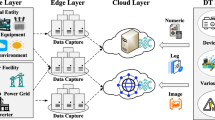
Abstract
The application of machine learning and deep learning is widely used in the business of the power grid. However, the business of the power grid is complicated, and the online service of deep learning faces greater performance challenges. In order to solve this problem, this paper proposes an online service EOSP based on go-tensorflow. EOSP service is divided into 3 modules, namely model configuration module, execution engine module and model management module. The model configuration module mainly includes functions such as online model configuration and model configuration information synchronization. The execution engine can execute graphical model calls, and has optimized performance based on the characteristics of golang language coroutines. The model management module is responsible for model registration, update, uninstallation and version management. Experiments show that the EOSP service is highly stable, which greatly reduces the time consumption of online services.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Witten, I.H., et al.: Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques, 4th edn. Morgan Kaufmann, Cambridge (2017)
Marsland, S.: Machine Learning: An Algorithmic Perspective, 2nd edn., p. 2014. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2015)
Anonymous: Machine learning. Machine Learning (1986)
Jianya, G., Shunping, J.: Photogrammetry and deep learning. Ce Hui Xue Bao 47(6), 693–704 (2018)
Schmidhuber, J.: Deep learning in neural networks: an overview. Neural Netw. 61, 85–117 (2015)
Shi, H., Xu, M., Li, R.: Deep learning for household load forecasting-a novel pooling deep RNN. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 9(5), 5271–5280 (2018)
Hsieh, J., et al.: Post-adoption switching behavior for online service substitutes: a perspective of the push–pull–mooring framework. Comput. Hum. Behav. 28(5), 1912–1920 (2012)
Brenot, H., et al.: Support to Aviation Control Service (SACS): an online service for near-real-time satellite monitoring of volcanic plumes. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 14(5), 1099–1123 (2014). https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-14-1099-2014
Mothersbaugh, D.L., et al.: Disclosure antecedents in an online service context: the role of sensitivity of information. J. Serv. Res. 15(1), 76–98 (2012)
Chung, Y.-L., Wu, S.: An effective toss-and-catch algorithm for fixed-rail mobile terminal equipment that ensures reliable transmission and non-interruptible handovers. Symmetry (Basel) 13(4), 582 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13040582
Hashemi, M.J., Masroor, A., Mosqueda, G.: Implementation of online model updating in hybrid simulation. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 43(3), 395–412 (2014)
Abouheaf, M., Gueaieb, W., Lewis, F.: Online model-free reinforcement learning for the automatic control of a flexible wing aircraft. IET Control Theory Appl. 14(1), 73–84 (2021)
Aksoylar, C., Dogramaci Aksoylar, N.: Online model identification and updating in multi-platform pseudo-dynamic simulation of steel structures – experimental applications. J. Earthq. Eng.: JEE 1–25 (2021)
Yuying, G., Hui, S., Zhenming, L.: Exploration of OLT converged edge computing for industrial internet. Diànzǐ Jìshù Yīngyòng 47(4), 5–8 (2021)
Li, Y., Song, T., Yang, Y.: Combinatorial auction-based mechanism for task offloading in edge computing. Jisuanji Kexue Yu Tansuo 15(1), 73–83 (2021)
Arena, F., Pau, G.: When edge computing meets IoT systems: analysis of case studies. China Commun. 17(10), 50–63 (2020)
Chen, T., Guestrin, C.: XGBoost: a scalable tree boosting system (2016). https://doi.org/10.1145/2939672.2939785
Li, H., et al.: XGBoost model and its application to personal credit evaluation. IEEE Intell. Syst. 35(3), 52–61 (2020)
Li, Z., et al.: Application of XGBoost in P2P default prediction. In: Journal of Physics Conference Series, vol. 1871, no. 1 (2021)
Zhang, J., et al.: LightGBM: an effective and scalable algorithm for prediction of chemical toxicity–application to the Tox21 and mutagenicity data sets. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 59(10), 4150–4158 (2019)
Al-kasassbeh, M., Abbadi, M., Al-Bustanji, A.: LightGBM algorithm for malware detection. In: Arai, K., Kapoor, S., Bhatia, R. (eds.) Intelligent Computing, pp. 391–403. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-52243-8_28
Sun, X., Liu, M., Sima, Z.: A novel cryptocurrency price trend forecasting model based on LightGBM. Finan. Res. Lett. 32, 101084 (2020)
Smirnov, E.A., et al.: Comparison of regularization methods for ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. AASRI Procedia 6, 89–94 (2014)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 60(6), 84–90 (2017)
Rastegari, M., et al.: XNOR-net: ImageNet classification using binary convolutional neural networks. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) Computer Vision – ECCV 2016, pp. 525–542. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46493-0_32
