Abstract
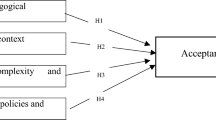
In the Higher Education Sector (HES), we see increasingly Artificial Intelligent (AI) agents in the form of chatbots or interactive virtual agents indistinguishable from people and a unique example of human-machine interaction using natural language processing. They are becoming one of the main technological tools to ensure accreditation and e-learning, while providing better adaptive learning. This conceptual paper aims to examine the factors that affect the intention to use AI agents/chatbots for adaptive learning in HEI from a sociomateriality perspective taking into consideration the mcdonaldization effect. An extended UTAUT (Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology) model is proposed to be evaluated in the HES context.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Wit, H., Philip, G.: Altbach: internationalization in higher education: global trends and recommendations for its future. Pol. Rev. High. Educ. 5(1), 28–46 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/23322969.2020.1820898
Mendoza, N.F.: Zoom Losing to Teams in the Video Conference Race to the Top, Tech Republic Publishing (2020). www.techrepublic.com
Kabudi, T., Pappas, I., Olsen, D.: AI-enabled adaptive learning systems: a systematic mapping of the literature. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2, 100017, ISSN 2666-920X (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2021.100017
Chedrawi, C., Howayeck, P., Tarhini, A.: CSR and legitimacy in higher education accreditation programs, an isomorphic approach of Lebanese business schools. Qual. Assur. Educ. 27(1), 70–81 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1108/QAE-04-2018-0053
Expert AI Team.: Chatbot: What is a Chatbot? Why are Chatbots Important? (2020). https://www.expert.ai/blog/chatbot/
Subedi, S., Hetényi, G., Shackleton, R.: Impact of an educational program on earthquake awareness and preparedness in Nepal. Geosci. Commun. 3, 279–290 (2020). https://doi.org/10.5194/gc-3-279-2020
Oberländer, A.M., Röglinger, M., Rosemann, M., Kees, A.: Conceptualizing business-to-thing interactions–A sociomaterial perspective on the internet of things. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 27(4), 486–502 (2018)
Moura, E., Bispo, M.: Sociomateriality: theories, methodology, and practice. Canadian J. Adm. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/cjas.1548
Garland, C.: The mcdonaldization of higher education? Notes on the UK Experience, Fast Capitalism, 4(1) (2008). https://doi.org/10.32855/fcapital.200801.011
Ritzer, G.: The McDonaldization Thesis: Explorations and Extensions. Pine Forge Press, Thousand Oaks (1998)
Azim, M., Hussain, Z., Bhatti, A., Iqbal, M.: McDonaldization of education in Pakistan: a step towards dehumanization. Int. J. Innov. Creat. Change. 15(2) (2021). www.ijicc.net
Vrontis, D., Christofi, M., Pereira, V., Tarba, S., Makrides, A., Trichina, E.: Artificial intelligence, robotics, advanced technologies and human resource management: a systematic review. Int. J. Human Resour. Manag. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/09585192.2020.1871398
Schuetzler, R., Grimes, M.G., Giboney, J.S.: The impact of chatbot conversational skill on engagement and perceived humanness. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 37(3), 875–900 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/07421222.2020.1790204
Ritzer, G.: The McDonaldization of Society. Pine Forge Press, Thousand Oaks (1993)
Orlikowski, W.J.: Sociomaterial practices: exploring technology at work. Organ. Stud. 28(9), 1435–1448 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1177/0170840607081138
Sharma, M., Biros, D.: AI and Its Implications for Organisations. In: Lee, Z.W.Y., Chan, T.K.H., Cheung, C.M.K. (eds.) Information Technology in Organisations and Societies: Multidisciplinary Perspectives from AI to Technostress, pp. 1–24. Emerald Publishing Limited, Bingley (2021). https://doi.org/10.1108/978-1-83909-812-320211001
Kaplan, A., Haenlein, M.: Siri, Siri, in my hand: Who’s the fairest in the land? On the interpretations, illustrations, and implications of artificial intelligence. Bus. Horiz. 62(1), 15–25 (2019)
