Abstract
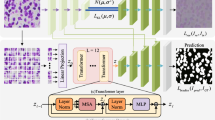
Medical image segmentation based on the deep learning codec network achieves highly accurate segmentation. However, the structure of the tandem decoder at different scales makes it difficult for the model to segment detailed regions well. Although such detailed areas are small, they are very important in clinical medicine, and therefore one current challenge is to improve detail segmentation. In this paper, we propose a method called the MPNet (Multi-scale Parallel Codec Net), which contains a structure with parallel encoder-decoder routes that respectively comprise a scale transformer and convolution. They extract characteristics at various scales, and the feature maps of each scale are fused through an intersection module to predict the output. The parallel multi-scale routes increase the width of the model, and thus a deep architecture is not needed to obtain precise segmentation. These shallow paths independently learn semantic features at different scales and make the gradient back-propagation faster and more stable. Moreover, a new time-varying loss function is also proposed to speed up network convergence further. Experimental results on four public datasets show that the proposed method performs better than some state-of-the-art methods.
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62027827, 62032022, 61929104, 61972375, 61671426), the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (4182071) and Scientific Research Program of Beijing Municipal Education Commission (KZ201911417048).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, L.C., Papandreou, G., Kokkinos, I., Murphy, K., Yuille, A.L.: DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40(4), 834–848 (2017)
Chen, L.C., Zhu, Y., Papandreou, G., Schroff, F., Adam, H.: Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 801–818 (2018)
Drozdzal, M., Vorontsov, E., Chartrand, G., Kadoury, S., Pal, C.: The importance of skip connections in biomedical image segmentation. In: Carneiro, G., et al. (eds.) LABELS/DLMIA -2016. LNCS, vol. 10008, pp. 179–187. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46976-8_19
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 770–778 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
Hesamian, M.H., Jia, W., He, X., Kennedy, P.: Deep learning techniques for medical image segmentation: achievements and challenges. J. Digit. Imaging 32(4), 582–596 (2019)
Isensee, F., et al.: nnU-Net: self-adapting framework for U-Net-based medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.10486 (2018)
Jia, Y., Huang, C., Darrell, T.: Beyond spatial pyramids: receptive field learning for pooled image features. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3370–3377. IEEE (2012)
Kavur, A.E., Selver, M.A., Dicle, O., Barış, M., Gezer, N.S.: CHAOS - combined (CT-MR) healthy abdominal organ segmentation challenge data, April 2019. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3362844
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 60(6), 84–90 (2017)
Lin, G., Milan, A., Shen, C., Reid, I.: RefineNet: multi-path refinement networks for high-resolution semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1925–1934 (2017)
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3431–3440 (2015)
Luo, W., Li, Y., Urtasun, R., Zemel, R.: Understanding the effective receptive field in deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 29, 4898–4906 (2016)
Maška, M., et al.: A benchmark for comparison of cell tracking algorithms. Bioinformatics 30(11), 1609–1617 (2014)
Milletari, F., Navab, N., Ahmadi, S.A.: V-net: fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In: 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), pp. 565–571. IEEE (2016)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Shvets, A.A., Rakhlin, A., Kalinin, A.A., Iglovikov, V.I.: Automatic instrument segmentation in robot-assisted surgery using deep learning. In: 2018 17th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), pp. 624–628. IEEE (2018)
Simpson, A.L., et al.: A large annotated medical image dataset for the development and evaluation of segmentation algorithms. arXiv preprint arXiv:1902.09063 (2019)
Sinha, A., Dolz, J.: Multi-scale self-guided attention for medical image segmentation. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 25, 121–130 (2020)
Szegedy, C., et al.: Going deeper with convolutions. In: 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1–9 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298594
Wang, G., Sun, C., Sowmya, A.: ERL-net: entangled representation learning for single image de-raining. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 5643–5651 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00574
Xue, Y., Xu, T., Zhang, H., Long, L.R., Huang, X.: SegAN: adversarial network with multi-scale l 1 loss for medical image segmentation. Neuroinformatics 16(3), 383–392 (2018)
Zhao, H., Shi, J., Qi, X., Wang, X., Jia, J.: Pyramid scene parsing network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2881–2890 (2017)
Zhou, Z., Rahman Siddiquee, M.M., Tajbakhsh, N., Liang, J.: UNet++: a nested U-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In: Stoyanov, D., et al. (eds.) DLMIA/ML-CDS -2018. LNCS, vol. 11045, pp. 3–11. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00889-5_1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Huang, B., Xue, J., Lu, K., Tan, Y., Zhao, Y. (2021). MPNet: Multi-scale Parallel Codec Net for Medical Image Segmentation. In: Fang, L., Chen, Y., Zhai, G., Wang, J., Wang, R., Dong, W. (eds) Artificial Intelligence. CICAI 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13069. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-93046-2_42
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-93046-2_42
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-93045-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-93046-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)