Zaremba, W., Sutskever, I., Vinyals, O.: Recurrent Neural Network Regularization, arXiv:1409.2329 (2014)
Chien, J., Lu, T.: Deep recurrent regularization neural network for speech recognition (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2015.7178834
Albahar, M.A.: Recurrent neural network model based on a new regularization technique for real-time intrusion detection in SDN environments. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2019, 1–9 (2019)
Shi, X., et al.: Convolutional LSTM network: a machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting (2015)
Zhao, R., et al.: Learning to monitor machine health with convolutional bi-directional LSTM networks. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland) 17(2), 273 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/s17020273
Rampasek, L., Goldenberg, A.: TensorFlow: biology’s gateway to deep learning? Cell Syst. 2(1), 12–14 (2016)
Cabañas, R., Salmerón, A., Masegosa, A.R.: InferPy: probabilistic modeling with Tensorflow made easy. Knowl.-Based Syst. 168, 25–27 (2019)
Hao, L., et al.: TensorD: a tensor decomposition library in TensorFlow. Neurocomput. (Amsterdam) 318, 196–200 (2018)
Gai, K., Qiu, M., Elnagdy, S.: A novel secure big data cyber incident analytics framework for cloud-based cybersecurity insurance. In: IEEE BigDataSecurity (2016)
Lu, Z., Wang, N., Wu, J., Qiu, M.: IoTDeM: an IoT big data-oriented MapReduce performance prediction extended model in multiple edge clouds. JPDC 118, 316–327 (2018)
Guo, Y., Zhuge, Q., Hu, J., et al.: Optimal data allocation for scratch-pad memory on embedded multi-core systems. In: IEEE ICPP Conference, pp. 464–471 (2011)
Lu, R., Jin, X., Zhang, S., Qiu, M., Wu, X.: A study on big knowledge and its engineering issues. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 31(9), 1630–1644 (2018)
Qiu, H., Qiu, M., Lu, Z.: Selective encryption on ECG data in body sensor network based on supervised machine learning. Inf. Fusion 55, 59–67 (2020)
Du, Y., et al.: A deep learning network‐assisted bladder tumour recognition under cystoscopy based on Caffe deep learning framework and EasyDL platform. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assisted Surg. 17(1), 1–8 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/rcs.2169
Roy, P., et al.: NUMA-Caffe: numa-aware deep learning neural networks. ACM Trans. Archit. Code Optim. 15(2), 1–26 (2018)
Garea, A.S., Heras, D.B., Argüello, F.: Caffe CNN-based classification of hyperspectral images on GPU. J. Supercomput. 75(3), 1065–1077 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-018-2300-2
Li, S., et al.: PyTorch distributed: experiences on accelerating data parallel training. Proc. VLDB Endow. 13(12), 3005–3018 (2020)
Steppa, C., Holch, T.L.: HexagDLy—processing hexagonally sampled data with CNNs in PyTorch. Softwarex 9, 193–198 (2019)
Gao, X., et al.: TorchANI: a free and open source PyTorch-based deep learning implementation of the ANI neural network potentials. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 60(7), 3408–3415 (2020)
Le Grand, S., Götz, A.W., Walker, R.C.: SPFP: speed without compromise—a mixed precision model for GPU accelerated molecular dynamics simulations. Comput. Phys. Commun. 184(2), 374–380 (2013)
Owens, J.D., et al.: GPU computing. Proc. IEEE 96(5), 879–899 (2008)
Hong, C.-H., Spence, I., Nikolopoulos, D.S.: GPU virtualization and scheduling methods: a comprehensive survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 50(3), 1–37 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1145/3068281
Guazzelli, A., et al.: PMML: an open standard for sharing models. R J. 1(1), 60 (2009). https://doi.org/10.32614/RJ-2009-010
Fernández, S., et al.: Using automated planning for improving data mining processes. Knowl. Eng. Rev. 28(2), 157–173 (2013)
Acknowledgment
This work financially supported by Science and Technology Program of State Grid Corporation of China under Grant No.: 5700-202055183A-0-0-00, which named Research on Technology of Big Data Monitoring Analysis in Power Grid by Coordination of Data Middle platform & Edge Calculation. Without their help, it would be much harder to finish the program and this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liu, P., Lu, Y., Wang, G., Zhou, W. (2022). Efficient Online Service Based on Go-Tensorflow in the Middle-Station Scenario of Grid Service. In: Qiu, M., Gai, K., Qiu, H. (eds) Smart Computing and Communication. SmartCom 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13202. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-97774-0_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-97774-0_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-97773-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-97774-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)