wang, R., Dong, W. (eds) Artificial Intelligence. CICAI 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13069. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-93046-2_22
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-93046-2_22
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-93045-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-93046-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)