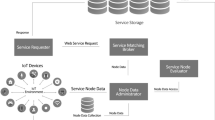
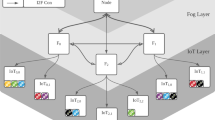
Abstract
The Internet-of-Things (IoT) generate increasingly significant amount of data that needs to be stored and analysed. The use of IoT devices as a service makes it more accessible and exploitable, this could be achieved using of cloud computing. Multi-cloud service composition and selection are required to fulfill increasingly complicated user requests for services. A service request is made from a cloud broker to cloud providers (CP) to deliver the required Quality of Service (QoS). Selecting services and optimizing service compositions to satisfy functional and non-functional conflicting requirements across various cloud service providers is an non-deterministic polynomial-time hardness problem (NP-hard). Multiobjective (MO) metaheuristics are known to be performant to solve such a problem. This study examines how to select IoT services to achieve the best performances on the eight selected QoS across multiple CP. The experiment results reveal that among the 18 compared algorithms, the parallel NSGAII provides the most efficient and optimal outcomes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asghari, P., Rahmani, A.M., Javadi, H.H.S.: Privacy-aware cloud service composition based on QoS optimization in internet of things. J. Amb. Intell. Human. Comput. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-01723-7
Baker, T., Asim, M., Tawfik, H., Aldawsari, B., Buyya, R.: An energy-aware service composition algorithm for multiple cloud-based IoT applications. J. Netw. Comput. App. 89, 96–108 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2017.03.008
Chauhan, S.S., Pilli, E.S., Joshi, R., Singh, G., Govil, M.: Brokering in interconnected cloud computing environments: a survey. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 133, 193–209 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpdc.2018.08.001
Choudhary, G., Jain, A.: Internet of things: a survey on architecture, technologies, protocols and challenges. In: 2016 International Conference on Recent Advances and Innovations in Engineering (ICRAIE). IEEE (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/icraie.2016.7939537
Deb, K., Pratap, A., Agarwal, S., Meyarivan, T.: A fast and elitist multi-objective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 6(2), 182–197 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1109/4235.996017
Durillo, J.J., Nebro, A.J., Luna, F., Alba, E.: A study of master-slave approaches to parallelize NSGA-II. In: 2008 IEEE International Symposium on Parallel and Distributed Processing. IEEE (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/ipdps.2008.4536375
Durillo, J.J., Nebro, A.J., Luna, F., Alba, E.: On the effect of the steady-state selection scheme in multi-objective genetic algorithms. In: Ehrgott, M., Fonseca, C.M., Gandibleux, X., Hao, J.K., Sevaux, M. (eds.) Evolutionary Multi-criterion Optimization. EMO 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. LNCS, vol. 5467, pp. 183–197. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-01020-0_18
Feng, J., Shen, W.Z., Xu, C.: Multi-objective random search algorithm for simultaneously optimizing wind farm layout and number of turbines. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 753, 032011 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/753/3/032011
Hatton, M.: The IoT in 2030: 24 billion connected things generating \$1.5 trillion (2020). https://alhena.io/the-iot-in-2030-24-billion-connected-things-generating-1-5-trillion/. Accessed 23 Sep 2021
Kumrai, T., Ota, K., Dong, M., Kishigami, J., Sung, D.K.: Multi-objective optimization in cloud brokering systems for connected internet of things. IEEE Internet Things J. 4(2), 404–413 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/jiot.2016.2565562
Lakhdari, A., Bouguettaya, A., Mistry, S., Neiat, A.G.G.: Composing energy services in a crowdsourced IoT environment. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 99, 1 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/tsc.2020.2980258
Lancinskas, A., Zilinskas, J.: Approaches to parallelize pareto ranking in NSGA-II algorithm. In: Wyrzykowski, R., Dongarra, J., Karczewski, K., Wasniewski, J. (eds.) Parallel Processing and Applied Mathematics. PPAM 2011. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 7204, pp. 371–380. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-31500-8_38
Li, H., Zhang, Q.: Multi-objective optimization problems with complicated pareto sets, MOEA/d and NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 13(2), 284–302 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/tevc.2008.925798
Liu, J., et al.: A cooperative evolution for QoS-driven IoT service composition. Automatika 54(4), 438–447 (2013). https://doi.org/10.7305/automatika.54-4.417
Maltese, J., Ombuki-Berman, B.M., Engelbrecht, A.P.: A scalability study of many-objective optimization algorithms. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 22(1), 79–96 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/tevc.2016.2639360
Martínez, S.Z., Coello, C.A.C.: A multi-objective particle swarm optimizer based on decomposition. In: Proceedings of the 13th Annual Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation - GECCO 2011. ACM Press (2011). https://doi.org/10.1145/2001576.2001587
Nebro, A.J., Durillo, J., García-Nieto, J., Coello, C., Luna, F., Alba, E.: SMPSO: a new PSO metaheuristic for multi-objective optimization (2009)