Benbya, H., Leidner, D.: How Allianz UK used an idea management platform to harness employee innovation. MIS Q. Executive 17(2), 141–157 (2018)
Haddad, G., Chedrawi, C.: Artificial Intelligence and the inclusion-exclusion paradox: a sociomaterial perspective. In: ICTO Conference 2019: The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Business (2019)
Rai, A., Constantinides, P., Sarker, S.: Next-generation digital platforms: toward human–AI hybrids. MIS Q. 43(1), iii–x (2019)
Rajpurohit, N., Saxena, M., Yadav, R., Chande, P.K.: Investigating impact of artificial intelligence in deployment of effective project teams. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Technol. Scopus 29(8), 382–391 (2020)
Vázquez-Cano, E., Mengual-Andrés, S., López-Meneses, E.: Chatbot to improve learning punctuation in Spanish and to enhance open and flexible learning environments. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 18(1), 1–20 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-021-00269-8
Zawacki-Richter, O., Marín, V.I., Bond, M., Gouverneur, F.: Systematic review of research on artificial intelligence applications in higher education – where are the educators? Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 16(1), 1–27 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-019-0171-0
Gan, W., Lin, J.C.-W., Chao, H.-C., Vasilakos, A., Yu, P.: Utility-driven data analytics on uncertain data. IEEE Syst. J. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2020.2979279
Callo, E., Yazon, A.D.: Exploring the factors influencing the readiness of faculty and students on online teaching and learning as an alternative delivery mode for the new normal. Univ. J. Educ. Res. 8(8), 3509–3518 (2020)
World Economic Forum: The COVID-19 pandemic has changed education forever. This is how (2020). https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2020/04/coronavirus-education-global-covid19-online-digital-learning/
Pereira J.: Leveraging chatbots to improve self-guided learning through conversational quizzes. In: ACM International Conference Proceeding Series (2016). https://doi.org/10.1145/3012430.3012625
Reiswich, A., Haag, M.: Evaluation of chatbot prototypes for taking the virtual patient’s history. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 260, 73–80 (2019)
Molnár, G., Szüts, Z.: The role of chatbots in formal education. In: 2018 IEEE 16th International Symposium on Intelligent Systems and Informatics (SISY). IEEE (2018)
Fleming, M., et al.: Streamlining student course requests using chatbots. In: 29th Australasian Association for Engineering Education Conference (AAEE 2018), Engineers Australia (2018)
Mullamaa, K.: Student centred teaching and motivation. Adv. Soc. Sci. Res. J. 4(1), 16 (2017)
Tyson, M.M., Sauers, N.J.: School leaders’ adoption and implementation of artificial intelligence. J. Educ. Adm. 59(3), 271–285 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1108/JEA-10-2020-0221
Sandu, N., Gide, E.: Adoption of AI-chatbots to enhance student learning experience in higher education in India. In: 2019 18th International Conference on Information Technology Based Higher Education and Training (ITHET), pp. 1–5 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ITHET46829.2019.8937382
Palvia, S., et al.: Online education: worldwide status, challenges, trends, and implications. J. Glob. Inf. Technol. Manag. 21(4), 233–241 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/1097198X.2018.1542262
Statista E-learning and digital education (2020). https://www.statista.com/topics/3115/e-learningand-digital-education/
Šarmanová, J., Kostolányová, K.: Adaptive e-learning: from theory to practice. ICTE J. 4(4), 34–47 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1515/ijicte-2015-0018
Bryson, J.R., Andres, L.: Covid-19 and rapid adoption and improvisation of online teaching: curating resources for extensive versus intensive online learning experiences. J. Geogr. High. Educ. 44(4), 608–623 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/03098265.2020.1807478
Educause: 7 things you should know about adaptive learning (2017). https://library.educause.edu/~/media/files/library/2017/1/eli7140.pdf
