Abstract
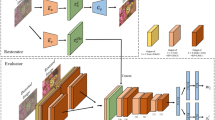
Image restoration has been receiving extensive attention owing to its widespread applications, and numerous restoration algorithms have been proposed. However, how to accurately evaluate the performances of image restoration algorithms remains largely unexplored. Current image restoration quality metrics make predictions solely based on the restored images without making full use of the original degraded image, which we believe also provides valuable information. For image restoration quality assessment, accurate measurement of the perceptual discrepancy between the degraded image and the restored images is crucial. Motivated by this, this paper presents a perceptual discrepancy learning (PDL) framework for image restoration quality assessment, where the original degraded image is utilized as reduced-reference to achieve reliable predictions. First, a large-scale paired image quality database with weakly annotated labels is built, based on which a prior quality model is trained using Siamese network. Then, based on the prior model, the degraded-restored image pairs (DRIPs) are further used to train the perceptual discrepancy prediction model in an end-to-end manner. Finally, the performances of image restoration algorithms can be obtained based on the predicted relative perceptual discrepancy (RPD) values directly. Experimental results on four image restoration quality databases demonstrate the advantage of the proposed metric over the state-of-the-arts.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, K., Zuo, W.M., Chen, Y.J., Meng, D.Y., Zhang, L.: Beyond a Gaussian denoiser: Residual learning of deep CNN for image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(7), 3142–3155 (2017)
Pan, J.S., Sun, D.Q., Pfister, H., Yang, M.-H.: Deblurring images via dark channel prior. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40(10), 2315–2328 (2018)
Dong, C., Loy, C.C., He, K.M., Tang, X.O.: Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 38(2), 295–307 (2016)
He, K.M., Sun, J., Tang, X.O.: Single image haze removal using dark channel prior. Int. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 33(12), 1956–1963 (2009)
Lai, W.S., Huang, J.B., Hu, Z., Ahuja, N., Yang, M.-H.: A comparative study for single image blind deblurring. In: International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1701–1709. Las Vegas, USA (2016)
Sheikh, H.R., Sabir, M.F., Bovik, A.C.: A statistical evaluation of recent full reference image quality assessment algorithms. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(11), 3440–3451 (2006)
Larson, E.C., Chandler, D.M.: Most apparent distortion: full reference image quality assessment and the role of strategy. J. Electron. Imaging 19(1), 1–21 (2010)
Ponomarenko, N., et al.: Color image database TID2013: peculiarities and preliminary results. In: 4th European Workshop Visual Information Processing (EUVIP), pp. 106–111. IEEE, Paris, France (2013)
Hu, B., Li, L.D., Wu, J.J., Qian, J.S.: Subjective and objective quality assessment for image restoration: a critical survey. Signal Process. Image Commun. 85, 1–19 (2020)
Zhu, X., Milanfar, P.: Automatic parameter selection for denoising algorithms using a no-reference measure of image content. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 19(12), 3116–3132 (2010)
Liu, Y.M., Wang, J., Cho, S., Finkelstein, A., Rusinkiewicz, S.: A no-reference metric for evaluating the quality of motion deblurring. ACM Trans. Graph. 32(6), 1–12 (2013)
Hu, B., Li, L.D., Qian, J.S.: Perceptual quality evaluation for motion deblurring. IET Comput. Vis. 12(6), 796–805 (2018)
Hautiere, N., Tarel, J.-P., Aubert, D., Dumont, E.: Blind contrast enhancement assessment by gradient ratioing at visible edges. J. Image Anal. Stereol. 27(2), 87–95 (2008)
Min, X.K., Zhai, G.T., Gu, K., et al.: Quality evaluation of image dehazing methods using synthetic hazy images. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 21(9), 2319–2333 (2019)
Kim, J., Lee, S.: Fully deep blind image quality predictor. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Sign. Process. 11(1), 206–220 (2017)
Wang, Z., Bovik, A.C., Sheikh, H.R., Simoncelli, E.P.: Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13(4), 600–612 (2004)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for largescale image recognition. In: International Conference on Learning Representations. San Diego, CA (2015)
Bradley, R.A., Terry, M.E.: Rank analysis of incomplete block designs the method of paired comparisons. Biometrika 39(3–4), 324–345 (1952)
Ma, K.D., Liu, W.T., Wang, Z.: Perceptual evaluation of single image dehazing algorithms. In: IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, pp. 3600–3604. IEEE, Quebec City, Canada (2015)
Moorthy, A.K., Bovik, A.C.: A two-step framework for constructing blind image quality indices. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 17(5), 513–516 (2010)
Zhang, Y., Chandler, D.M.: “No-reference image quality assessment based on log derivative statistics of natural scenes. J. Electr. Imag. 22(4), 1–11 (2013)
Moorthy, A.K., Bovik, A.C.: Blind image quality assessment: from natural scene statistics to perceptual quality. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 20(12), 3350–3364 (2011)
Saad, M.A., Bovik, A.C.: Blind image quality assessment: a natural scene statistics approach in the DCT domain. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21(8), 3339–3352 (2012)
Mittal, A., Moorthy, A.K., Bovik, A.C.: No-reference image quality assessment in the spatial domain. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21(12), 4695–4708 (2012)
Gu, K., Zhai, G.T., Yang, X.K., Zhang, W.J.: Using free energy principle for blind image quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 17(1), 50–63 (2015)
Ye, P., Kumar, J., Kang, L., Doermann, D.: Unsupervised feature learning framework for no-reference image quality assessment. In: Int. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (CVPR), pp. 1098–1105. IEEE, Providence, USA (2012)
Xue, W.F., Mou, X.Q., Zhang, L., Bovik, A.C., Feng, X.C.: Blind image quality assessment using joint statistics of gradient magnitude and laplacian features. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 23(11), 4850–4862 (2014)
Gu, K., et al.: FISBLIM: a five-step blind metric for quality assessment of multiply distorted images. In: IEEE Workshop on Signal Processing Systems (SiPS 2013), pp. 241–246. IEEE, Taipei City, Taiwan, China (2013)
Gu, K., Zhai, G.T., Yang, X.K., Zhang, W.J.: Hybrid no-reference quality metric for singly and multiply distorted images. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 60(3), 555–567 (2014)
Li, Q.H., Lin, W.S., Fang, Y.M.: No-reference quality assessment for multiply-distorted images in gradient domain. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 23(4), 541–545 (2016)
Hu, B., Li, L.D., Liu, H.T., Lin, W.S., Qian, J.S.: Pairwise-comparison-based rank learning for benchmarking image restoration algorithms. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 21(8), 2042–2056 (2019)
Kim, J., Lee, S.: Deep learning of human visual sensitivity in image quality assessment framework. In: International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1969–1977. IEEE, Honolulu, USA (2017)
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 61771473, 61991451 and 61379143, Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province under Grant BK20181354, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grant JBF211902, the Key Project of Shaanxi Provincial Department of Education under Grant 20JY024, the Science and Technology Plan of Xian under Grant 20191122015KYPT011JC013, and the Six Talent Peaks High- level Talents in Jiangsu Province under Grant XYDXX-063.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Li, L., Hu, B., Huang, Y., Zhu, H. (2021). Reduced-reference Perceptual Discrepancy Learning for Image Restoration Quality Assessment. In: Fang, L., Chen, Y., Zhai, G., Wang, J., Wang, R., Dong, W. (eds) Artificial Intelligence. CICAI 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13069. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-93046-2_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-93046-2_31
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-93045-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-93046-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)