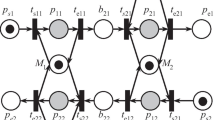
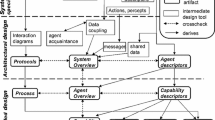
Abstract
Dynamic scheduling is a hot topic in recent years. Most existing dynamic scheduling algorithms process the rescheduling in an off-line way through the modification of created schedules in advance of further execution. However, in open and stochastic environments, such as manufacturing systems, streams of exogenous events may cause information changes inside of jobs and resources during the job execution stage, so as to increase the environmental uncertainties and rescheduling computational complexity. In such environments, the frequent occurrence of dynamic events requires scheduling methods to provide efficient and robust online rescheduling services for ensuring the success rate of jobs. This paper investigates the dynamic events during the execution stage in open and stochastic environments and proposes a multiagent-based rescheduling mechanism with the hybrid structure for such cases. Three types of agents are proposed to implement the rescheduling mechanism. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed hybrid mechanism own higher efficiency and robustness in dealing with dynamic events in open and stochastic scheduling environments than that of existing centralized and decentralized methods.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baykasoğlu, A., Karaslan, F.S.: Solving comprehensive dynamic job shop scheduling problem by using a grasp-based approach. Int. J. Prod. Res. 55(11), 3308–3325 (2017)
Bittencourt, L.F., Goldman, A., Madeira, E.R., da Fonseca, N.L., Sakellariou, R.: Scheduling in distributed systems: a cloud computing perspective. Comput. Sci. Rev. 30, 31–54 (2018)
Dhurasevic, M., Jakobovic, D.: A survey of dispatching rules for the dynamic unrelated machines environment. Expert Syst. Appl. 113, 555–569 (2018)
Guizzi, G., Revetria, R., Vanacore, G., Vespoli, S.: On the open job-shop scheduling problem: a decentralized multi-agent approach for the manufacturing system performance optimization. Procedia CIRP 79, 192–197 (2019)
Gupta, D., Maravelias, C.T., Wassick, J.M.: From rescheduling to online scheduling. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 116, 83–97 (2016)
Hsieh, F.-S.: Dynamic configuration and collaborative scheduling in supply chains based on scalable multi-agent architecture. J. Ind. Eng. Int. 15(2), 249–269 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40092-018-0291-5
Huang, Z., Zhuang, Z., Cao, Q., Lu, Z., Guo, L., Qin, W.: A survey of intelligent algorithms for open shop scheduling problem. Procedia CIRP 83, 569–574 (2019)
Ikonen, T.J., Heljanko, K., Harjunkoski, I.: Reinforcement learning of adaptive online rescheduling timing and computing time allocation. Comput. Chem. Eng. 141, 106994 (2020)
Kan, C., Yang, H., Kumara, S.: Parallel computing and network analytics for fast industrial internet-of-things (IIOT) machine information processing and condition monitoring. J. Manuf. Syst. 46, 282–293 (2018)
Kantamneni, A., Brown, L.E., Parker, G., Weaver, W.W.: Survey of multi-agent systems for microgrid control. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 45, 192–203 (2015)
Luo, S.: Dynamic scheduling for flexible job shop with new job insertions by deep reinforcement learning. Appl. Soft Comput. 91, 106208 (2020)
Panda, S.K., Gupta, I., Jana, P.K.: Task scheduling algorithms for multi-cloud systems: allocation-aware approach. Inf. Syst. Front. 21(2), 241–259 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-017-9742-6
Tighazoui, A., Sauvey, C., Sauer, N.: Predictive-reactive strategy for flowshop rescheduling problem: minimizing the total weighted waiting times and instability. J. Syst. Sci. Syst. Eng. 30(3), 253–275 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11518-021-5490-8
Weiqing, G., Yanru, C.: Task-scheduling algorithm based on improved genetic algorithm in cloud computing environment. Recent Adv. Electr. Electron. Eng. (Formerly Recent Patents Electr. Electron. Eng.) 14(1), 13–19 (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yang, Y., Ren, F., Zhang, M. (2022). A Hybrid Multiagent-Based Rescheduling Mechanism for Open and Stochastic Environments Concerning the Execution Stage. In: Long, G., Yu, X., Wang, S. (eds) AI 2021: Advances in Artificial Intelligence. AI 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13151. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-97546-3_45
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-97546-3_45
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-97545-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-97546-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)