Yakin, M., Linden, K.: Adaptive e-learning platforms can improve student performance and engagement in dental education. J. Dent. Educ. 85, 1309–1315 (2021)
Mitchell, J.E.: How do we think about labs and practical skills in an online context? In: Gibbs, B., Wood, G.C. (eds.) Emerging Stronger: Lasting Impact from Crisis Innovation, p. 35. Engineering Professors’ Council, Godalming (2020)
Paramythis, A., Loidl-Reisinger, S.: Adaptive learning environments and e-learning standards. Electron. J. e-Learn. 2(1), (2004)
Ralph, N.: The McDonaldization of nursing education in Australia, Unpublished doctoral thesis, Monash University, Australia (2013)
Holmes, C., Lindsay, D.: Do you Want Fries with that?: The McDonaldization of University Education—Some Critical Reflections on Nursing Higher Education. SAGE Publications (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244018787229journals.sagepub.com/home/sgo
Fenwick, T., Edwards, R., Sawchuk, P.: Emerging Approaches to Educational Research: Tracing the Socio-Material. Routledge, London (2011)
Fenwick, T.: Sociomateriality in medical practice learning: attuning to what matters. Med. Educ. 48(1), 44–52 (2014)
Leonardi, P.M.: Why do people reject new technologies and stymie organizational changes of which they are in favor? Exploring misalignments between social interactions and materiality. Human Commun. Res. 35(3), 407–441 (2009)
Orlikowski, W.J., Scott, S.V.: Sociomateriality: challenging the separation of technology, work and organization. Acad. Manag. Ann. 2(1), 433–474 (2008)
Acton, R.: Place-people-practice-process: using sociomateriality in university physical spaces research. Educ. Philos. Theory 49(14), 1441–1451 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/00131857.2017.1309637
Scott, D., Hargreaves, E.: The sociomateriality theory. In: The SAGE Handbook of Learning (2020)
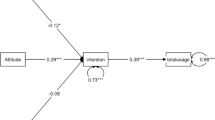
Venkatesh, V., Morris, M.G., Gordon, B.D., Davis, F.D.: User acceptance of information technology: toward a unified view. MIS Q. 27(3), 425–478 (2003)
Šumak, B., Šorgo, A.: The acceptance and use of interactive whiteboards among teachers: differences in UTAUT determinants between pre- and post-adopters. Comput. Hum. Behav. 64, 602–620 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2016.07.037
Hoque, R., Sorwar, G.: Understanding factors influencing the adoption of mHealth by the elderly: an extension of the UTAUT model. Int. J. Med. Inform. 101, 75–84 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2017.02.002
Chauhan, S., Jaiswal, M.: Determinants of acceptance of ERP software training in business schools: empirical investigation using UTAUT model. Int. J. Manage. Educ. 14, 248–262 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2016.05.005
Wang, W., Siau, K.: Trust in health chatbots. In: International Conference on Information Systems (ICIS 2018), San Francisco, CA (2018)
Smutny, P., Schreiberova, P.: Chatbots for learning: a review of educational Chatbots for the Facebook Messenger. Comput. Educ. 151, 103862, ISSN 0360-1315 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2020.103862
Klein, H.K., Myers, M.D.: A set of principles for conducting and evaluating interpretive field studies in information systems. MIS Q. 23(1), 67–93 (1999)
Straub, D., Boudreau, M., Gefen, D.: Validation guidelines for IS positivist research. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 13, 24 (2004). https://doi.org/10.17705/1CAIS.01324
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kazoun, N., Kokkinaki, A., Chedrawi, C. (2022). Factors that Affects the Use of AI Agents in Adaptive Learning: A Sociomaterial and Mcdonaldization Approach in the Higher Education Sector. In: Themistocleous, M., Papadaki, M. (eds) Information Systems. EMCIS 2021. Lecture Notes in Business Information Processing, vol 437. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-95947-0_29
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-95947-0_29
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-95946-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-95947-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)