Nebro, A.J., Durillo, J.J.: A study of the parallelization of the multi-objective metaheuristic MOEA/D. In: Blum, C., Battiti, R. (eds.) Learning and Intelligent Optimization. LION 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. LNCS, vol. 6073, pp. 303–317. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-13800-3_32
Nebro, A.J., Durillo, J.J., Luna, F., Dorronsoro, B., Alba, E.: Design issues in a multi-objective cellular genetic algorithm. In: Obayashi, S., Deb, K., Poloni, C., Hiroyasu, T., Murata, T. (eds.) Evolutionary Multi-Criterion Optimization. EMO 2007. LNCS, vol. 4403, pp. 126–140. Springer, Heidelberg (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-70928-2_13
Nebro, A.J., Durillo, J.J., Luna, F., Dorronsoro, B., Alba, E.: MOCell: a cellular genetic algorithm for multi-objective optimization. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 24(7), 726–746 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/int.20358
Nebro, A.J., Durillo, J.J., Machin, M., Coello Coello, C.A., Dorronsoro, B.: A study of the combination of variation operators in the NSGA-II Algorithm. In: Advances in Artificial Intelligence. CAEPIA 2013. LNCS, vol. 8109, pp. 269–278. Springer, Heidelberg (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-40643-0_28
Olariu, S., Zomaya, A.Y. (eds.): Handbook of Bioinspired Algorithms and Applications. Chapman and Hall/CRC, Boco Raton (2005). https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420035063
de Oliveira, L.B., Marcelino, C.G., Milanes, A., Almeida, P.E.M., Carvalho, L.M.: A successful parallel implementation of NSGA-II on GPU for the energy dispatch problem on hydroelectric power plants. In: 2016 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC). IEEE, July 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/cec.2016.7744337
Pang, B., Hao, F., Park, D.S., Maio, C.D.: A multi-criteria multi-cloud service composition in mobile edge computing. Sustainability 12(18), 7661 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187661
Singh, M., Baranwal, G., Tripathi, A.K.: QoS-aware selection of IoT-based service. Arabian J. Sci. Eng. 45(12), 10033–10050 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04601-8
Sun, M., Zhou, Z., Wang, J., Du, C., Gaaloul, W.: Energy-efficient IoT service composition for concurrent timed applications. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 100, 1017–1030 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2019.05.070
Toutouh, J., Alba, E.: Parallel multi-objective metaheuristics for smart communications in vehicular networks. Soft Comput. 21(8), 1949–1961 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-015-1891-2
Vakili, M., Jahangiri, N., Sharifi, M.: Cloud service selection using cloud service brokers: approaches and challenges. Front. Comput. Sci. 13(3), 599–617 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-017-6124-7
Wang, H., Qian, F.: Improved PSO-based multi-objective optimization using inertia weight and acceleration coefficients dynamic changing, crowding and mutation. In: 2008 7th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation. IEEE (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/wcica.2008.4593644
Wang, H., Qian, F.: Improved PSO-based multi-objective optimization using inertia weight and acceleration coefficients dynamic changing, crowding and mutation. In: 2008 7th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, pp. 4479–4484 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/WCICA.2008.4593644
Wang, W., Niu, D., Li, B., Liang, B.: Dynamic cloud resource reservation via cloud brokerage. In: 2013 IEEE 33rd International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems. IEEE, July 2013. https://doi.org/10.1109/icdcs.2013.20
Yang, C., Peng, T., Lan, S., Shen, W., Wang, L.: Towards IoT-enabled dynamic service optimal selection in multiple manufacturing clouds. J. Manuf. Syst. 56, 213–226 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2020.06.004
Zhang, M., Liu, L., Liu, S.: Genetic algorithm based QoS-aware service composition in multi-cloud. In: 2015 IEEE Conference on Collaboration and Internet Computing (CIC). IEEE, October 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/cic.2015.23
Zhang, X., Geng, J., Ma, J., Liu, H., Niu, S.: A QoS-driven service selection optimization algorithm for internet of things, September 2020. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-69961/v1
Zitzler, E., Künzli, S.: Indicator-based selection in multi-objective search. In: Yao, X., et al. (eds.) Parallel Problem Solving from Nature - PPSN VIII. PPSN 2004. LNCS, vol. 3242, pp. 832–842. Springer, Heidelberg (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-30217-9_84
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zebouchi, A., Aklouf, Y. (2022). A Survey on the Quality of Service and Metaheuristic Based Resolution Methods for Multi-cloud IoT Service Selection. In: Abraham, A., et al. Innovations in Bio-Inspired Computing and Applications. IBICA 2021. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 419. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-96299-9_40
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-96299-9_40
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-96298-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-96299-9
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)